Risky Drinking And Alcohol Use Disorder Epidemiology Pathogenesis
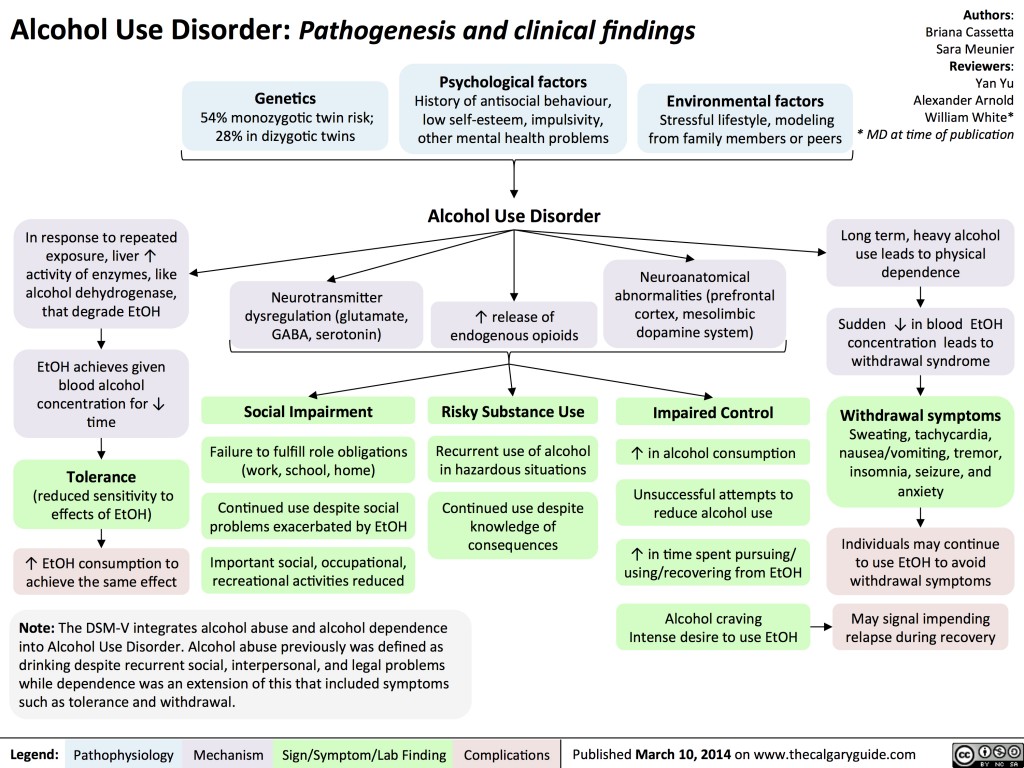
Alcohol Use Disorder Pathogenesis And Clinical Findings Calgary Guide Unhealthy alcohol use ranges from use that puts patients at risk of health consequences to use causing multiple medical and or behavioral problems meeting the american psychiatric association’s diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, fifth edition (dsm 5) diagnostic criteria for alcohol use disorder. the epidemiology. Alcohol is the most commonly used substance in the united states, with 84% of people 18 and older reporting lifetime use, according to data from the 2022 national survey on drug use and health. alcohol use exists along a spectrum from low risk to alcohol use disorder (aud). the intervening category, known as risky drinking, includes heavy drinking as well as binge drinking.[1] aud is a chronic.

Risky Drinking And Alcohol Use Disorder Epidemiology Pathogenesis Introduction. alcohol use disorders (auds) are serious psychiatric conditions often leading to major adverse consequences. the 2018 world health organization’s (who) global status report on alcohol and health determined that in 2016 harmful use of alcohol caused approximately 3 million deaths (or 5.3% of all deaths), more than hypertension and diabetes combined. High fasd prevalence reflects the high prevalence of alcohol use and pae: approximately 25% of 18–34 year old men and women binge drink (defined by niaa as five of more drinks per occasion for men and four or more for women), 11 and 7·3% of pregnancies are alcohol exposed. 12 approximately 45% of pregnancies are unplanned, 13 and many are. Alcohol use disorders are among the most prevalent mental disorders globally, affecting 8·6% (95% ci 8·1–9·1) of men and 1·7% (1·6–1·9) of women in 2016 (total point estimate 5·1%; 4·9–5·4). 1,2 although the prevalence of alcohol use disorder in men is still five times that in women, globally some signs exist of the gender gap. Increases in alcohol use, high risk drinking, and dsm iv aud in the us population and among subgroups, especially women, older adults, racial ethnic minorities, and the socioeconomically disadvantaged, constitute a public health crisis. taken together, these findings portend increases in many chroni ….

Comments are closed.