Rna Processing In Eukaryotes вђ Biology 2e Part I 2nd Edition

Rna Processing In Eukaryotes вђ Biology 2e Part I 2nd E Figure 15.11 eukaryotic pre mrna processing. in addition to 5’ cap and 3’ poly a tail addition, introns must be precisely removed and exons joined to generate a functional mrna. nucleotides upstream (towards the 5’cap) of the translation start codon are part of the 5’ untranslated region (5’ utr). nucleotides downstream (towards 3. The three most important steps of pre mrna processing are the addition of stabilizing and signaling factors at the 5′ and 3′ ends of the molecule, and the removal of the introns ((figure)). in rare cases, the mrna transcript can be “edited” after it is transcribed. eukaryotic mrna contains introns that must be spliced out.
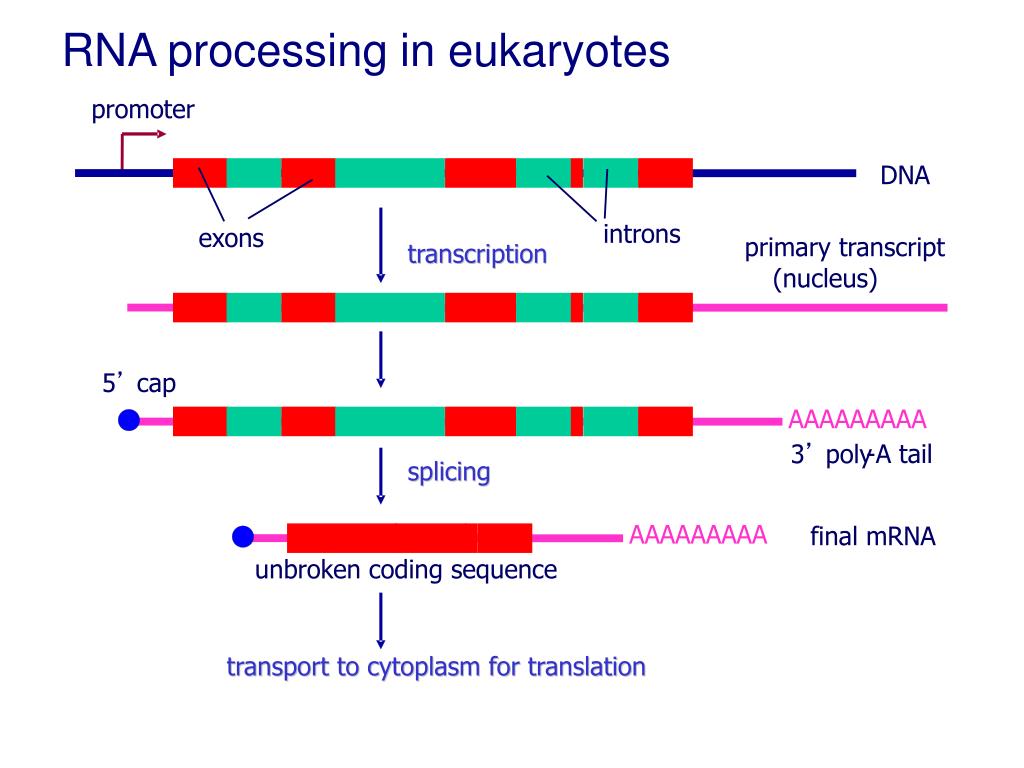
Ppt Rna Processing In Eukaryotes Powerpoint Presentation Free Study biology online for free by downloading openstax's college biology 2e book and using our accompanying online resources including a biology study guide. Eukaryotic pre mrnas undergo extensive processing after transcription but before translation. for clarity, this module’s discussion of transcription and translation in eukaryotes will use the term “mrnas” to describe only the mature, processed molecules that are ready to be translated. Figure 15.8.1 15.8. 1: poly (a) polymerase adds a 3′ poly (a) tail to the pre mrna.: the pre mrna is cleaved off the rest of the growing transcript before rna polymerase ii has stopped transcribing. this cleavage is done by an endonuclease containing protein complex that binds to an aauaaa sequence upstream of the cleavage site and to a gu. The 5′ untranslated region (5′ utr; also called the leader) is a nucleotide sequence at the 5′ end of the mrna that does not encode any of amino acids. in bacterial mrna, this region consists of the consensus sequence termed as the shine dalgarno sequence. during translation, shine dalgarno sequence serves as a ribosome binding site.
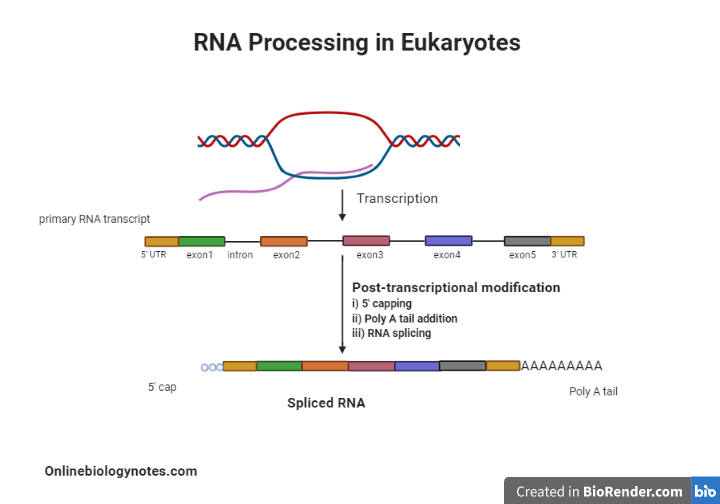
Rna Processing In Eukaryotes Online Biology Notes Figure 15.8.1 15.8. 1: poly (a) polymerase adds a 3′ poly (a) tail to the pre mrna.: the pre mrna is cleaved off the rest of the growing transcript before rna polymerase ii has stopped transcribing. this cleavage is done by an endonuclease containing protein complex that binds to an aauaaa sequence upstream of the cleavage site and to a gu. The 5′ untranslated region (5′ utr; also called the leader) is a nucleotide sequence at the 5′ end of the mrna that does not encode any of amino acids. in bacterial mrna, this region consists of the consensus sequence termed as the shine dalgarno sequence. during translation, shine dalgarno sequence serves as a ribosome binding site. 10.1: introduction. transcription, the synthesis of rna based on a dna template, is the central step of the central dogma proposed by crick in 1958. the basic steps of transcription are the same as for replication: initiation, elongation and termination. differences between transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes are in the details. Rna processing and turnover. although transcription is the first and most highly regulated step in gene expression, it is usually only the beginning of the series of events required to produce a functional rna. most newly synthesized rnas must be modified in various ways to be converted to their functional forms.

Comments are closed.