Randomisation Techniques

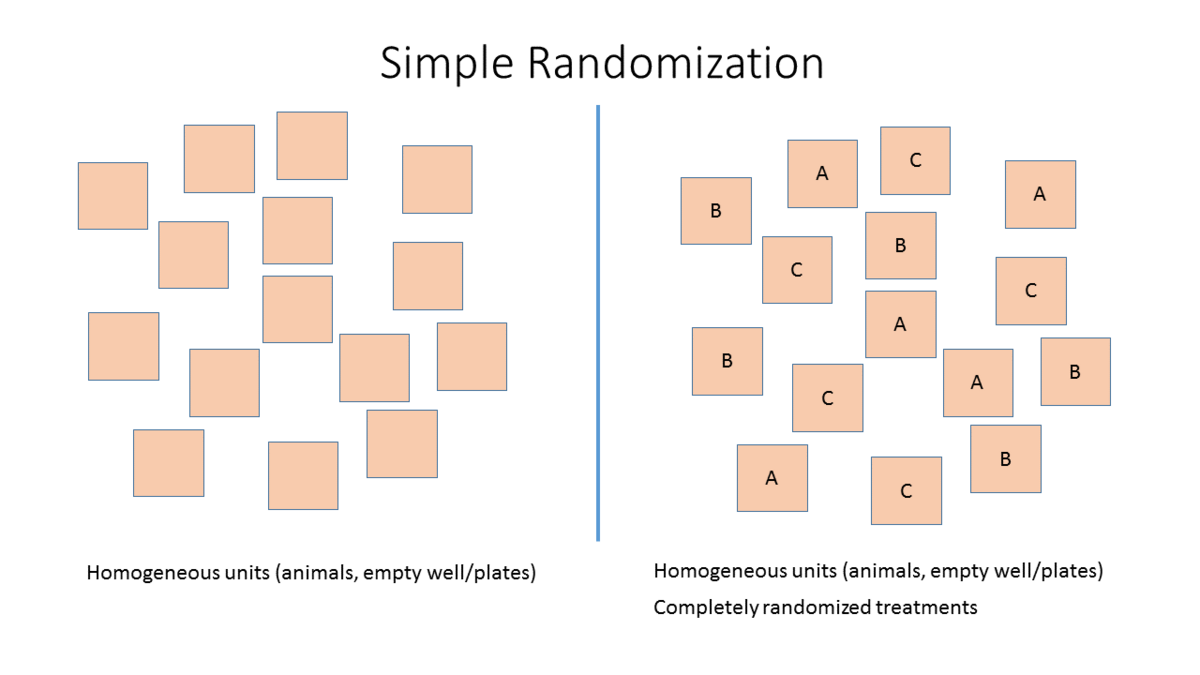
Ppt Chapter 5 Randomization Methods Powerpoint Presentation Free Objective: to review and describe randomization techniques used in clinical trials, including simple, block, stratified, and covariate adaptive techniques. background: clinical trials are required to establish treatment efficacy of many athletic training procedures. in the past, we have relied on evidence of questionable scientific merit to aid. Types of randomization. many procedures have been proposed for the random assignment of participants to treatment groups in clinical trials. in this article, common randomization techniques, including simple randomization, block randomization, stratified randomization, and covariate adaptive randomization, are reviewed.
