Refraction
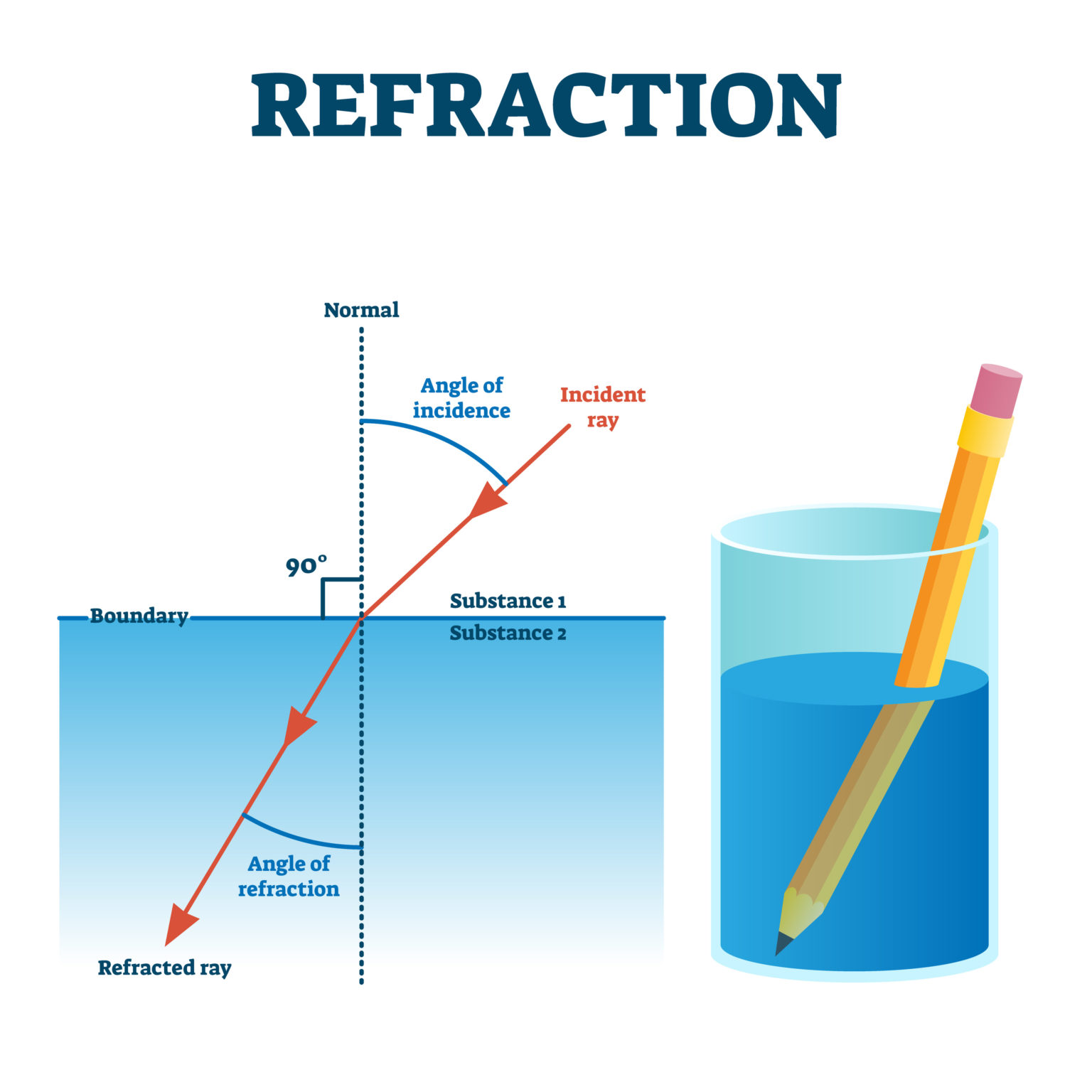
What Is Refraction Refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another due to a change in speed or medium. learn how refraction follows snell's law, causes dispersion of light, and affects optical phenomena such as rainbows and prisms. Refraction, in physics, the change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to another caused by its change in speed. for example, waves travel faster in deep water than in shallow. if an ocean wave approaches a beach obliquely, the part of the wave farther from the beach will move faster than the part closer in, and so the wave will.

Refraction Definition Examples Facts Britannica Learn about refraction of light, the phenomenon of bending of light when it travels from one medium to another. find out the causes, laws, refractive index, applications, and solved problems of refraction of light. Learn how light bends as it travels from one substance to another, and how this affects lenses, prisms and rainbows. explore the refractive index, speed of light and angle of refraction with examples and activities. Learn how refraction changes the speed and direction of waves as they enter a new medium. find out the index of refraction, snell's law, and examples of refraction in light, sound, and water. In the situations shown in figure 25.3.3 25.3. 3, medium 2 has a greater index of refraction than medium 1. this means that the speed of light is less in medium 2 than in medium 1. note that as shown in figure 25.3.3a 25.3. 3 a, the direction of the ray moves closer to the perpendicular when it slows down.

