Ppt Polyprotic Acid Titrations Polybasic Base Titrations Powerpoint
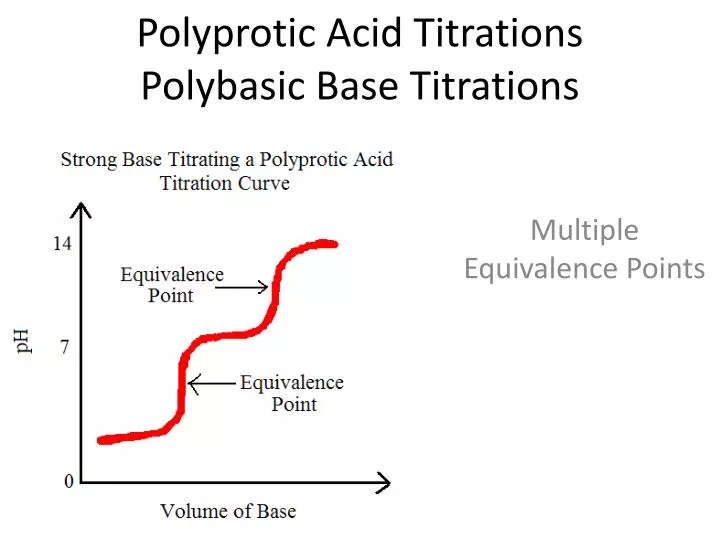
Ppt Polyprotic Acid Titrations Polybasic Base Titrations Powerpoint Jul 22, 2014. 60 likes | 614 views. polyprotic acid titrations polybasic base titrations. multiple equivalence points. titrations of polyprotic acids. when one titrates a polyprotic acid with a base there is an equivalence point for each dissociation. go to wikispace now!. 5. 5 acid base titrations • a quick and accurate method for determining acidic or basic substances in many samples. • the titrant is typically a strong acid or base. • the sample species can be either a strong or weak acid or base. 6. 6 acid base titration types of acid base titrations: 1)strong acid – strong base titration 2)weak acid.

Ppt Polyprotic Acid Titrations Polybasic Base Titrations Powerpoint Acid base titration poly acid titration: a polybasic acid may be considered as a mixture of acids i. e. it furnishes more than one proton on dissociation carbonic acid gives two protons, phosphoric acid gives three protons and hence are called as polybasic or polyprotic acids. each stage of dissociation gives a separate monobasic acid. D30.2 titration of polyprotic acids and bases. when a polyprotic acid is titrated, there are usually multiple equivalence points. for example, when h 2 so 3 is titrated with naoh, there are two equivalence points corresponding to the two acidic protons from the h 2 so 3 molecule. there are also as many midpoints as there are equivalence points. Polyprotic acid titrations polybasic base titrations. polyprotic acid titrations polybasic base titrations. multiple equivalence points. titrations of polyprotic acids. when one titrates a polyprotic acid with a base there is an equivalence point for each dissociation. go to wikispace now!. download titration graphs summary!. 618 views • 3 slides. Weak acid & strong base e.p > 7 ph starts higher as ch3cooh is a weaker acid. finding ka from the graph • the half equivalence point is when just enough base is added for half of the acid to be converted to the conjugate base. when this happens, the concentration of h ions equals the kavalue of the acid. take this one step further, ph = pka.

Polyprotic Acid Titrations Polybasic Base Titrations Pptx Pow Polyprotic acid titrations polybasic base titrations. polyprotic acid titrations polybasic base titrations. multiple equivalence points. titrations of polyprotic acids. when one titrates a polyprotic acid with a base there is an equivalence point for each dissociation. go to wikispace now!. download titration graphs summary!. 618 views • 3 slides. Weak acid & strong base e.p > 7 ph starts higher as ch3cooh is a weaker acid. finding ka from the graph • the half equivalence point is when just enough base is added for half of the acid to be converted to the conjugate base. when this happens, the concentration of h ions equals the kavalue of the acid. take this one step further, ph = pka. B of a conjugate acid base k a = acid dissociation constant (e.g. for nh 4 ) k b = base dissociation constant (e.g. for nh 3) since nh 3 and nh 4 are a conjugate acid base pair, it is not surprising that k a for nh 4 and k b for nh 3 are related. k ak b = k w = 1.0 x 10 14 (at 25 °c) (k a for a weak acid)(k b for its conjugate base) = k w. In the titration of a polyprotic acid like sulfurous acid with a strong base such as sodium hydroxide, the base first neutralizes the initial ionizable proton, forming an intermediate species (e.g., hydrogen sulfite ions). this step's titration curve resembles that of a weak monoprotic acid, with a half equivalence point where the ph equals the.

Ppt Polyprotic Acid Titrations Polybasic Base Titrations Powerpoint B of a conjugate acid base k a = acid dissociation constant (e.g. for nh 4 ) k b = base dissociation constant (e.g. for nh 3) since nh 3 and nh 4 are a conjugate acid base pair, it is not surprising that k a for nh 4 and k b for nh 3 are related. k ak b = k w = 1.0 x 10 14 (at 25 °c) (k a for a weak acid)(k b for its conjugate base) = k w. In the titration of a polyprotic acid like sulfurous acid with a strong base such as sodium hydroxide, the base first neutralizes the initial ionizable proton, forming an intermediate species (e.g., hydrogen sulfite ions). this step's titration curve resembles that of a weak monoprotic acid, with a half equivalence point where the ph equals the.

Comments are closed.