Protein Synthesis Rna Processing
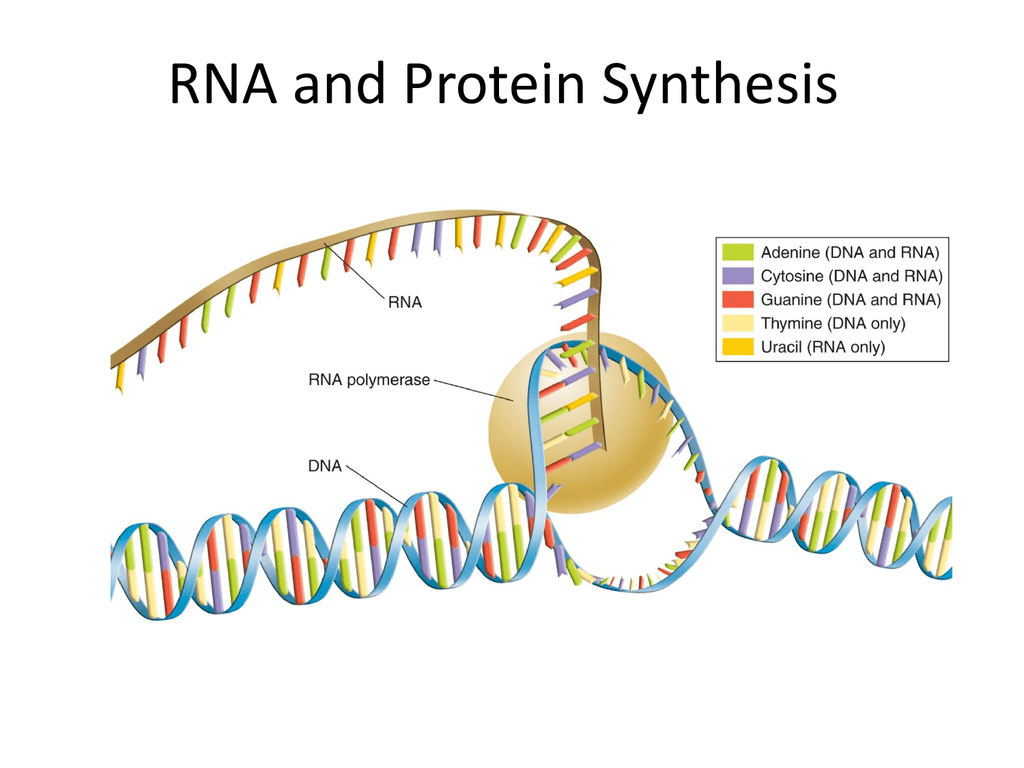
Rna And Protein Synthesis The process of translation can be seen as the decoding of instructions for making proteins, involving mrna in transcription as well as trna. the genes in dna encode protein molecules, which are. Chapter 7. protein synthesis, processing, and regulation. transcription and rna processing are followed by translation, the synthesis of proteins as directed by mrna templates. proteins are the active players in most cell processes, implementing the myriad tasks that are directed by the information encoded in genomic dna.
