Random Sampling Without Replacement
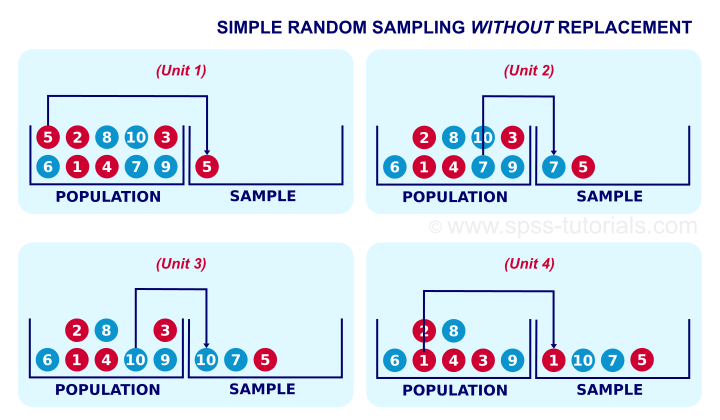
Simple Random Sampling Quick Simple Introduction There are two different ways to collect samples: sampling with replacement and sampling without replacement. this tutorial explains the difference between the two methods along with examples of when each is used in practice. sampling with replacement. suppose we have the names of 5 students in a hat: andy. karl. tyler. becca. jessica. 34.1 random sampling without replacement. randomly selecting records from a large data set may be helpful if your data set is so large as to prevent slow processing, or if one is conducting a survey and needs to select a random sample from some master database.
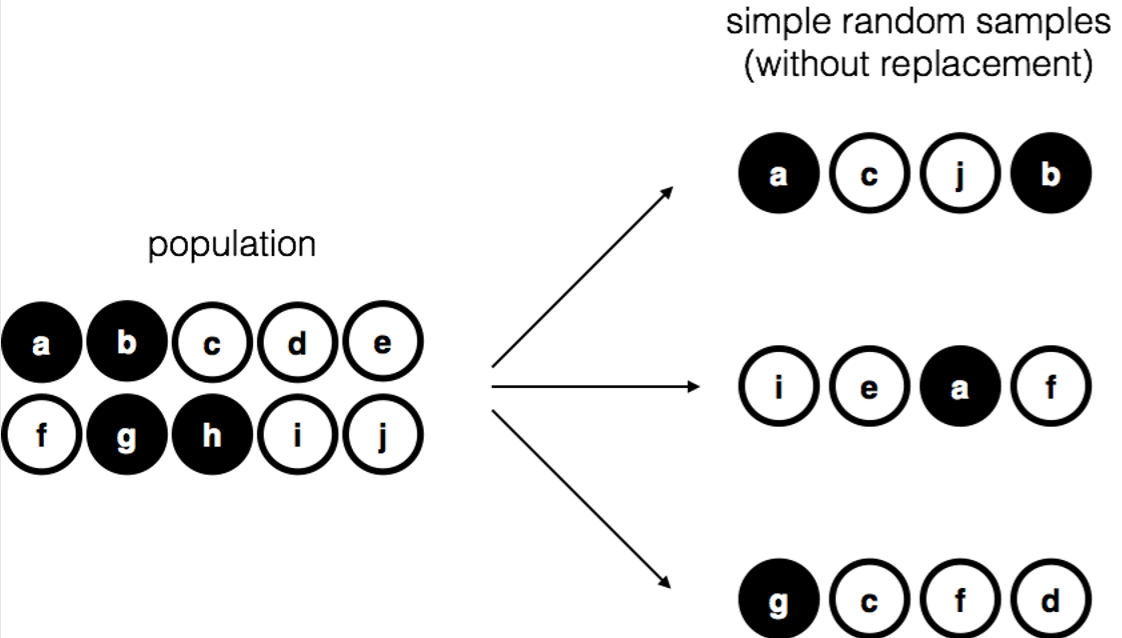
Learning Statistics With R A Tutorial For Psychology Students And Sampling and independent event. sampling with replacement – independent events. sampling without replacement – dependent events. treating sampling without replacement as independent if one of the following are satisfied: a) assume a very big population when population size is not given. only p(a) is given. b) use 5% guideline for cumbersome. What is sampling with and without replacement? sampling without replacement is where items are chosen randomly, and once an observation is chosen it cannot be chosen again. on the other hand, when you sample with replacement, you also choose randomly but an item can be chosen more than once. Sampling with replacement can be defined as random sampling that allows sampling units to occur more than once. sampling with replacement consists of. a sampling unit (like a glass bead or a row of data) being randomly drawn from a population (like a jar of beads or a dataset). recording which sampling unit was drawn. In statistics, a simple random sample (or srs) is a subset of individuals (a sample) chosen from a larger set (a population) in which a subset of individuals are chosen randomly, all with the same probability. it is a process of selecting a sample in a random way.

Comments are closed.