Plate Tectonics Plate Boundaries And Hotspot Explanation
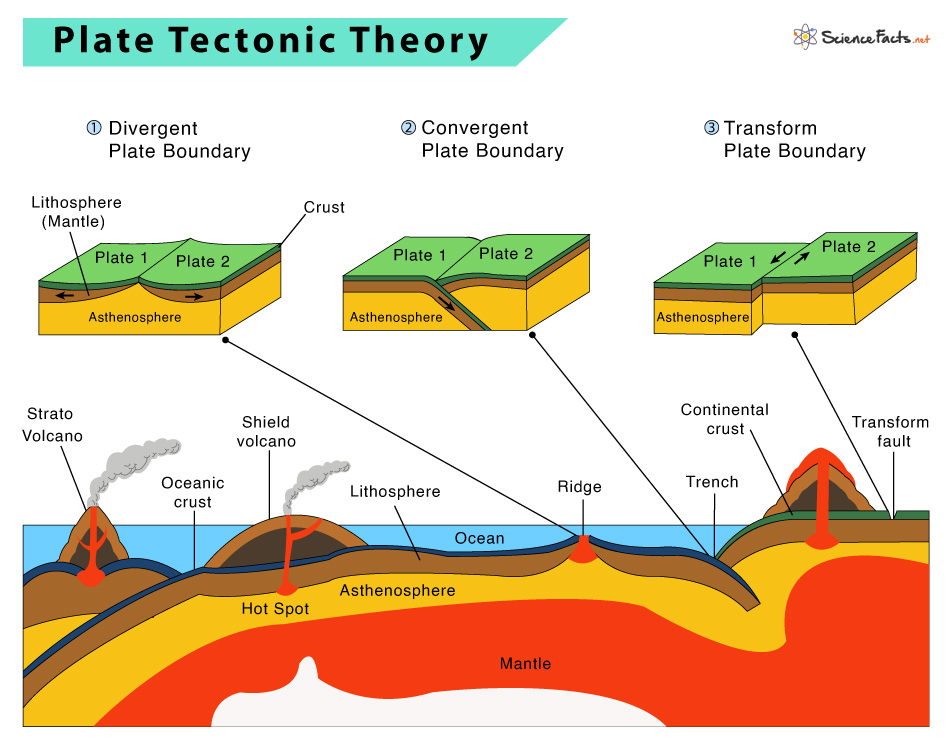
Plate Tectonics Plate Boundaries And Hotspot Explanation Plate tectonics. modified date: 10 11 2023. plate tectonics is a scientific theory that explains the movements and behaviors of the earth’s lithosphere, which is composed of the crust and uppermost mantle. the theory proposes that the earth’s lithosphere is broken into a series of plates that are in constant motion, driven by the heat. The melted rock rises into and through the overlying plate as magma, often forming a chain of volcanoes parallel to the plate boundary. powerful earthquakes are common along these boundaries. the pacific ring of fire is an example of a convergent plate boundary. two plates sliding past each other forms a transform plate boundary. one of the.
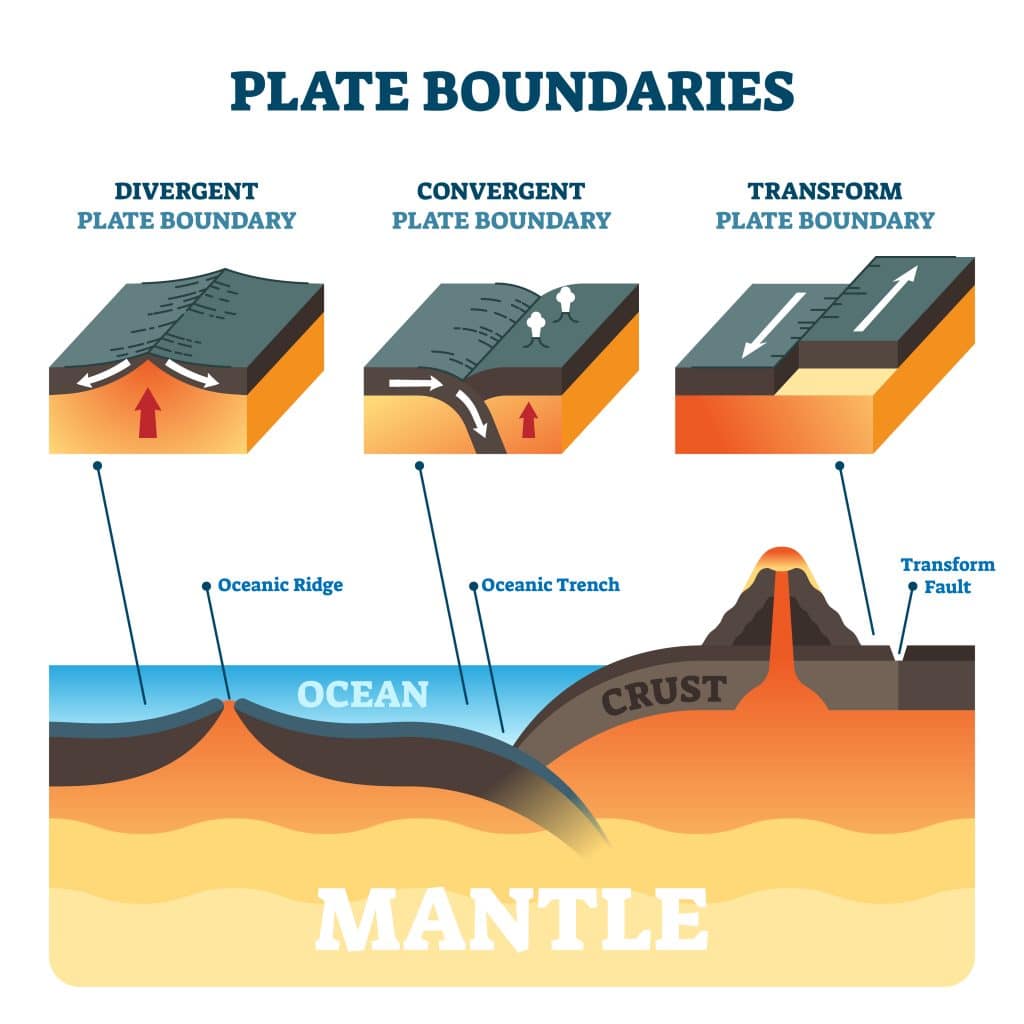
Plate Boundaries With Subduction At Richard Mauriello Blog Noun. boundary between two tectonic plates, where the plates are moving horizontally or vertically in opposite directions, not against or away from each other. also called a conservative plate boundary. trench. noun. long, deep depression, either natural or man made. volcano. The appalachian mountains are the remnants of a large mountain range that was created when north america rammed into eurasia about 250 million years ago. transform plate boundaries occur when two tectonic plates slide (or grind) past parallel to each other. the most famous transform boundary is the san andreas fault where the pacific plate that. Plates move apart at mid ocean ridges where new seafloor forms. between the two plates is a rift valley. lava flows at the surface cool rapidly to become basalt, but deeper in the crust, magma cools more slowly to form gabbro. so the entire ridge system is made up of