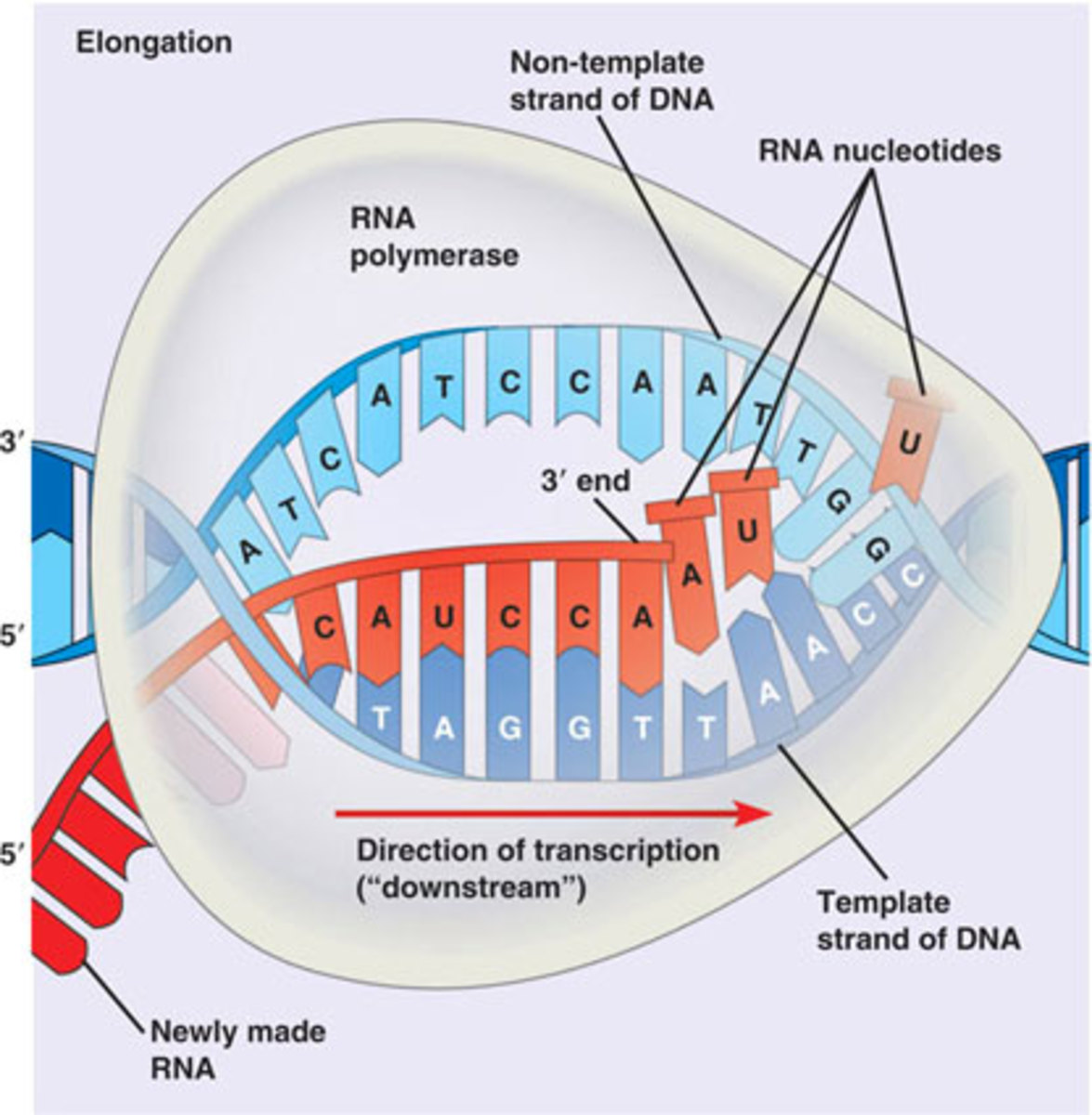
Dna Rna And Protein Synthesis Messenger rna (mrna) molecules carry the coding sequences for protein synthesis and are called transcripts; ribosomal rna (rrna) molecules form the core of a cell's ribosomes (the structures in. Rna helicases can drive the progression of mrnas between various rna processing factories, leading to protein synthesis or to mrna storage or decay. cyril f. bourgeois franck mortreux. In most cells, protein synthesis consumes more energy than any other biosynthetic process. at least four high energy phosphate bonds are split to make each new peptide bond: two are consumed in charging a trna molecule with an amino acid (see figure 6 56 ), and two more drive steps in the cycle of reactions occurring on the ribosome during. Intron processing. all introns in a pre mrna must be completely and precisely removed before protein synthesis. if the process errs by even a single nucleotide, the reading frame of the rejoined exons would shift, and the resulting protein would be dysfunctional. the process of removing introns and reconnecting exons is called splicing.
