Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Enzyme Molecule Photograph By Laguna Design Pix
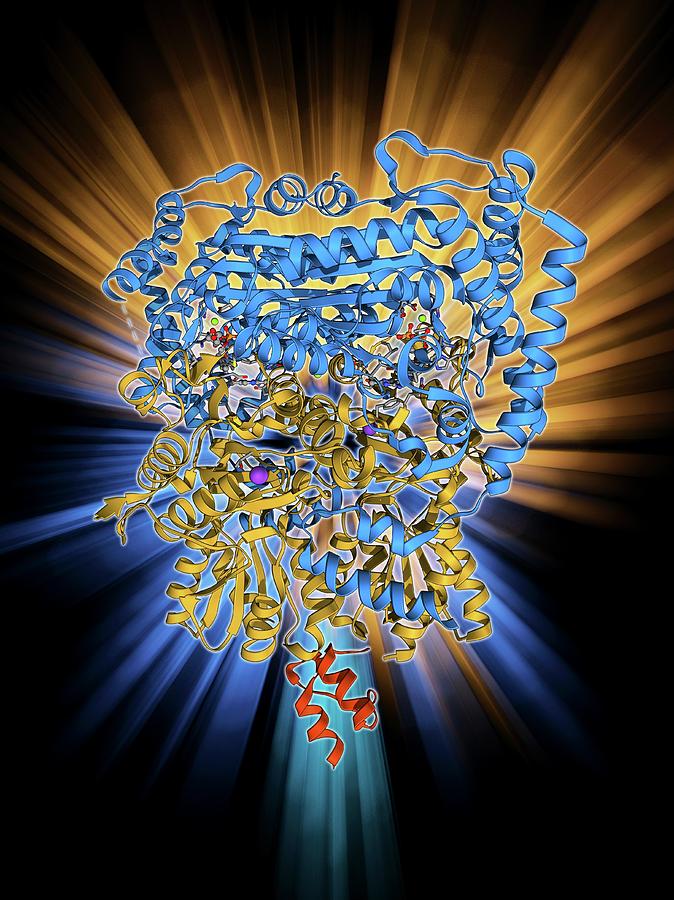
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Enzyme Molecule Photograph By Laguna D Purchase an art print of the photograph "pyruvate dehydrogenase complex enzyme" by laguna design. choose from multiple sizes and hundreds of frame and mat options. all prints are professionally printed, packaged, and shipped within 3 4 business days. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (pdhc) is a multienzyme complex of megadalton size that converts pyruvate into acetyl coenzyme a (fig. 1a, b), thereby linking glycolysis to the citric acid.
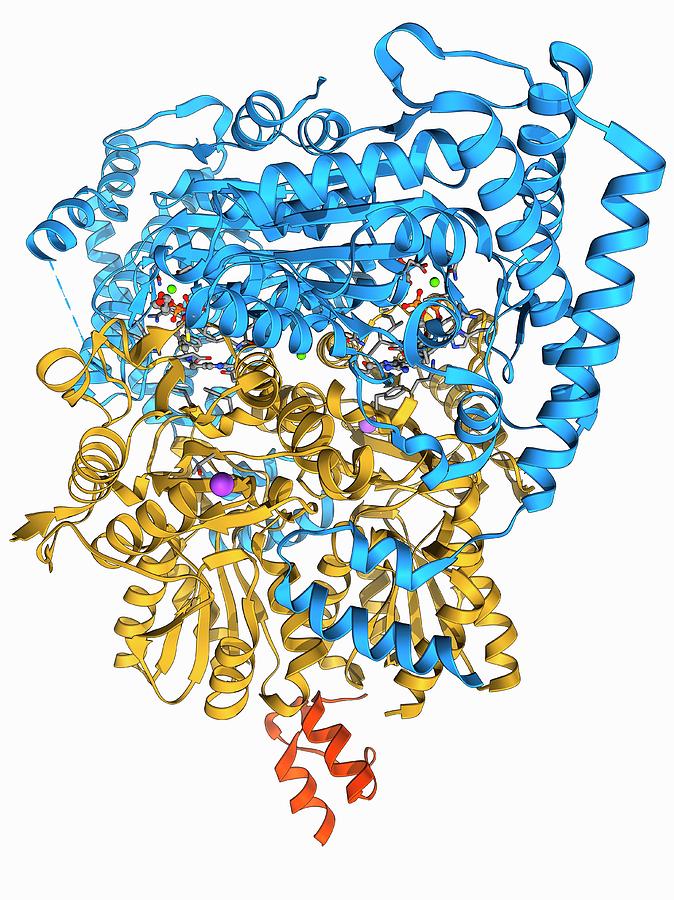
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Enzyme Molecule Photograph By Laguna D Introduction. a combination of crystallography, nmr spectroscopy and electron microscopy is revealing the secrets of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. the complex performs a central step in energy production, catalyzing the reaction that links glycolysis with the tricarboxylic acid cycle. the reaction is performed in three separate steps by three. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes (pdcs) from all known living organisms comprise three principal catalytic components for their mission: e1 and e2 generate acetyl coenzyme a, whereas the fad nad dependent e3 performs redox recycling. here we compare bacterial (escherichia coli) and human pdcs, as they represent the two major classes of the superfamily of 2 oxo acid dehydrogenase complexes. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (pdc) is a complex of three enzymes that converts pyruvate into acetyl coa by a process called pyruvate decarboxylation. [1] acetyl coa may then be used in the citric acid cycle to carry out cellular respiration, and this complex links the glycolysis metabolic pathway to the citric acid cycle. Proteins. pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of pyruvate and a lipoamide to give the acetylated dihydrolipoamide and carbon dioxide. the conversion requires the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate. pyruvate dehydrogenase is usually encountered as a component, referred to as e1, of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (pdc).

Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex Enzyme 2 By Laguna Design Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (pdc) is a complex of three enzymes that converts pyruvate into acetyl coa by a process called pyruvate decarboxylation. [1] acetyl coa may then be used in the citric acid cycle to carry out cellular respiration, and this complex links the glycolysis metabolic pathway to the citric acid cycle. Proteins. pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of pyruvate and a lipoamide to give the acetylated dihydrolipoamide and carbon dioxide. the conversion requires the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate. pyruvate dehydrogenase is usually encountered as a component, referred to as e1, of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (pdc). The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (pdc) is the key enzyme system in the body that catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to form acetyl coenzyme a. by serving as a crossroad between glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid cycle, pdc plays a crucial role in aerobic metabolism [1]. pdc is comprised by three catalytic enzymes and their. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (pdhc) is a multienzyme assembly that links the two major metabolic pathways of glycolysis and citric acid cycle, thereby mediating energy production by oxidative phosphorylation. pdhc converts the product of glycolysis, pyruvate, into acetyl–coenzyme a (acetyl coa) that enters the citric acid cycle, which.

Comments are closed.