Proving Trigonometric Identities Example 10 Youtube
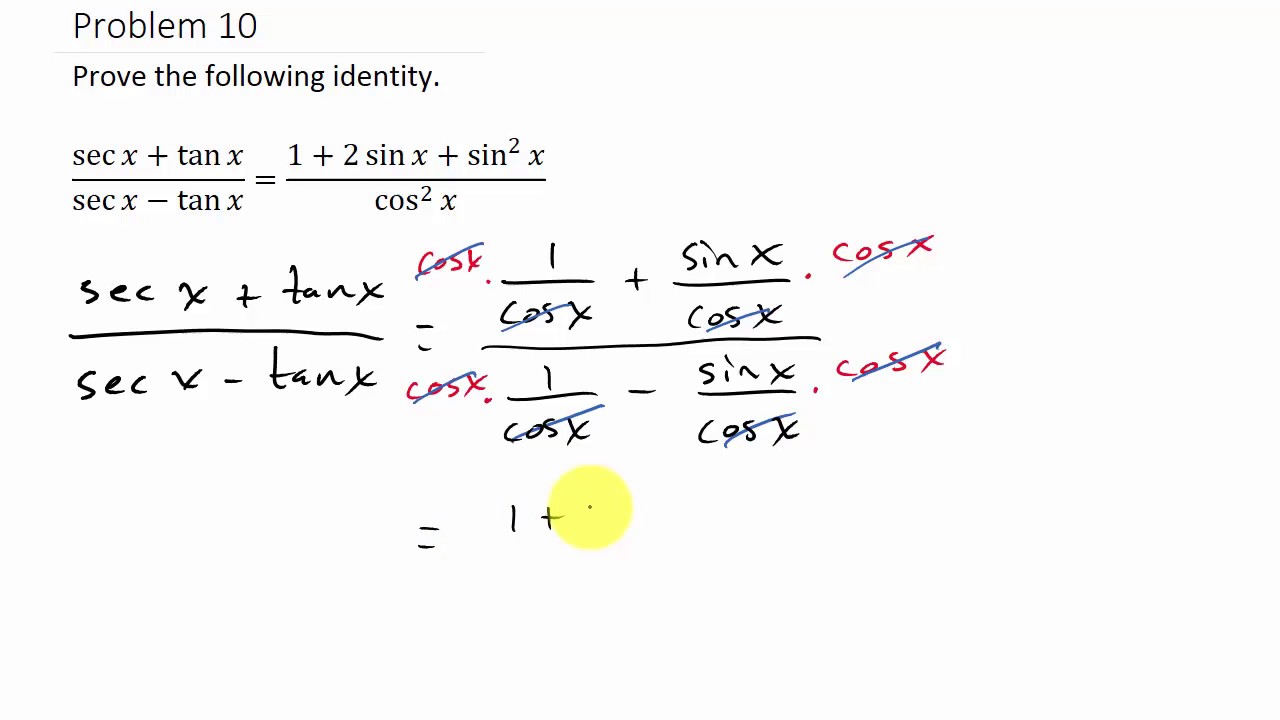
Proving Trigonometric Identities Example 10 Youtube This video shows how to prove trigonometric identities. Once you start getting a few more formulas and identities, you can use these to verify other identities. watch this video for a few examples and some good t.
How To Prove Trigonometric Identities Trigonometry Study This video explains the approach to proving trig identities and covers three examples, including question 8b of the 2019 euclid math contest. contents o. 15 powerful examples! now that we have become comfortable with the steps for verifying trigonometric identities it’s time to start proving trig identities! let’s quickly recap the major steps and ideas that we discovered in our previous lesson. can we plug in values for the angles to show that the left hand side of the equation equals the. Proving trigonometric identities basic. trigonometric identities are equalities involving trigonometric functions. an example of a trigonometric identity is. \sin^2 \theta \cos^2 \theta = 1. sin2 θ cos2 θ = 1. in order to prove trigonometric identities, we generally use other known identities such as pythagorean identities. In this first section, we will work with the fundamental identities: the pythagorean identities, the even odd identities, the reciprocal identities, and the quotient identities. we will begin with the pythagorean identities (see table 1 ), which are equations involving trigonometric functions based on the properties of a right triangle.

