Ras Raf Mek Erk Signaling And The Mtor Pathway Interactions And Regulation

Ras Raf Mek Erk And Pi3k Mtor Signaling Pathways Download The raf raf mek erk signaling cascade is a well established mapk pathway in cell biology that governs several crucial cellular processes such as development, differentiation, proliferation, and. The core ras–erk pathway is typically initiated at the plasma membrane, where guanosine triphosphate (gtp) loaded ras directly contacts the raf kinases and induces catalytic activity through a.

Ras Raf Mek Erk Signaling And The Mtor Pathway Interact Ras activates several signaling pathways, including the raf mek erk and the pi3k akt mtor pathways, with different prevalence depending on ras isoform, cell type, and context [8,9]. raf kinases, present in the cytoplasm as inactive monomers, bind to active gtp bound ras and to dimers of the 14−3−3 regulatory proteins. However, the ras raf mek erk signaling pathway is extremely complex and can generate a rich array of crosstalk with other signaling pathways. although we have a general overview of the interaction between the ras raf mek erk signaling pathway and autophagy, little is known about the precise mechanisms of their intricate interplay. The pi3k akt mtor and raf mek erk pathways are commonly activated by mutations and chromosomal translocation in vital targets. the pi3k akt mtor signaling pathway is dysregulated in nearly all kinds of neoplasms, with the component in this pathway alternations. raf mek erk signaling cascades are used to conduct signaling from the cell surface. Ras–raf–mek–erk is a classical pathway from the 1990s and transmits extracellular signals to specific intracellular targets (fig. 1, created with biorender ). 3 a vast map of substrates related to cell proliferation, differentiation, and metabolism are regulated by erk. 4, 5, 6 statistically, 33% of ras mutations and 8% of braf mutations are observed in all human cancers thus far. 7.
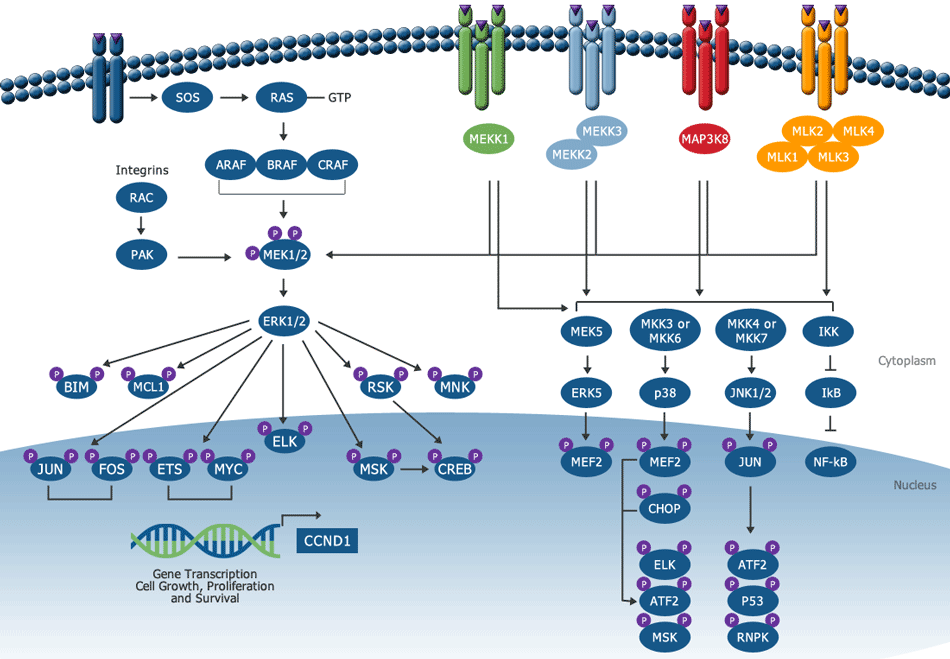
