Phase Changes And Phase Diagrams
Phase Change Diagrams вђ Overview Examples Expii A phase change or phase transition is a change between solid, liquid, gaseous, and sometimes plasma states of matter. the states of matter differ in the organization of particles and their energy. the main factors that cause phase changes are changes in temperature and pressure. at the phase transition, such as the boiling point between liquid. Phase diagram is a graphical representation of the physical states of a substance under different conditions of temperature and pressure. a typical phase diagram has pressure on the y axis and temperature on the x axis. as we cross the lines or curves on the phase diagram, a phase change occurs. in addition, two states of the substance coexist.

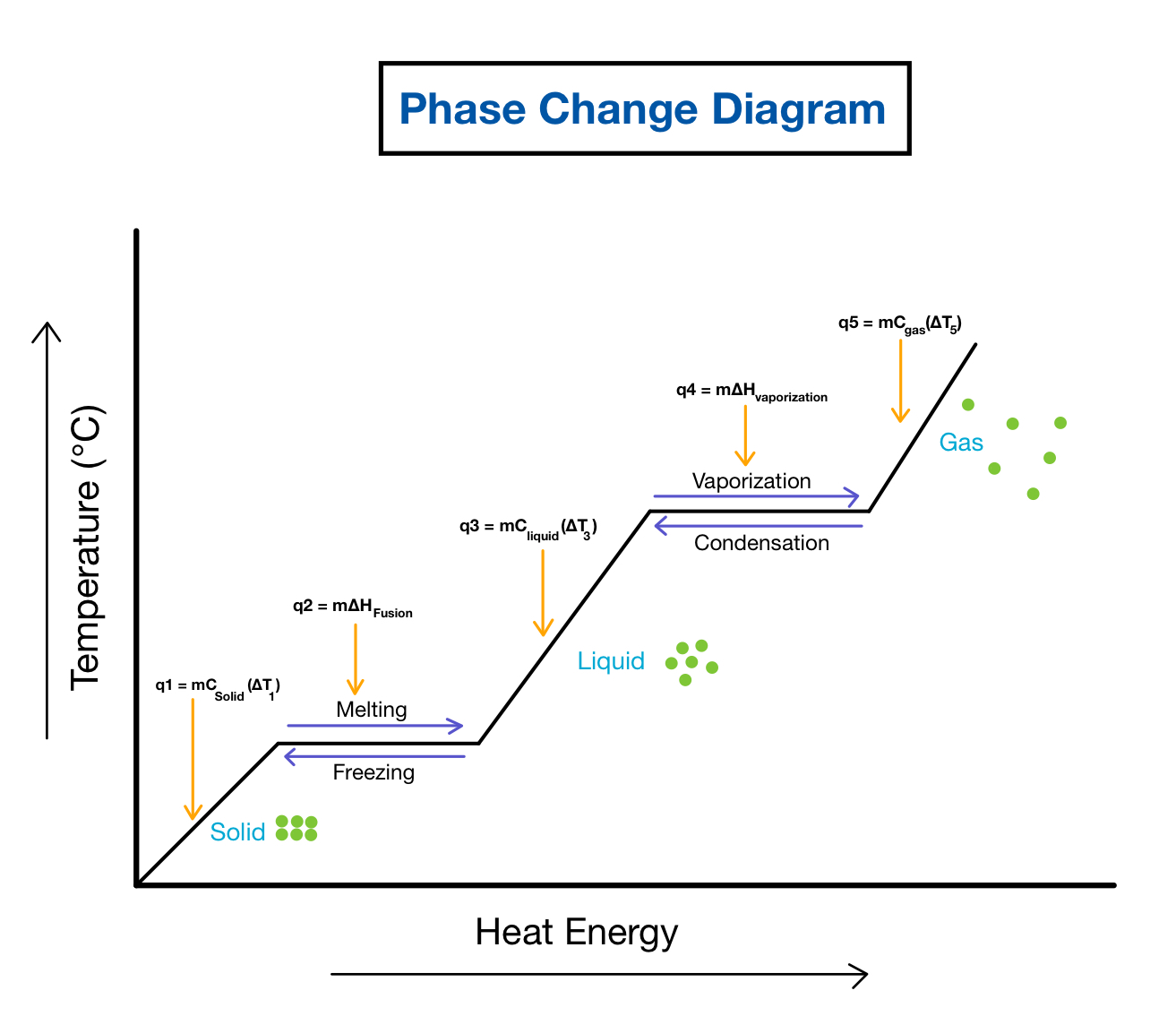
Phase Change Diagrams вђ Overview Examples Expii Solution: when two substances or objects at different temperatures are brought into contact, heat will flow from the warmer one to the cooler. the amount of heat that flows is given by. q = mcsΔt (16.3.1) (16.3.1) q = m c s Δ t. where q is heat, m is mass, cs is the specific heat, and Δ t is the temperature change. A phase diagram combines plots of pressure versus temperature for the liquid gas, solid liquid, and solid gas phase transition equilibria of a substance. these diagrams indicate the physical states that exist under specific conditions of pressure and temperature, and also provide the pressure dependence of the phase transition temperatures. Phase diagrams. the phase of a given substance depends on the pressure and temperature. thus, plots of pressure versus temperature showing the phase in each region provide considerable insight into thermal properties of substances. such a pt graph is called a phase diagram. figure \(\pageindex{1}\) shows the phase diagram for water. A phase diagram in physical chemistry, engineering, mineralogy, and materials science is a type of chart used to show conditions (pressure, temperature, etc.) at which thermodynamically distinct phases (such as solid, liquid or gaseous states) occur and coexist at equilibrium.
.PNG)
Phase Diagrams Presentation Chemistry Phase diagrams. the phase of a given substance depends on the pressure and temperature. thus, plots of pressure versus temperature showing the phase in each region provide considerable insight into thermal properties of substances. such a pt graph is called a phase diagram. figure \(\pageindex{1}\) shows the phase diagram for water. A phase diagram in physical chemistry, engineering, mineralogy, and materials science is a type of chart used to show conditions (pressure, temperature, etc.) at which thermodynamically distinct phases (such as solid, liquid or gaseous states) occur and coexist at equilibrium. Figure chapter4.7: eutectic phase diagram. the binary eutectic phase diagram has several distinctive features one being a solid solid phase mixture, limit of solubility at different temperatures, and an invariant point in the phase diagram, the eutectic point. the solubility limit is the maximum amount of solute that you can integrate into the. A generalized phase change diagram for a single substance. the solid green line shows the usual shape of a liquid solid equilibrium, while the dotted green line shows the anomalous behavior of water. [3] phase change diagrams show what phase a substance will be in at a given temperature and pressure.

What Is Phase Change Explained By Thermal Engineers Figure chapter4.7: eutectic phase diagram. the binary eutectic phase diagram has several distinctive features one being a solid solid phase mixture, limit of solubility at different temperatures, and an invariant point in the phase diagram, the eutectic point. the solubility limit is the maximum amount of solute that you can integrate into the. A generalized phase change diagram for a single substance. the solid green line shows the usual shape of a liquid solid equilibrium, while the dotted green line shows the anomalous behavior of water. [3] phase change diagrams show what phase a substance will be in at a given temperature and pressure.

Phase Changes Of Matter Phase Transitions

Comments are closed.