Light Refraction Reflection And Absorption Learn how refraction changes the speed and direction of waves as they enter a new medium. find out the index of refraction, snell's law, and examples of refraction in light, sound, and water. In the situations shown in figure 25.3.3 25.3. 3, medium 2 has a greater index of refraction than medium 1. this means that the speed of light is less in medium 2 than in medium 1. note that as shown in figure 25.3.3a 25.3. 3 a, the direction of the ray moves closer to the perpendicular when it slows down. Learn what refraction is, how it occurs, and why it is important for optical systems. find out the refractive indices of common materials, the laws of refraction, and the examples and applications of refraction. Learn about the law of refraction, the index of refraction, and the effects of refraction on light and sound. find examples, graphs, and tables of refractive indices for various materials and phenomena.

Refraction Of Light Experiment Pencil In Water 25747605 Vector Art At Learn what refraction is, how it occurs, and why it is important for optical systems. find out the refractive indices of common materials, the laws of refraction, and the examples and applications of refraction. Learn about the law of refraction, the index of refraction, and the effects of refraction on light and sound. find examples, graphs, and tables of refractive indices for various materials and phenomena.
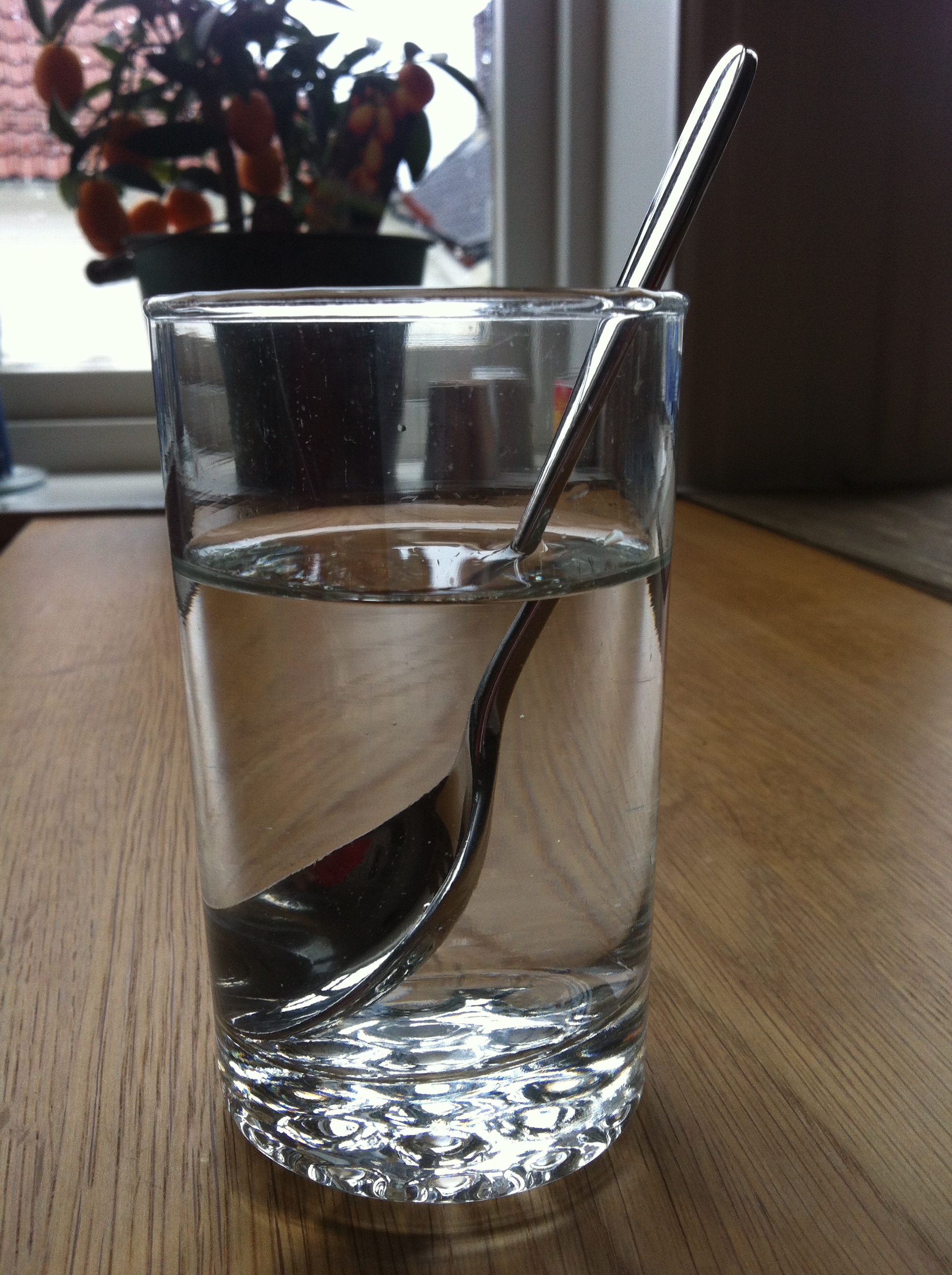

Refraction Of Light In Water Looking At A Couple Of Examples

Comments are closed.