Reducing Healthcare Associated Infections Patientcarelink

Reducing Healthcare Associated Infections вђ Patientcarelink Healthcare acquired infections (hais) catheter associated urinary tract infections (cauti) central line associated blood stream infections (clabsi) on the cusp: stop hai; clostridium difficile (c.diff cdi) surgical site infections (ssi) sepsis; hospital acquired conditions (hacs) adverse drug event (ade) airway safety & failure to rescue (ftr). In american hospitals alone, the centers for disease control (cdc) estimates that hais account for an estimated 1.7 million infections and 99,000 associated deaths each year. of these infections: 32 percent of all healthcare acquired infection are urinary tract infections; 22 percent are surgical site infections.
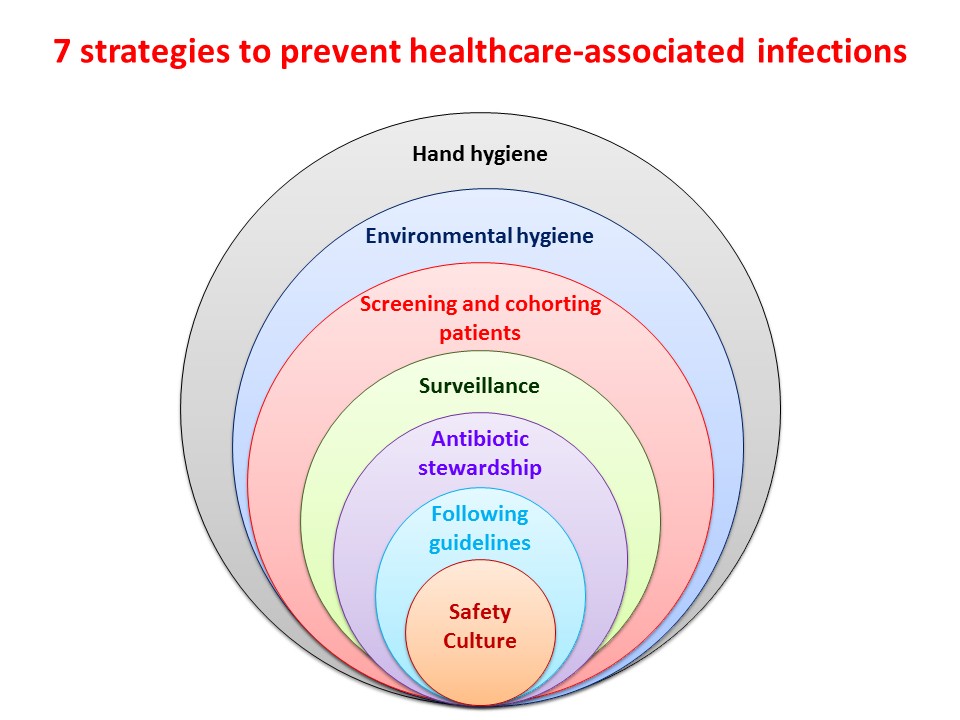
7 Strategies To Prevent Healthcare Associated Infections вђ Global Healthcare acquired infections (hais), also known as nosocomial infections, are infections that patients get while receiving treatment for medical or surgical conditions. hais occur in all settings of care, including hospitals, surgical centers, ambulatory clinics, and long term care facilities such as nursing homes and rehabilitation. Strategies to prevent healthcare associated infections. hcais (their prevention and control) are a significant global public health burden about which concerns have been raised from all healthcare stakeholders, including health professionals, patients, and the public. 45 – 48 their impact has dramatically increased because of the advent of multidrug resistant pathogenic microorganisms. 49. Clinical recommendation evidence rating comments; to reduce health care–associated infections, institutions should establish local infection prevention processes, including ongoing educational. A multimodal approach is required to reduce the burden of hcai, mainly involving the healthcare professionals’ education, implementing evidence based care bundles with attention to aseptic techniques, standardisation of procedures, and identifying local determinants of infection and improvement in reporting and surveillance for infections. 3–7 intravenous fluid and drug preparation and.

Comments are closed.