Reading Monopolies And Deadweight Loss Microeconomics
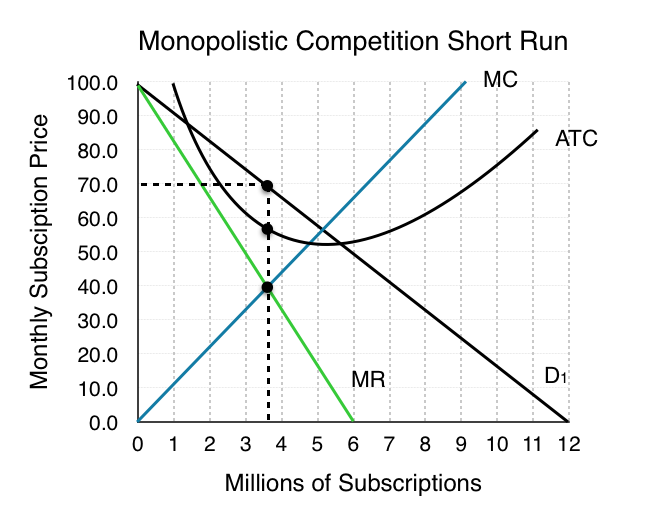
Deadweight Loss Monopoly Formula Kelly Clarkson Blog The monopolist restricts output to qm and raises the price to pm. reorganizing a perfectly competitive industry as a monopoly results in a deadweight loss to society given by the shaded area grc. it also transfers a portion of the consumer surplus earned in the competitive case to the monopoly firm. now, suppose that all the firms in the. The monopolist restricts output to qm and raises the price to pm. reorganizing a perfectly competitive industry as a monopoly results in a deadweight loss to society given by the shaded area grc. it also transfers a portion of the consumer surplus earned in the competitive case to the monopoly firm. now, suppose that all the firms in the.
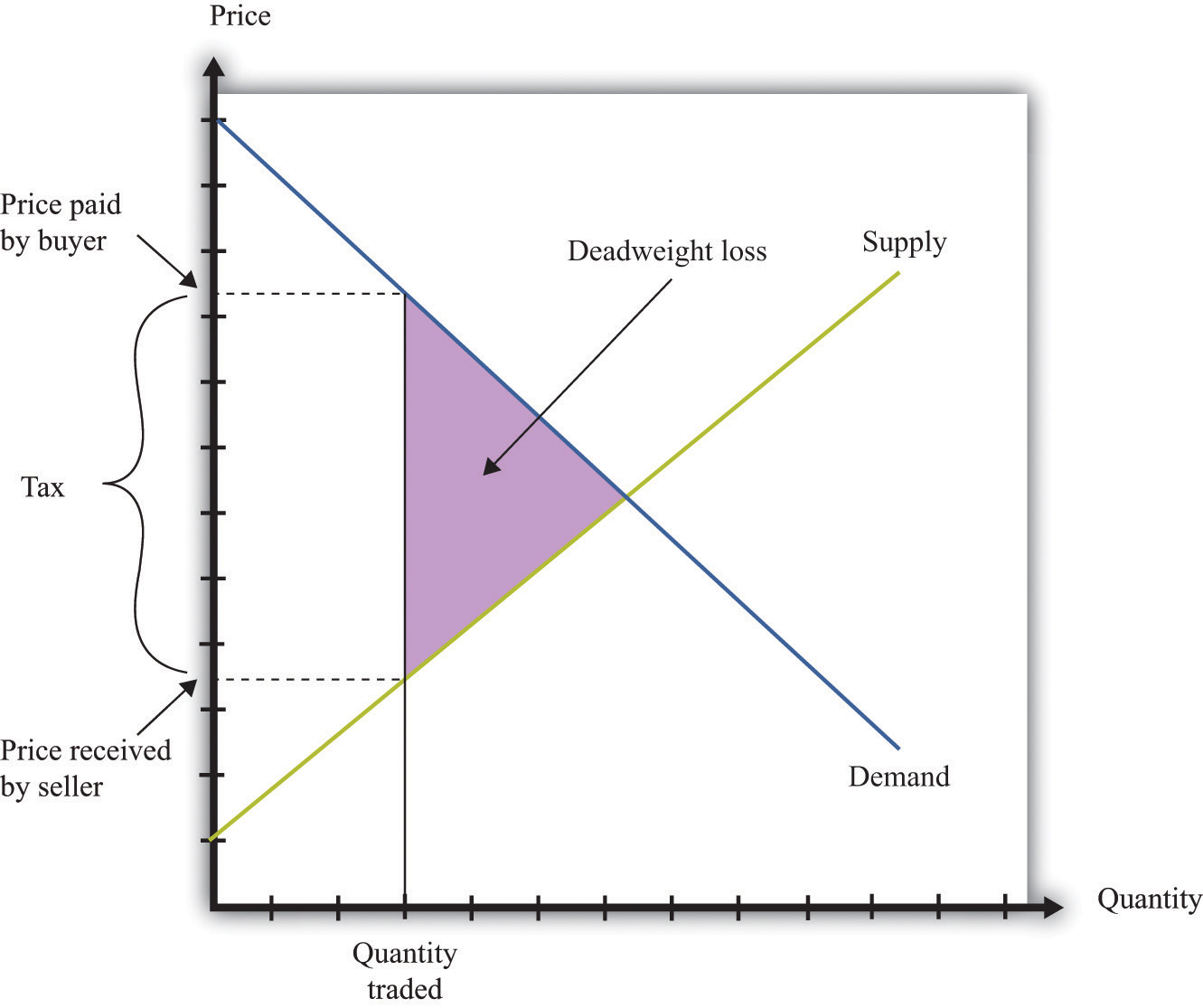
Deadweight Loss Monopoly Formula Kelly Clarkson Blog The monopolist restricts output to qm and raises the price to pm. reorganizing a perfectly competitive industry as a monopoly results in a deadweight loss to society given by the shaded area grc. it also transfers a portion of the consumer surplus earned in the competitive case to the monopoly firm. now, suppose that all the firms in the. Want to create or adapt books like this? learn more about how pressbooks supports open publishing practices. In other words, if an action can be taken where the gains outweigh the losses, and by compensating the losers everyone could be made better off, then there is a deadweight loss. when we move from a monopoly market to a competitive one, market surplus increases by $1.2 billion. this means that the monopoly causes a $1.2 billion deadweight loss. How monopolies form: barriers to entry. because of the lack of competition, monopolies tend to earn significant economic profits. these profits should attract vigorous competition as described in perfect competition, and yet, because of one particular characteristic of monopoly, they do not. barriers to entry home are the legal, technological.
