Properties Of Real Numbers Chart
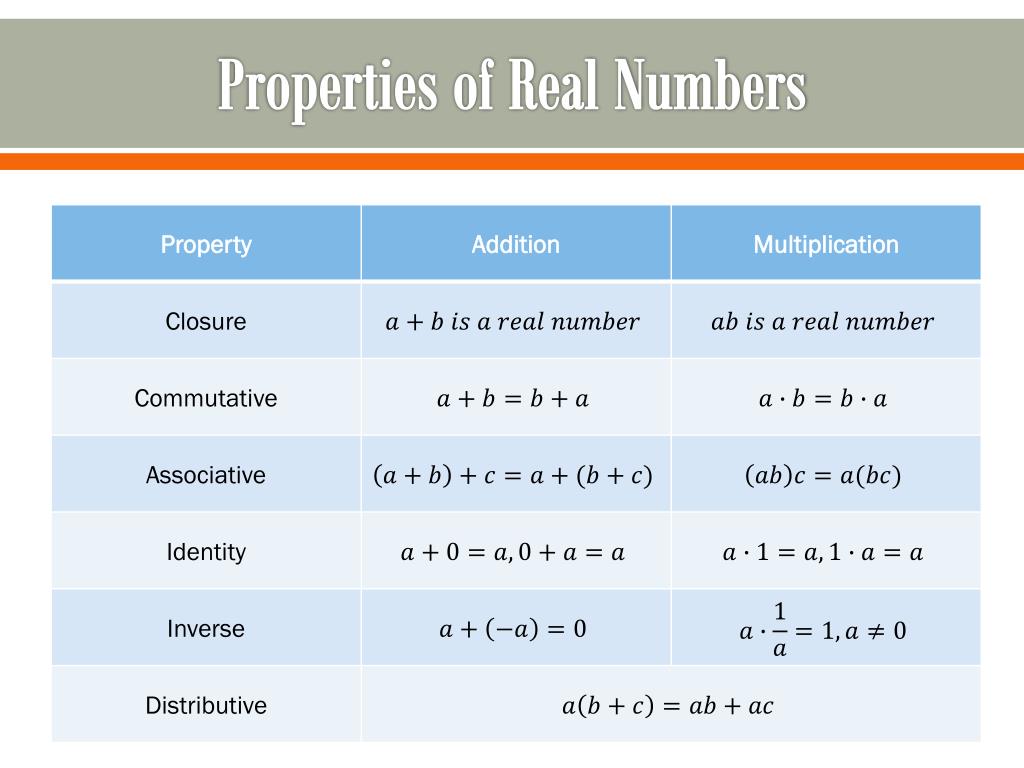
Properties Of Real Numbers Math Learn the definition, types and properties of real numbers, and how to use them in algebra. see a chart of 22 properties with examples, verbal hints and fyi notes. Real numbers are closed under the arithmetic operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. in other words, addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of two real numbers, ‘m’ and ‘n’, always give a real number. for example, 2 5 = 7. 0.9 – 0.6 = 0.3.
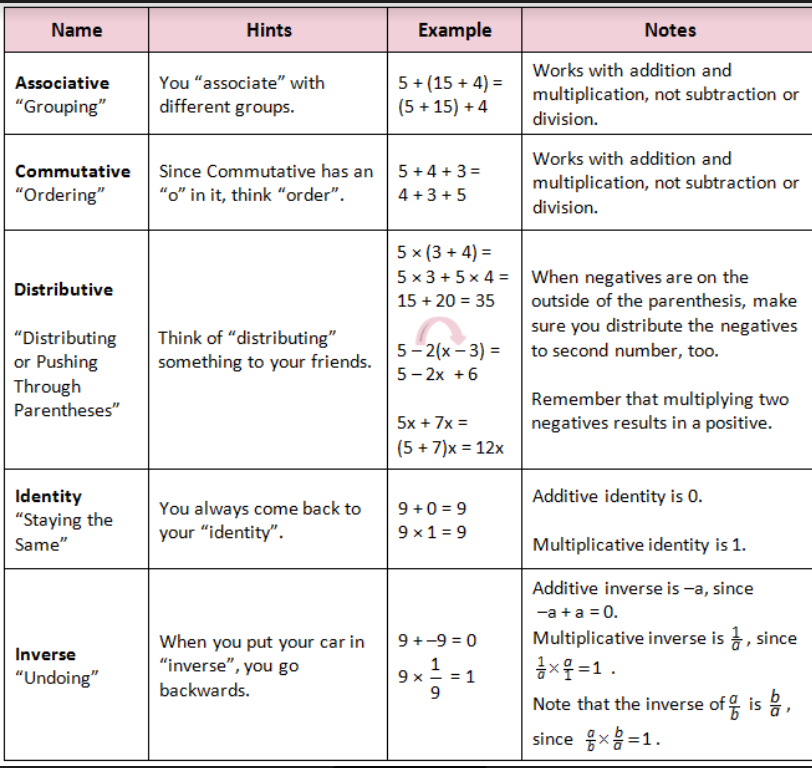
Properties Of Real Numbers Chart вђ Pearson Connexus Support Learn what real numbers are, how they are classified and how they behave under different operations. see the chart of real numbers and the properties of commutative, associative, distributive and identity. Learn the main properties of real numbers, such as commutative, associative, distributive, closure, identity, inverse and zero product. see examples, definitions and diagrams of real number sets. To keep it organized, i decided to divide the properties of real numbers into three (3) parts. the first one involves the addition operation. the second involves the operation of multiplication. while the third combines the operations of addition and multiplication. verbal description: if you add two real numbers, the sum is also a real number. Use the commutative and associative properties. the order we add two numbers doesn’t affect the result. if we add \ (8 9\) or \ (9 8\), the results are the same—they both equal 17. so, \ (8 9=9 8\). the order in which we add does not matter! similarly, when multiplying two numbers, the order does not affect the result.