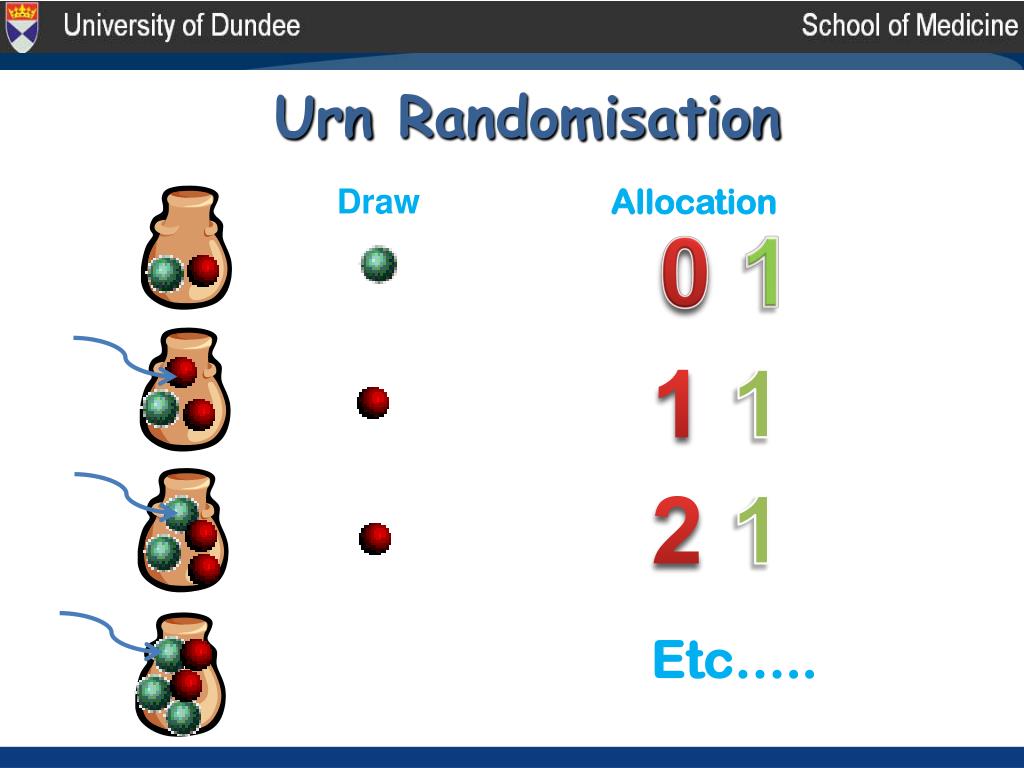
Ppt A Brief Introduction To Randomisation Methods Powerpoint Randomization as a method of experimental control has been extensively used in human clinical trials and other biological experiments. it prevents the selection bias and insures against the accidental bias. it produces the comparable groups and eliminates the source of bias in treatment assignments. finally, it permits the use of probability. Implementation of randomization in clinical trials is due to a. bradford hill who designed the first randomized clinical trial evaluating the use of streptomycin in treating tuberculosis in 1946 [9, 12, 13]. reference [14] provides a good summary of the rationale and justification for the use of randomization in clinical trials. Stratified randomization is used to obviate the unintentional impact that population characteristics or other independent variables, or “covariates,” may have on the trial result. 3, 7, 19 for stratified randomization, a subject is first placed in a specific stratum based on his her baseline characteristics, then randomization is applied to that stratum to determine their treatment group. Randomization is a statistical process in which a random mechanism is employed to select a sample from a population or assign subjects to different groups. [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] the process is crucial in ensuring the random allocation of experimental units or treatment protocols, thereby minimizing selection bias and enhancing the statistical.
Randomisation And Blinding Premier Stratified randomization is used to obviate the unintentional impact that population characteristics or other independent variables, or “covariates,” may have on the trial result. 3, 7, 19 for stratified randomization, a subject is first placed in a specific stratum based on his her baseline characteristics, then randomization is applied to that stratum to determine their treatment group. Randomization is a statistical process in which a random mechanism is employed to select a sample from a population or assign subjects to different groups. [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] the process is crucial in ensuring the random allocation of experimental units or treatment protocols, thereby minimizing selection bias and enhancing the statistical. Background randomization is the foundation of any clinical trial involving treatment comparison. it helps mitigate selection bias, promotes similarity of treatment groups with respect to important known and unknown confounders, and contributes to the validity of statistical tests. various restricted randomization procedures with different probabilistic structures and different statistical. Implementing the chosen randomisation method once the method of randomisation has been es tablished the next important step is to consider how to implement it. the recommended way is to enlist the services of a central randomisation office that can offer robust, validated techniques with the security and back up needed to imple.

Comments are closed.