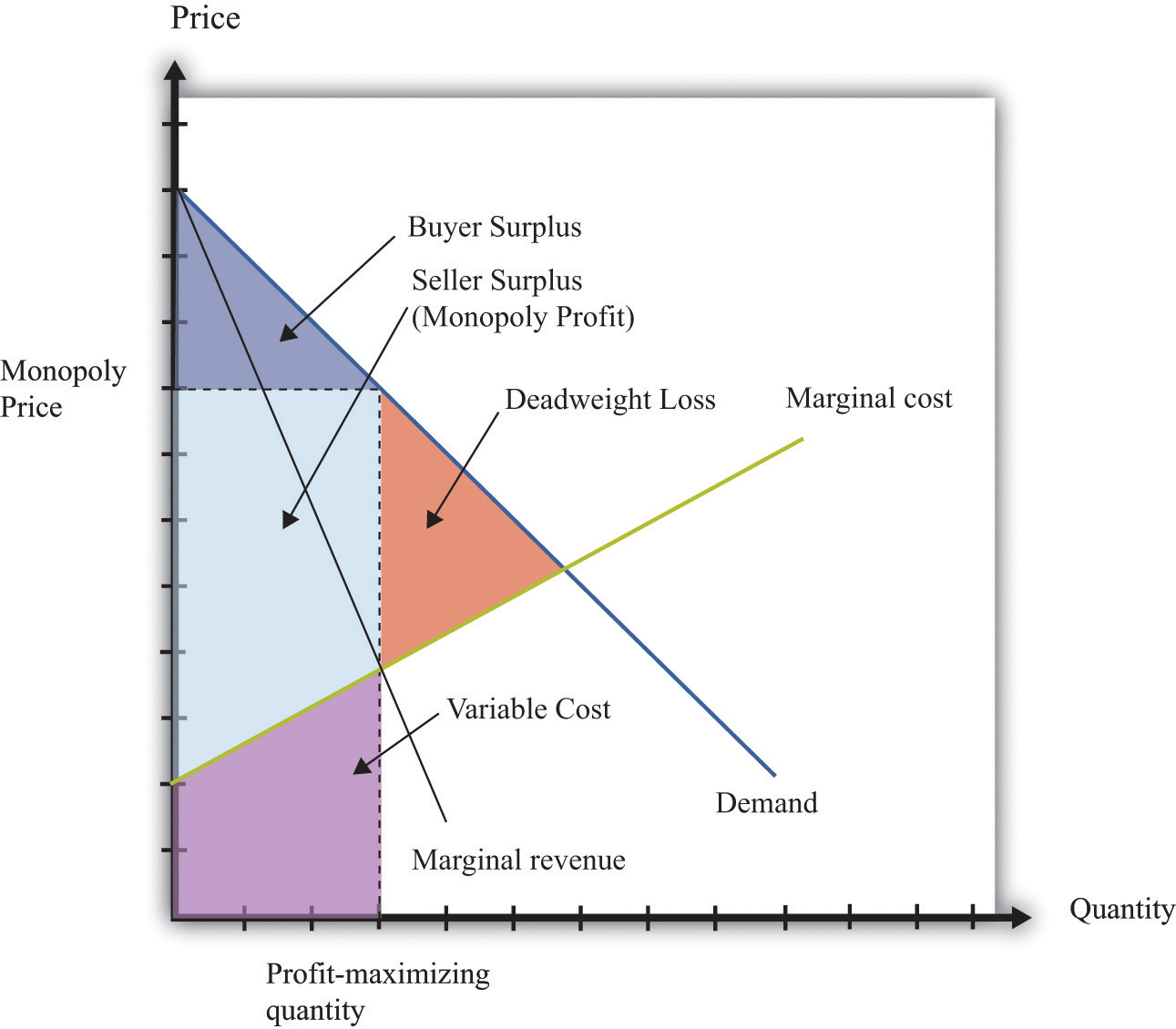
Efficiency And Deadweight Loss In other words, if an action can be taken where the gains outweigh the losses, and by compensating the losers everyone could be made better off, then there is a deadweight loss. when we move from a monopoly market to a competitive one, market surplus increases by $1.2 billion. this means that the monopoly causes a $1.2 billion deadweight loss. How monopolies form: barriers to entry. because of the lack of competition, monopolies tend to earn significant economic profits. these profits should attract vigorous competition as described in perfect competition, and yet, because of one particular characteristic of monopoly, they do not. barriers to entry home are the legal, technological. Courses on khan academy are always 100% free. start practicing—and saving your progress—now: khanacademy.org economics finance domain ap microec. Learn monopoly efficiency and deadweight loss with free step by step video explanations and practice problems by experienced tutors.

Monopoly Deadweight Loss Wize University Microeconomics Textbook Courses on khan academy are always 100% free. start practicing—and saving your progress—now: khanacademy.org economics finance domain ap microec. Learn monopoly efficiency and deadweight loss with free step by step video explanations and practice problems by experienced tutors.

Deadweight Loss What It Is Formula 3 Examples

Comments are closed.