Primary Consumers In A Forest
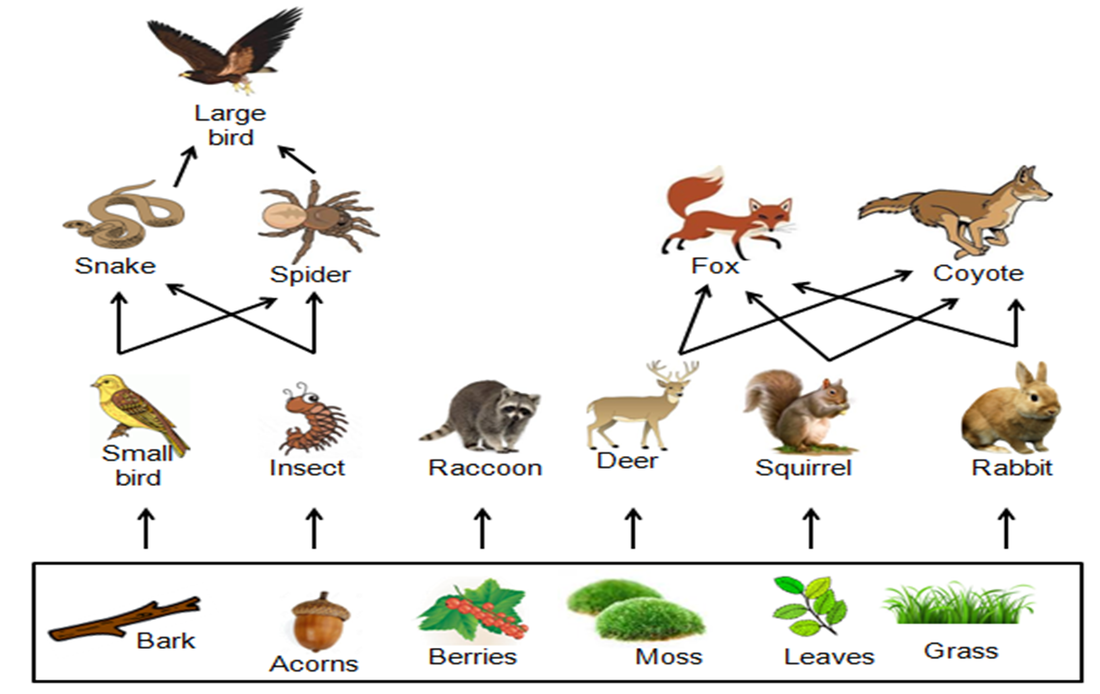
Food Webs And Trophic Levels Katie S Ecology Project Here’s a basic rundown of the parts of the forest food chain: producers: primary producers create the initial energy source in the forest ecosystem, typically using sunlight. primary consumers: these are herbivores that consume the producers. in a forest, there are usually deer, rabbits, and some insects in this position. A secondary consumer is an organism that ingests primary consumers as its main food source. these organisms may also eat producers–they may be omnivorous–but can also be carnivores and only eat other consumers. secondary consumer example. there are generally fewer secondary consumers in a forest ecosystem than primary consumers because.
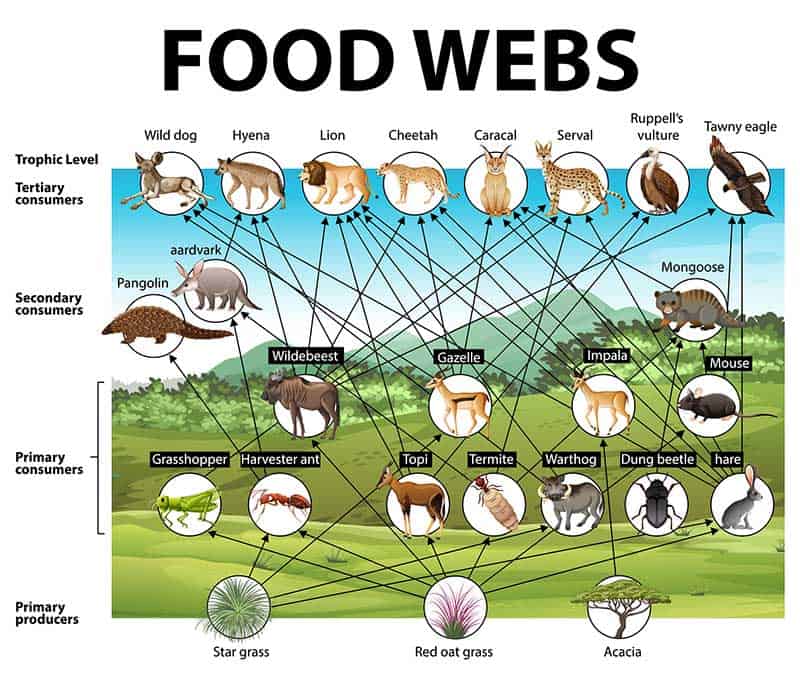
12 Examples Of Primary Consumers Pictures Diagram Wildlife Informer Consumers are unable to make their own food like plants do, so they must eat other organisms. there are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers in the deciduous forest. the primary consumers are the large herbivores like deer as well as insects, rabbits and rodents. these creatures eat mostly plants, seeds, berries and grasses. With over 40,000 plant species in the tropical rainforest, this trophic level is the most diverse and extensive food chain. they are the primary food source for organisms that feed on them for survival. trees such as bananas, bamboo, coconut, orchids, bromeliads, epiphytes, microscopic algae, ferns, and mosses make up the ecosystem’s flora. Deciduous forest food web activity. to understand the deciduous forest food web, first read about the deciduous forest biome using this link. then read about the different trophic levels of a typical food chain (below). the trophic level is the position that an organism (plant or animal) occupies in a food chain what it eats, and what eats it. In the kelp forest, sea otters are secondary consumers that hunt sea urchins. tertiary consumers eat the secondary consumers. they are at the fourth trophic level. in the desert ecosystem, an owl or eagle may prey on a snake. there may be more levels of consumers before a chain finally reaches its top predator.

Comments are closed.