Physics Thermodynamics 2 Ch 32 1 Def And Terms 9о
Laws Of Thermodynamics Visit ilectureonline for more math and science lectures!in this video i will explain the graphical representation of the van der waals equation in. Visit ilectureonline for more math and science lectures!in this video i will explain the pvt surface diagram for real substances.next video in thi.

Physics Thermodynamics 2 Ch 32 1 Def And Terms 25 Of Visit ilectureonline for more math and science lectures!in this video i will explain the pvt surface where pressure, volume, and temperature are g. We have summarized the laws discussed in this chapter in table 44–1. in the next chapter we shall apply these laws to discover the relationship between the heat generated in the expansion of a rubber band, and the extra tension when it is heated. table 44–1 summary of the laws of thermodynamics. first law:. Many texts use this definition of work, and not the definition based on internal pressure, as the basis of the first law of thermodynamics. this definition reverses the sign conventions for work, and results in a statement of the first law that becomes Δ e int = q w Δ e int = q w.). If t 1 = t 2 and t 1 = t 3, then t 2 = t 3. 3.1 this is the most fundamental way of defining temperature: two objects must be at the same temperature thermodynamically if the net heat transfer between them is zero when they are put in thermal contact and have reached a thermal equilibrium.

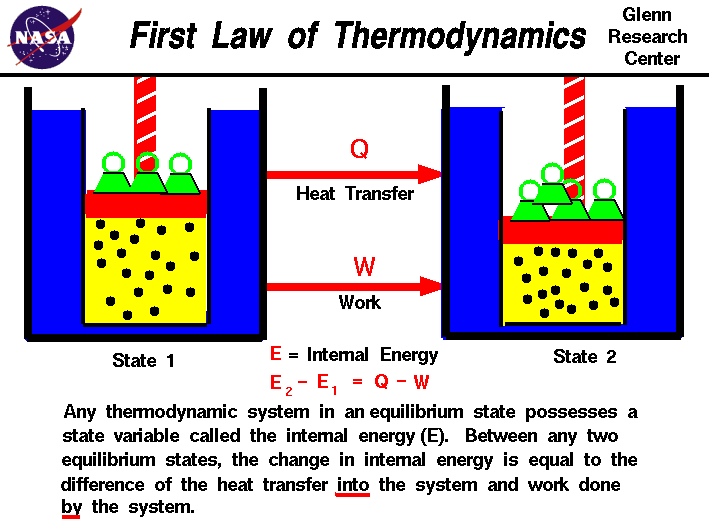
Physics Thermodynamics 2 Ch 32 1 Def And Terms 9о Many texts use this definition of work, and not the definition based on internal pressure, as the basis of the first law of thermodynamics. this definition reverses the sign conventions for work, and results in a statement of the first law that becomes Δ e int = q w Δ e int = q w.). If t 1 = t 2 and t 1 = t 3, then t 2 = t 3. 3.1 this is the most fundamental way of defining temperature: two objects must be at the same temperature thermodynamically if the net heat transfer between them is zero when they are put in thermal contact and have reached a thermal equilibrium. Table 15.1 presents a summary of terms relevant to the first law of thermodynamics. figure 15.5 (a) the first law of thermodynamics applied to metabolism. heat transferred out of the body ( q q ) and work done by the body ( w w ) remove internal energy, while food intake replaces it. The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy of a system equals the net heat transfer into the system minus the net work done by the system. in equation form, the first law of thermodynamics is. Δu = q−w. Δ u = q − w. here Δu Δ u is the change in internal energyu u of the system. q q is the net heat.

Physics Thermodynamics 2 Ch 32 1 Def And Terms 1о Table 15.1 presents a summary of terms relevant to the first law of thermodynamics. figure 15.5 (a) the first law of thermodynamics applied to metabolism. heat transferred out of the body ( q q ) and work done by the body ( w w ) remove internal energy, while food intake replaces it. The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy of a system equals the net heat transfer into the system minus the net work done by the system. in equation form, the first law of thermodynamics is. Δu = q−w. Δ u = q − w. here Δu Δ u is the change in internal energyu u of the system. q q is the net heat.

Physics Thermodynamics 2 Ch 32 1 Def And Terms 5 Of

Comments are closed.