Severe Sepsis And Septic Shock
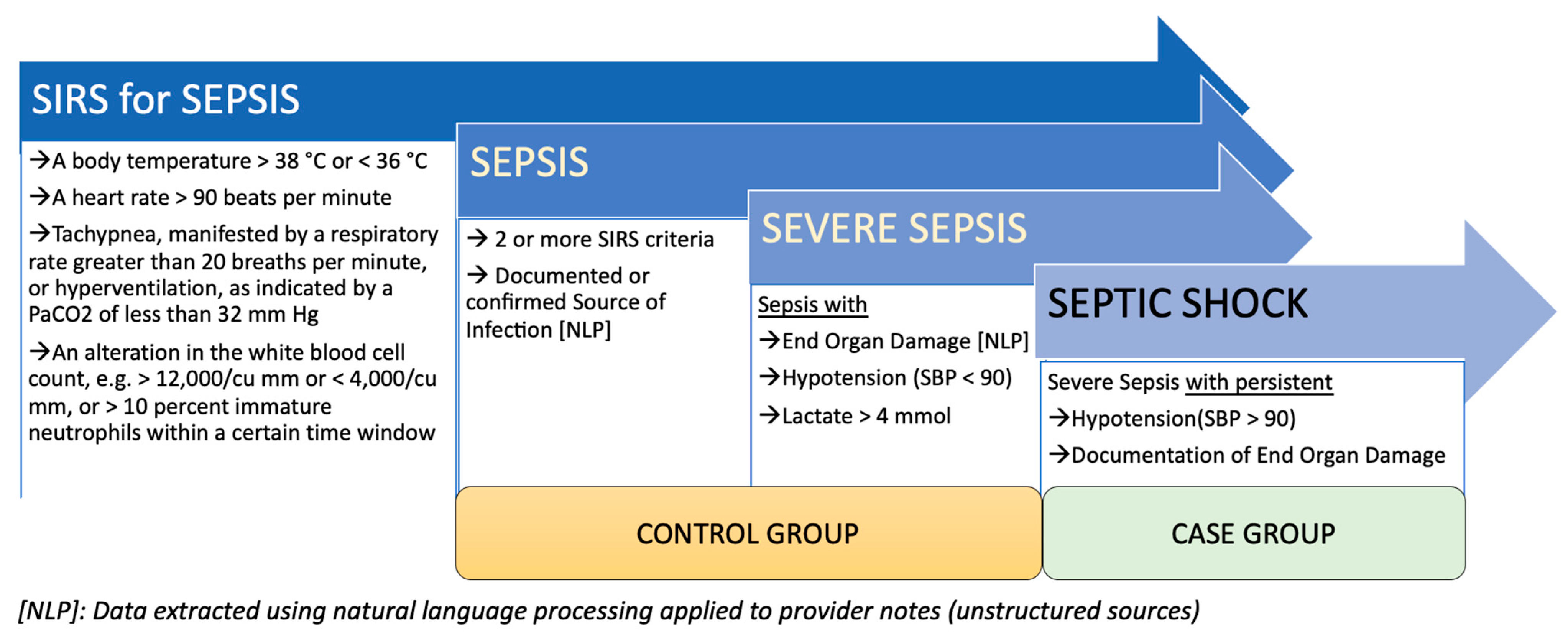
Stages Of Sepsis And Septic Shock Severe sepsis and septic shock. this article has been corrected. sepsis is one of the oldest and most elusive syndromes in medicine. hippocrates claimed that sepsis (σήψις) was the process by. 1. introduction. sepsis is defined as a life threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection. septic shock should be considered a subset of sepsis in which underlying circulatory, cellular, and metabolic abnormalities contribute to a greater risk of mortality than that posed by sepsis alone [].

Difference Between Sepsis And Septic Shock Causes And Risk Factors Severe sepsis was defined as the progression of sepsis to organ dysfunction, tissue hypoperfusion, or hypotension. septic shock was described as hypotension and organ dysfunction that persisted despite volume resuscitation, necessitating vasoactive medication, and with 2 or more of the sirs criteria listed above. Septic shock is the last and most severe stage of sepsis. sepsis occurs when your immune system has an extreme reaction to an infection. the inflammation throughout your body can cause dangerously low blood pressure. you need immediate treatment if you have septic shock. treatment may include antibiotics, oxygen and medication. Severe sepsis has been defined as sepsis plus evidence of organ dysfunction (eg, hypotension, oliguria, and metabolic acidosis), and septic shock has been defined as sepsis with persistent signs of hypotension despite fluid resuscitation. 1,2. the incidence of severe sepsis in the united states has been reported as approximately 300 cases per. Sepsis may cause atypical blood clotting. the resulting small clots or burst blood vessels may damage or destroy tissues. most people recover from mild sepsis, but the mortality rate for septic shock is about 30% to 40%. also, an episode of severe sepsis raises the risk for future infections.

Difference Between Sepsis And Septic Shock Causes And Risk Factors Severe sepsis has been defined as sepsis plus evidence of organ dysfunction (eg, hypotension, oliguria, and metabolic acidosis), and septic shock has been defined as sepsis with persistent signs of hypotension despite fluid resuscitation. 1,2. the incidence of severe sepsis in the united states has been reported as approximately 300 cases per. Sepsis may cause atypical blood clotting. the resulting small clots or burst blood vessels may damage or destroy tissues. most people recover from mild sepsis, but the mortality rate for septic shock is about 30% to 40%. also, an episode of severe sepsis raises the risk for future infections. Septic shock is a subset of sepsis with significantly increased mortality due to severe abnormalities of circulation and or cellular metabolism. septic shock involves persistent hypotension (defined as the need for vasopressors to maintain mean arterial pressure ≥ 65 mm hg, and a serum lactate level > 18 mg dl [2 mmol l] despite adequate. Sepsis is a clinical syndrome characterized by a dysregulated host response to infection. there is a continuum of severity ranging from sepsis to septic shock. although wide ranging and dependent upon the population studied, mortality has been estimated to be ≥10 percent and ≥40 percent when shock is present [1,2].

Initial Resuscitation Of Sepsis And Septic Shock Amir Salari Official Septic shock is a subset of sepsis with significantly increased mortality due to severe abnormalities of circulation and or cellular metabolism. septic shock involves persistent hypotension (defined as the need for vasopressors to maintain mean arterial pressure ≥ 65 mm hg, and a serum lactate level > 18 mg dl [2 mmol l] despite adequate. Sepsis is a clinical syndrome characterized by a dysregulated host response to infection. there is a continuum of severity ranging from sepsis to septic shock. although wide ranging and dependent upon the population studied, mortality has been estimated to be ≥10 percent and ≥40 percent when shock is present [1,2].

Comments are closed.