Properties Of Real Numbers Teach Math Interactive To keep it organized, i decided to divide the properties of real numbers into three (3) parts. the first one involves the addition operation. the second involves the operation of multiplication. while the third combines the operations of addition and multiplication. verbal description: if you add two real numbers, the sum is also a real number. Use the commutative and associative properties. the order we add two numbers doesn’t affect the result. if we add \ (8 9\) or \ (9 8\), the results are the same—they both equal 17. so, \ (8 9=9 8\). the order in which we add does not matter! similarly, when multiplying two numbers, the order does not affect the result. Inverse property. of addition: for any real number \(a, a (−a)=0\). a number and its opposite add to zero. \(−a\) is the additive inverse of a. of multiplication: for any real number \(a,(a\neq 0)a\cdot\frac{1}{a}=1\). a number and its reciprocal multiply to one. \(\frac{1}{a}\) is the multiplicative inverse of a. properties of zero. for. Learn the properties of real numbers with videos, examples, and solutions. find the table of properties, worksheets, games, and activities to practice and apply them.
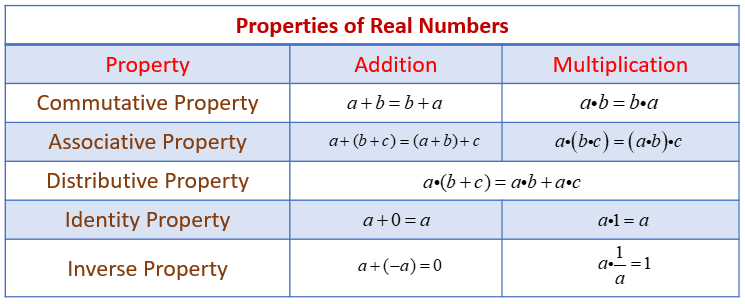
Different Math Properties And Examples Inverse property. of addition: for any real number \(a, a (−a)=0\). a number and its opposite add to zero. \(−a\) is the additive inverse of a. of multiplication: for any real number \(a,(a\neq 0)a\cdot\frac{1}{a}=1\). a number and its reciprocal multiply to one. \(\frac{1}{a}\) is the multiplicative inverse of a. properties of zero. for. Learn the properties of real numbers with videos, examples, and solutions. find the table of properties, worksheets, games, and activities to practice and apply them.
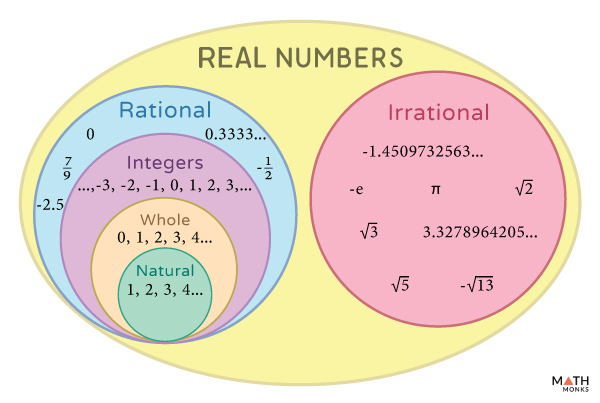
Real Numbers вђ Definition Symbol Properties Chart Examples

Comments are closed.