Mek Erk Pathway Antibodies Rockland The pi3k akt mtor and raf mek erk pathways are commonly activated by mutations and chromosomal translocation in vital targets. the pi3k akt mtor signaling pathway is dysregulated in nearly all kinds of neoplasms, with the component in this pathway alternations. raf mek erk signaling cascades are used to conduct signaling from the cell surface. Ras–raf–mek–erk is a classical pathway from the 1990s and transmits extracellular signals to specific intracellular targets (fig. 1, created with biorender ). 3 a vast map of substrates related to cell proliferation, differentiation, and metabolism are regulated by erk. 4, 5, 6 statistically, 33% of ras mutations and 8% of braf mutations are observed in all human cancers thus far. 7. The mapk pathway relaying cellular signal through ras raf mek erk plays a critical role in cell cycle and proliferation. the mapk cascade is initiated by activation of receptor tyrosine kinases. Introduction: the ras raf map kinase erk kinase (mek) extracellular signal regulated kinase (erk) (mapk) and the pi3k akt mammalian target of rapamycin (mtor) (pi3k) pathways are frequently deregulated in human cancer as a result of genetic alterations in their components or upstream activation of cell surface receptors. these signalling.
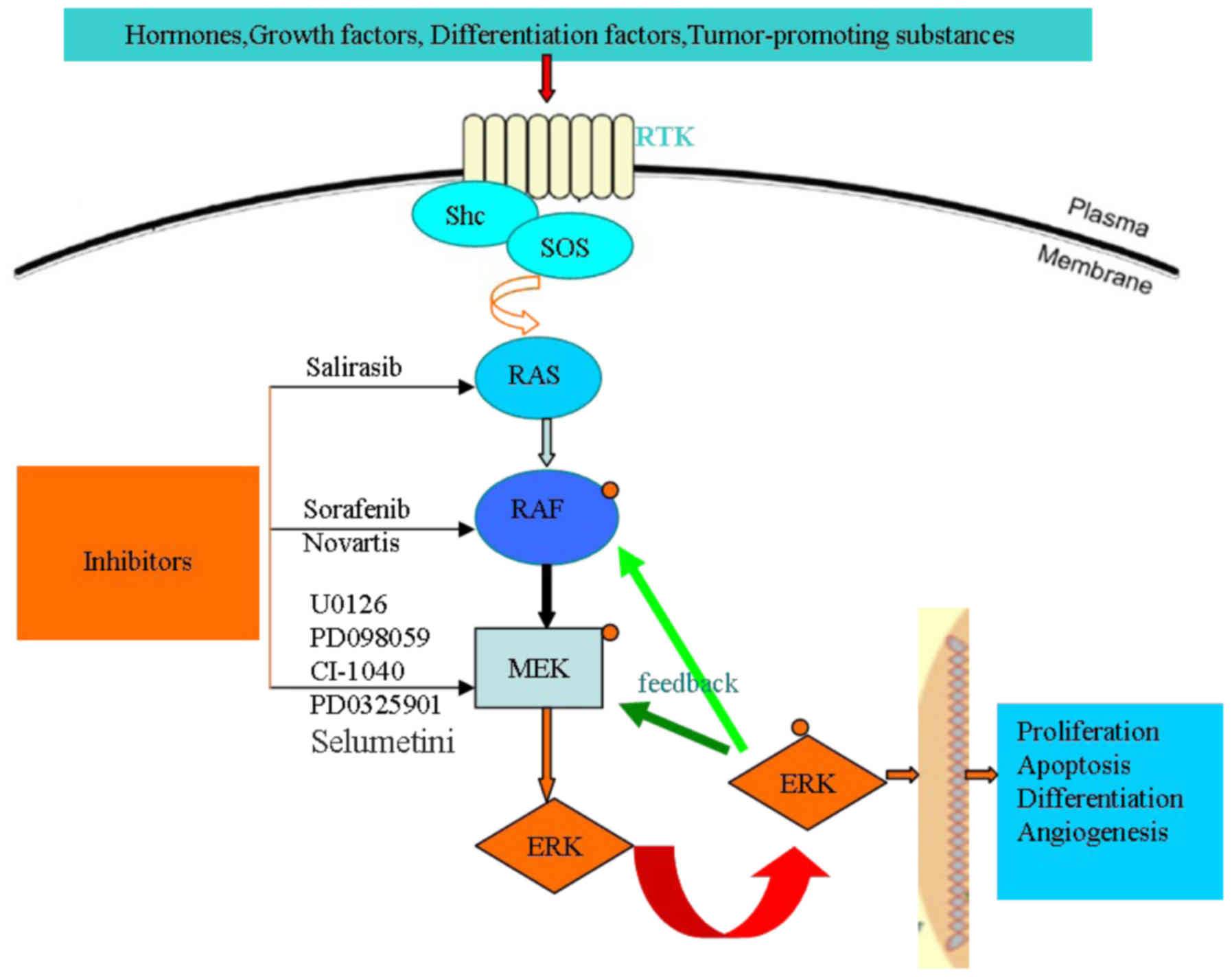
Targeting The Ras Raf Mek Erk Pathway In Hepatocellular Carcinoma Revi The mapk pathway relaying cellular signal through ras raf mek erk plays a critical role in cell cycle and proliferation. the mapk cascade is initiated by activation of receptor tyrosine kinases. Introduction: the ras raf map kinase erk kinase (mek) extracellular signal regulated kinase (erk) (mapk) and the pi3k akt mammalian target of rapamycin (mtor) (pi3k) pathways are frequently deregulated in human cancer as a result of genetic alterations in their components or upstream activation of cell surface receptors. these signalling.

Comments are closed.