Proving Trigonometric Identities Example 5 Youtube Proving trigonometric identities basic. trigonometric identities are equalities involving trigonometric functions. an example of a trigonometric identity is. \sin^2 \theta \cos^2 \theta = 1. sin2 θ cos2 θ = 1. in order to prove trigonometric identities, we generally use other known identities such as pythagorean identities. In this first section, we will work with the fundamental identities: the pythagorean identities, the even odd identities, the reciprocal identities, and the quotient identities. we will begin with the pythagorean identities (see table 1 ), which are equations involving trigonometric functions based on the properties of a right triangle. Example 6.3.14: verify a trigonometric identity 2 term denominator. use algebraic techniques to verify the identity: cosθ 1 sinθ = 1 − sinθ cosθ. (hint: multiply the numerator and denominator on the left side by 1 − sinθ, the conjugate of the denominator.) solution. The trigonometric identities are equations that are true for right angled triangles. periodicity of trig functions. sine, cosine, secant, and cosecant have period 2π while tangent and cotangent have period π. identities for negative angles. sine, tangent, cotangent, and cosecant are odd functions while cosine and secant are even functions.
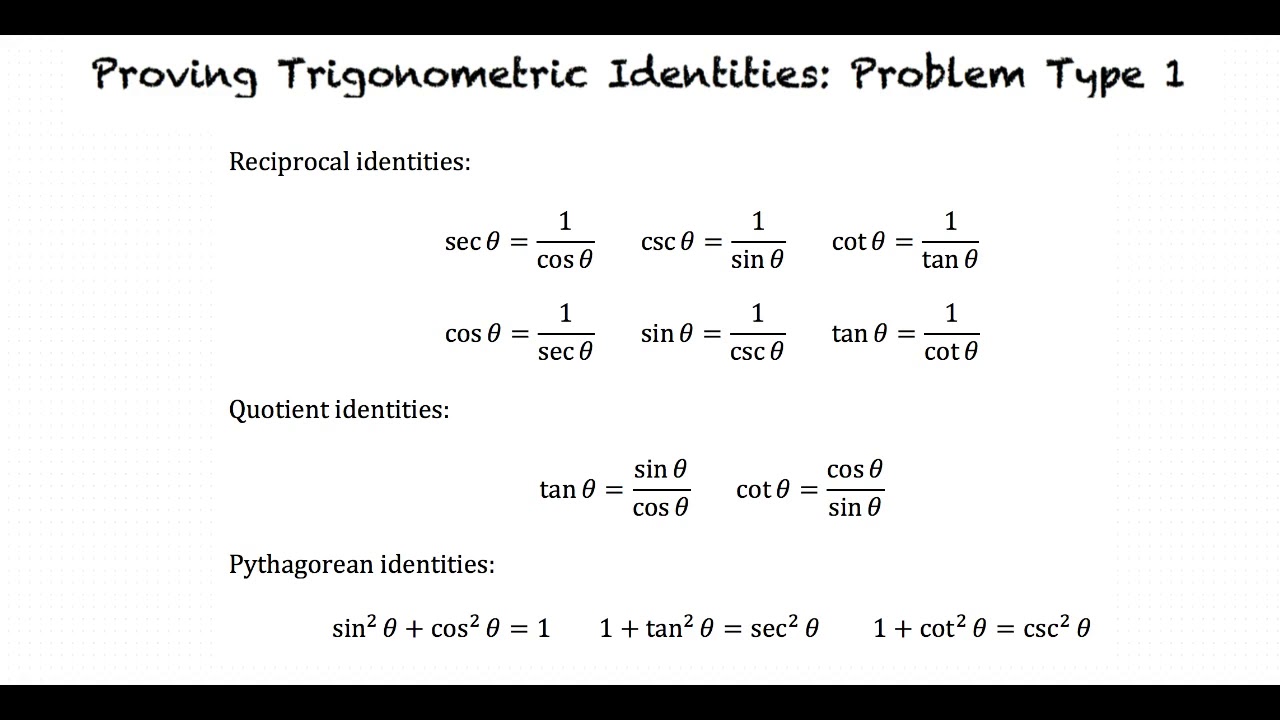
Proving Trigonometric Identities Problem Type 1 Youtube Example 6.3.14: verify a trigonometric identity 2 term denominator. use algebraic techniques to verify the identity: cosθ 1 sinθ = 1 − sinθ cosθ. (hint: multiply the numerator and denominator on the left side by 1 − sinθ, the conjugate of the denominator.) solution. The trigonometric identities are equations that are true for right angled triangles. periodicity of trig functions. sine, cosine, secant, and cosecant have period 2π while tangent and cotangent have period π. identities for negative angles. sine, tangent, cotangent, and cosecant are odd functions while cosine and secant are even functions.

Comments are closed.