P 2 2 Absolute Value Of A Real Number

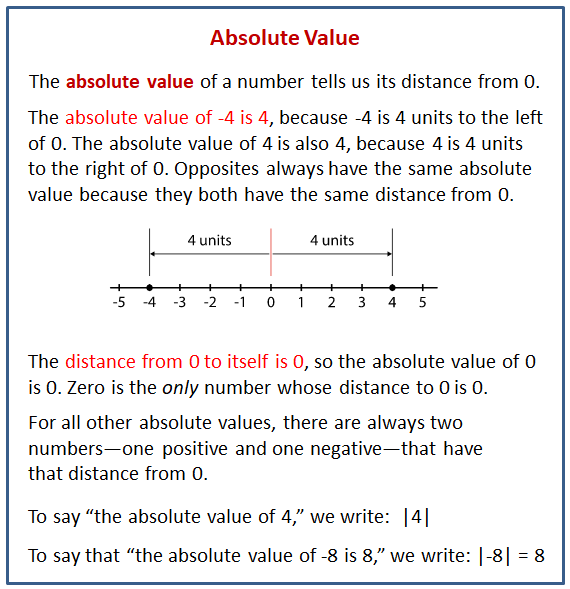
P 2 2 Absolute Value Of A Real Number Youtube The absolute value51 of a real number a, denoted | a |, is defined as the distance between zero (the origin) and the graph of that real number on the number line. since it is a distance, it is always positive. for example, | − 4 | = 4 and | 4 | = 4. both 4 and − 4 are four units from the origin, as illustrated below:. The absolute value of a number may be thought of as its distance from zero. in mathematics, the absolute value or modulus of a real number , denoted , is the non negative value of without regard to its sign. namely, if is a positive number, and if is negative (in which case negating makes positive), and . for example, the absolute value of 3 is.
Absolute Value Of Numbers De nition if ais a real number, the absolute value of ais jaj= ˆ a if a 0 a if a<0 example evaluate j2j, j 10j, j5 9j, j9 5j. algebraic properties of the absolute value 1. jaj 0 for all real numbers a. 2. jaj= j ajfor all real numbers a. 3. jabj= jajjbj, the absolute value of the product of two numbers is the product of the absolute values. 4. To find the absolute value of a real number, we consider only the number and remove the sign. some of the examples of absolute value of a number are: |2| = 2 | 9. |a| = √(a 2) squaring a makes it positive or zero (for a as a real number). then taking the square root will "undo" the squaring, but leave it positive or zero. |a × b| = |a| × |b| means these are the same: the absolute value of (a times b), and (the absolute value of a) times (the absolute value of b) which can also be useful when solving. Steps 2 and 3: draw a number line and mark this critical value on the line. the next step requires that we place the expression inside the absolute value bars, namely 3 − 2x, underneath the line at its left end. step 4: next, determine the sign of 3 − 2x for values of x on each side of 3 2.
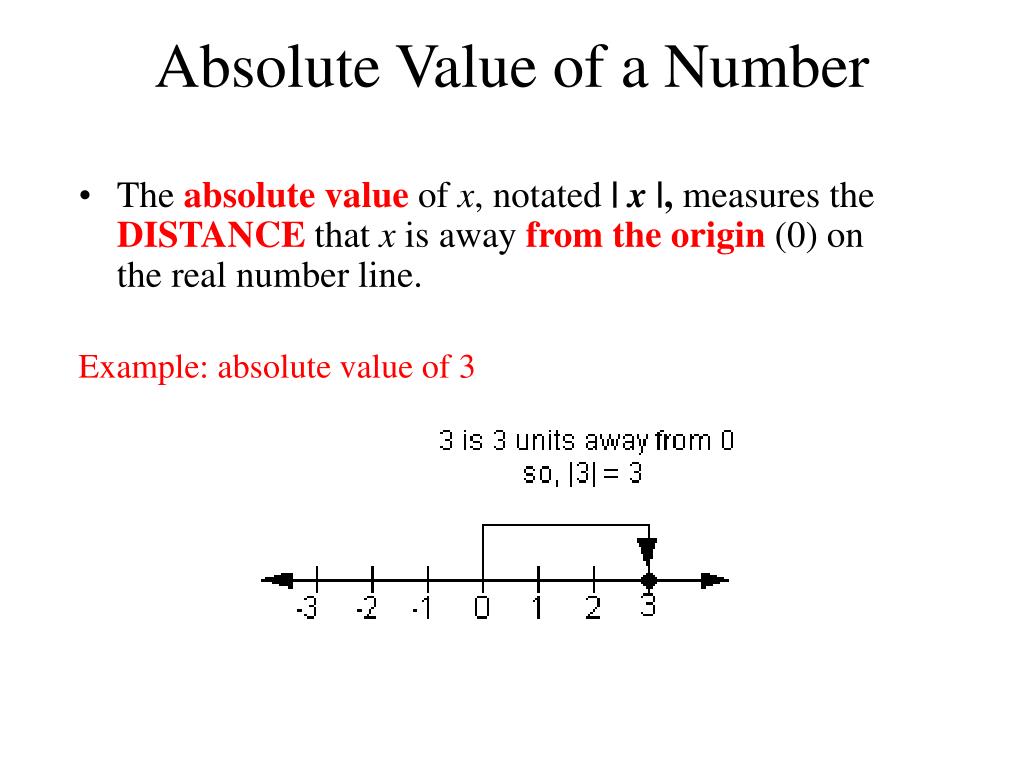
Ppt The Real Number System Powerpoint Presentation Free Download |a| = √(a 2) squaring a makes it positive or zero (for a as a real number). then taking the square root will "undo" the squaring, but leave it positive or zero. |a × b| = |a| × |b| means these are the same: the absolute value of (a times b), and (the absolute value of a) times (the absolute value of b) which can also be useful when solving. Steps 2 and 3: draw a number line and mark this critical value on the line. the next step requires that we place the expression inside the absolute value bars, namely 3 − 2x, underneath the line at its left end. step 4: next, determine the sign of 3 − 2x for values of x on each side of 3 2. 8 others. contributed. the absolute value of a real number is the distance of the number from 0 0 on a number line. the absolute value of x x is written as \left|x\right|. ∣x∣. for example, \left|5\right| = \left| 5\right| = 5. ∣5∣ = ∣−5∣ = 5. this is a special case of the magnitude of a complex number. before reading this page. The property states that, for every real number a, there is a unique number, called the multiplicative inverse (or reciprocal), denoted 1 a, that, when multiplied by the original number, results in the multiplicative identity, 1. a ⋅ 1 a = 1. for example, if a = − 2 3, the reciprocal, denoted 1 a, is − 3 2 because.

How To Find The Absolute Value Of A Real Number Algebra Study 8 others. contributed. the absolute value of a real number is the distance of the number from 0 0 on a number line. the absolute value of x x is written as \left|x\right|. ∣x∣. for example, \left|5\right| = \left| 5\right| = 5. ∣5∣ = ∣−5∣ = 5. this is a special case of the magnitude of a complex number. before reading this page. The property states that, for every real number a, there is a unique number, called the multiplicative inverse (or reciprocal), denoted 1 a, that, when multiplied by the original number, results in the multiplicative identity, 1. a ⋅ 1 a = 1. for example, if a = − 2 3, the reciprocal, denoted 1 a, is − 3 2 because.

Comments are closed.