Series And Parallel Circuits Top 5 Differences Circuit Diagram A

Series And Parallel Circuits Top 5 Differences Circuit Series and parallel circuits – top 5 differences, circuit diagram and explanation. in electrical engineering, two terminal components can be connected in series or parallel configurations. electrical components connected in series are along a single “electrical path”. each component in the series network has the same flow of electric. All of the resistors, as well as the battery, are connected between these two sets of points. this means that the same voltage (v) is dropped across all components in a parallel circuit. series vs parallel circuit review: in a series circuit, all components are connected end to end, forming a single path for current flow.
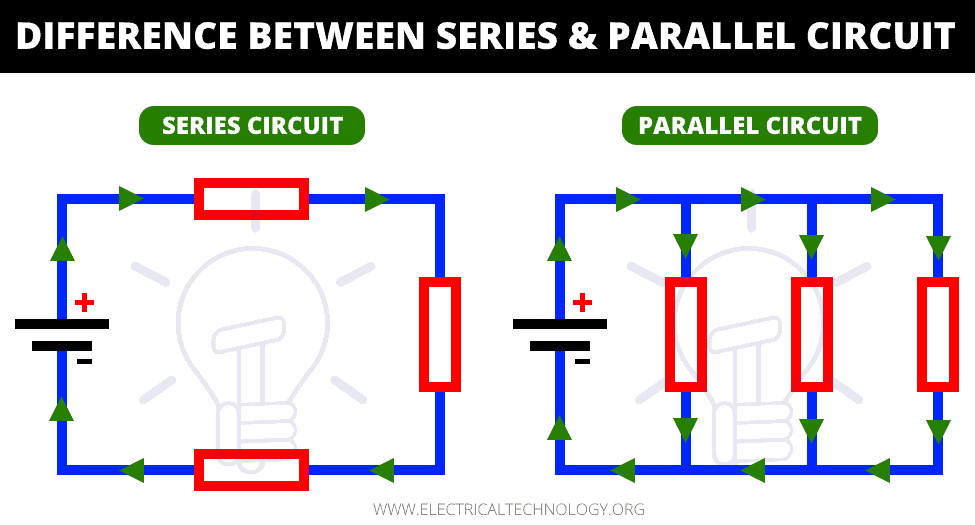
Difference Between A Parallel And Series Circuit In a series circuit, the same amount of current flows through all the components placed in it. on the other hand, in parallel circuits, the components are placed in parallel with each other due to which the circuit splits the current flow. the current flowing from the source will be divided into the current flowing through each of these components. In this tutorial, we’ll first discuss the difference between series circuits and parallel circuits, using circuits containing the most basic of components resistors and batteries to show the difference between the two configurations. we’ll then explore what happens in series and parallel circuits when you combine different types of. Where series components all have equal currents running through them, parallel components all have the same voltage drop across them series:current::parallel:voltage. series and parallel circuits working together. from there we can mix and match. in the next picture, we again see three resistors and a battery. A parallel circuit is like a freeway. ramps allow cars to exit and enter a freeway without interrupting the main highway. a parallel circuit has many off and on ramps. a failure in any single loop never shuts down the entire circuit. a series circuit is like a circular road with multiple bridges.
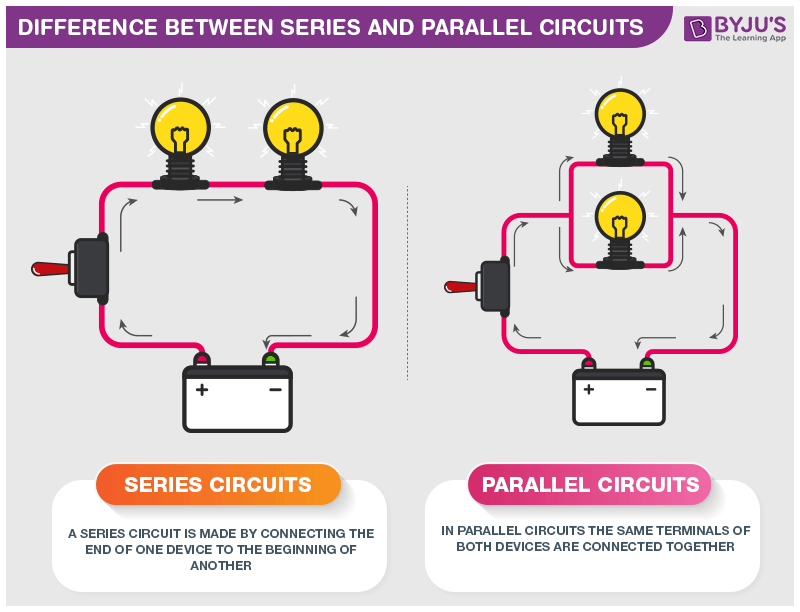
Diagram Of Series And Parallel Circuit Where series components all have equal currents running through them, parallel components all have the same voltage drop across them series:current::parallel:voltage. series and parallel circuits working together. from there we can mix and match. in the next picture, we again see three resistors and a battery. A parallel circuit is like a freeway. ramps allow cars to exit and enter a freeway without interrupting the main highway. a parallel circuit has many off and on ramps. a failure in any single loop never shuts down the entire circuit. a series circuit is like a circular road with multiple bridges. 1 r = 1 r1 1 r2 r = (1 r1 1 r2) − 1. [equivalent resistance of two resistors in parallel] two resistors in parallel, c 4, are equivalent to a single resistor with a value given by the above equation. example 10: two lamps on the same household circuit. you turn on two lamps that are on the same household circuit. Because the circuit is a combination of both series and parallel, we cannot apply the rules for voltage, current, and resistance “across the table” to begin analysis like we could when the circuits were one way or the other. for instance, if the above circuit were simple series, we could just add up r 1 through r 4 to arrive at a total.

Comments are closed.