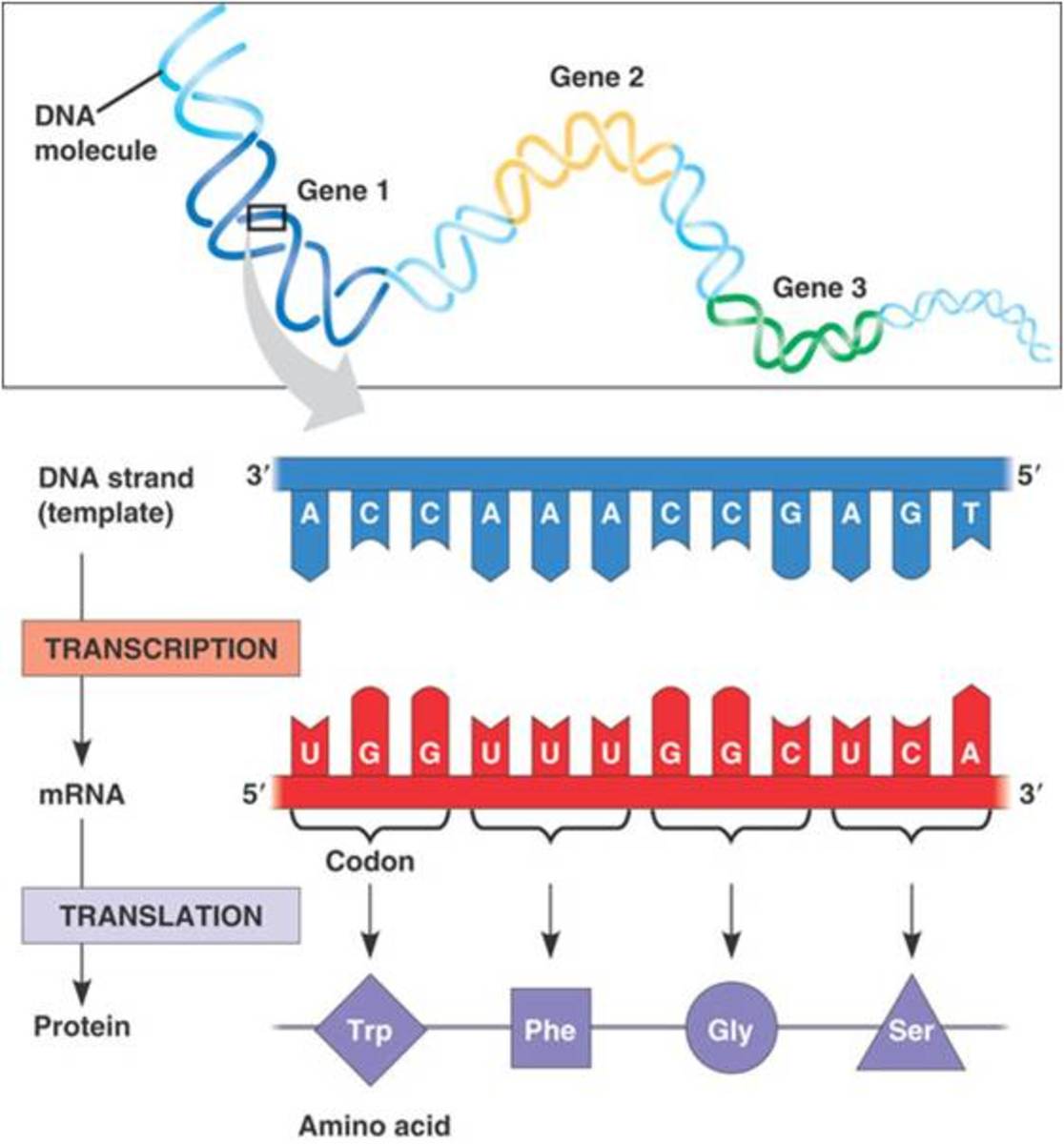
Protein Synthesis Rna Processing Diagram In most cells, protein synthesis consumes more energy than any other biosynthetic process. at least four high energy phosphate bonds are split to make each new peptide bond: two are consumed in charging a trna molecule with an amino acid (see figure 6 56 ), and two more drive steps in the cycle of reactions occurring on the ribosome during. Intron processing. all introns in a pre mrna must be completely and precisely removed before protein synthesis. if the process errs by even a single nucleotide, the reading frame of the rejoined exons would shift, and the resulting protein would be dysfunctional. the process of removing introns and reconnecting exons is called splicing. If the process errs by even a single nucleotide, the reading frame of the rejoined exons would shift, and the resulting protein would be dysfunctional. the process of removing introns and reconnecting exons is called splicing. pre mrna splicing involves the precise removal of introns from the primary rna transcript, leaving the exons present. The mechanism by which cells turn the dna code into a protein product is a two step process, with an rna molecule as the intermediate. figure 3.4.1 – the genetic code: dna holds all of the genetic information necessary to build a cell’s proteins. the nucleotide sequence of a gene is ultimately translated into an amino acid sequence of the.

Comments are closed.