Parametric Curves Basic Graphing

Parametric Curves Basic Graphing Youtube Thanks to all of you who support me on patreon. you da real mvps! $1 per month helps!! 🙂 patreon patrickjmt !! ** in my first example, th. The graph of parametric equations is called a parametric curve or plane curve, and is denoted by c. notice in this definition that x and y are used in two ways. the first is as functions of the independent variable t. as t varies over the interval i, the functions x(t) and y(t) generate a set of ordered pairs (x, y).

Parametric Equations Introduction Eliminating The Paremeter T Explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. Technology note: most graphing utilities can graph functions given in parametric form.often the word "parametric'' is abbreviated as "par'' or "param'' in the options. the user usually needs to determine the graphing window (i.e, the minimum and maximum \(x\) and \(y\) values), along with the values of \(t\) that are to be plot. Definition. if x x and y y are continuous functions of t t on an interval i i, then the equations. x=x(t)andy=y(t) x = x (t) and y = y (t) are called parametric equations and t t is called the parameter. the set of points (x,y) (x, y) obtained as t t varies over the interval i i is called the graph of the parametric equations. The first is direction of motion. the equation involving only x and y will not give the direction of motion of the parametric curve. this is generally an easy problem to fix however. let’s take a quick look at the derivatives of the parametric equations from the last example. they are, dx dt = 2t 1 dy dt = 2.
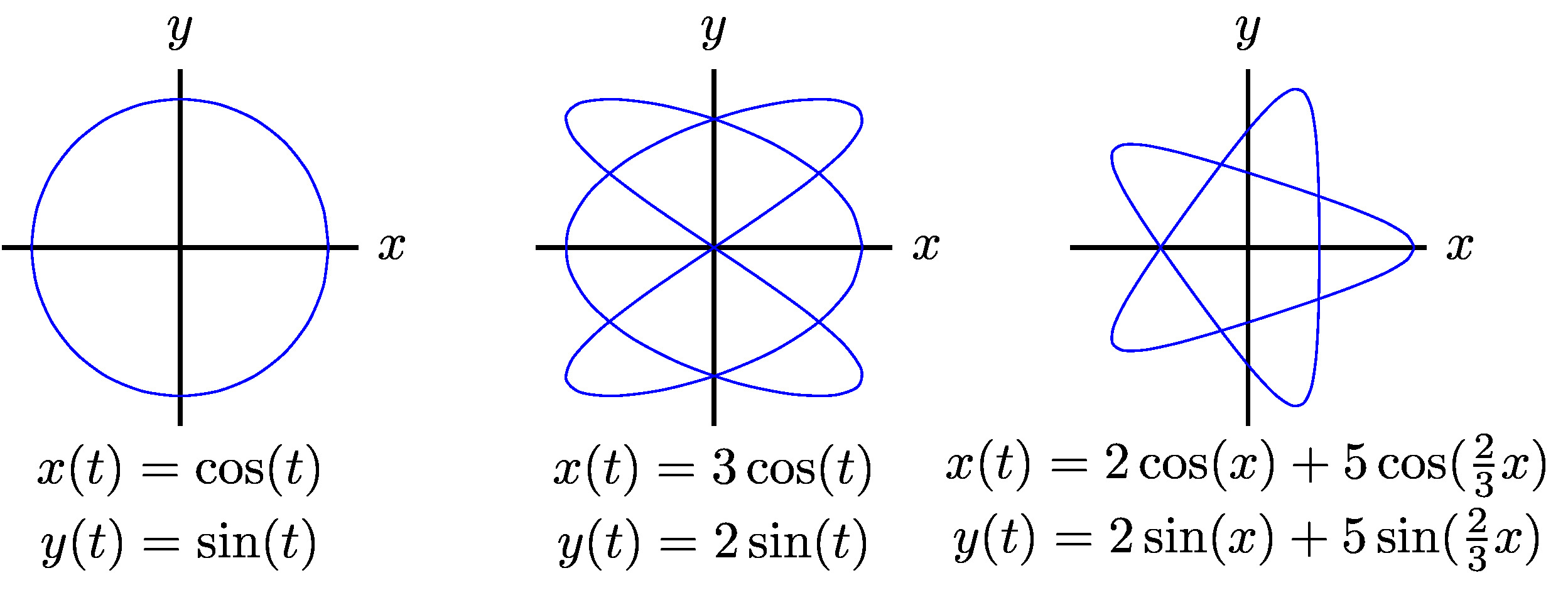
Parametric Curves Definition. if x x and y y are continuous functions of t t on an interval i i, then the equations. x=x(t)andy=y(t) x = x (t) and y = y (t) are called parametric equations and t t is called the parameter. the set of points (x,y) (x, y) obtained as t t varies over the interval i i is called the graph of the parametric equations. The first is direction of motion. the equation involving only x and y will not give the direction of motion of the parametric curve. this is generally an easy problem to fix however. let’s take a quick look at the derivatives of the parametric equations from the last example. they are, dx dt = 2t 1 dy dt = 2. This formula rotates any function f (x) f (x) around the x x axis. for instance, try rotating f (x) = √(x) f (x) = (x) with this parametric surface. adjust the inputs beneath the expression to 0 ≤ u ≤ 5 0 ≤ u ≤ 5 and 0 ≤ v ≤ 2π 0 ≤ v ≤ 2 π. to connect this rotation to a slider, create a slider b b from 0 0 to 2π 2 π and. 7.1.1 plot a curve described by parametric equations. 7.1.2 convert the parametric equations of a curve into the form y = f (x). y = f (x). 7.1.3 recognize the parametric equations of basic curves, such as a line and a circle. 7.1.4 recognize the parametric equations of a cycloid.

Comments are closed.