Research Suite Randomization Feature Explained

Research Suite Randomization Feature Explained Youtube Join dan fleetwood and learn how to excel in your surveys with questionpro's unique features. avoid biased data: if the respondents keep on selecting a sin. Background randomization is the foundation of any clinical trial involving treatment comparison. it helps mitigate selection bias, promotes similarity of treatment groups with respect to important known and unknown confounders, and contributes to the validity of statistical tests. various restricted randomization procedures with different probabilistic structures and different statistical.

Randomization Clinical Research Glossary This is the randomization method recommended for large scale clinical trials, because the likelihood of imbalance in trials with a small number of subjects is high [6–8]. 6) however, as the number of subjects does not always increase, other solutions need to be considered. a block randomization is helpful to resolve the imbalance in number of. Randomized controlled trials (rcts) have traditionally been viewed as the gold standard of clinical trial design, residing at the top of the hierarchy of levels of evidence in clinical study; this is because the process of randomization can minimize differences in characteristics of the groups that may influence the outcome, thus providing the. The idea sounds so simple that defining it becomes almost a joke: randomisation is “putting participants into the treatment groups randomly”. if only it were that simple. randomisation can be a minefield, and not everyone understands what exactly it is or why they are doing it. a key feature of a randomised controlled trial is that it is. Random allocation is a technique that chooses individuals for treatment groups and control groups entirely by chance with no regard to the will of researchers or patients' condition and preference. this allows researchers to control all known and unknown factors that may affect results in treatment groups and control groups.
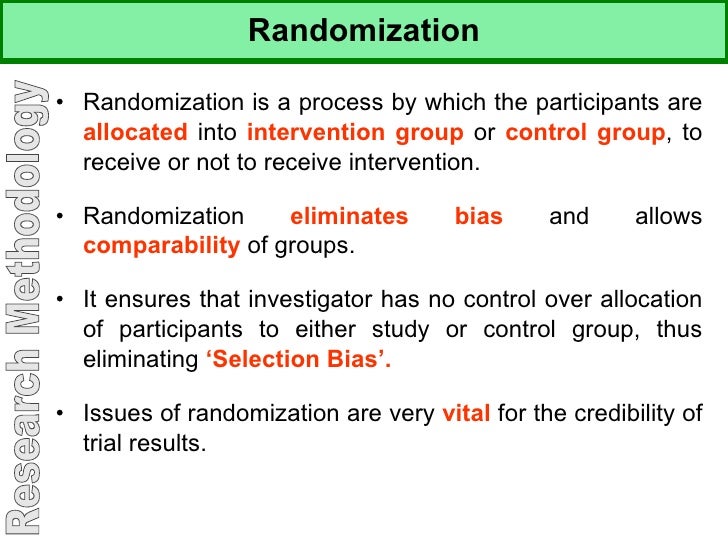
Research Methodology The idea sounds so simple that defining it becomes almost a joke: randomisation is “putting participants into the treatment groups randomly”. if only it were that simple. randomisation can be a minefield, and not everyone understands what exactly it is or why they are doing it. a key feature of a randomised controlled trial is that it is. Random allocation is a technique that chooses individuals for treatment groups and control groups entirely by chance with no regard to the will of researchers or patients' condition and preference. this allows researchers to control all known and unknown factors that may affect results in treatment groups and control groups. Online randomization with castor. to guarantee a validated variable block randomization for your clinical trial, castor edc uses a carefully curated randomization algorithm. the special algorithm is constructed to divide randomized inclusions across groups in variable block sizes to ensure true randomness. the groups as well as the block sizes. A study design that randomly assigns participants into an experimental group or a control group. as the study is conducted, the only expected difference between the control and experimental groups in a randomized controlled trial (rct) is the outcome variable being studied. advantages. good randomization will "wash out" any population bias.

Comments are closed.