igneous rock that is either extrusive or intrusive. The two types of plate boundaries that are most likely to produce volcanic activity are divergent plate boundaries and convergent plate boundaries. divergent plate boundaries at a divergent boundary, tectonic plates move apart from one another. they never really separate because magma continuously moves up from the mantle into this boundary.

Plate Tectonics Plate Boundaries And Hotspot Explanation Atelier Plates move apart at mid ocean ridges where new seafloor forms. between the two plates is a rift valley. lava flows at the surface cool rapidly to become basalt, but deeper in the crust, magma cools more slowly to form gabbro. so the entire ridge system is made up of igneous rock that is either extrusive or intrusive. The two types of plate boundaries that are most likely to produce volcanic activity are divergent plate boundaries and convergent plate boundaries. divergent plate boundaries at a divergent boundary, tectonic plates move apart from one another. they never really separate because magma continuously moves up from the mantle into this boundary. In essence, plate tectonic theory is elegantly simple. earth ’s surface layer, 50 to 100 km (30 to 60 miles) thick, is rigid and is composed of a set of large and small plates. together, these plates constitute the lithosphere, from the greek lithos, meaning “ rock.”. the lithosphere rests on and slides over an underlying partially molten. 2.7: hotspots. the wilson cycle provides a broad overview of the tectonic plate movement. to analyze plate movement more precisely, scientists study hotspots. first postulated by j. tuzo wilson in 1963, a hotspot is an area in the lithospheric plate where molten magma breaks through and creates a volcanic center, islands in the ocean and.

Comments are closed.