Show That For Any Sets A And B Aa∩b∪a B And A∪b A A∪b 🔥🔥 Worldeez Academy

Show That For Any Sets A And B A Aв B в є Aвђ B And Aв є B Using properties of sets, show that for any two sets a and b, a ∪ b ∩ a ∩ b. '. = a. q. show that for any sets a and b, ( by using the properties of sets ) a =(a∩b)∩(a−b). Let a and b be sets. define the symmetric difference of a and b as a∆b= (a ∪ b) − (a ∩ b). (a) prove that a∆b = (a − b) ∪ (b − a) i tried to start this but am getting really lost. if someone could try to help that would be great.

Elementary Set Theory Draw Venn Diagrams To Describe Sets A в B в Let a, b and c be sets. then show that a ∩ (b ∪ c) = (a ∩ b) ∪ (a ∩ c) in a town of 10,000 families it was found that 40% families buy newspaper a, 20% families buy newspaper b, 10% families buy newspaper c, 5% families buy a and b, 3% buy b and c and 4% buy a and c. if 2% families buy all the three newspapers. Thus, a−b = a∩bc. here are some basic subset proofs about set operations. theorem for any sets a and b, a∩b ⊆ a. proof: let x ∈ a∩b. by definition of intersection, x ∈ a and x ∈ b. thus, in particular, x ∈ a is true. theorem for any sets a and b, b ⊆ a∪ b. proof: let x ∈ b. thus, it is true that at least one of x ∈ a. Identity 1. let a and b be sets. show that a∪(b −a) = a∪b proof. a∪(b −a) = a∪(b ∩ac) set difference = a∪(ac ∩b) commutative = (a∪ac)∩(a∪b) distributive = u ∩(a∪b) complement = a∪b identity proof. let x ∈ a ∪ (b − a). then x ∈ a or x ∈ (b − a) by definition of union. so x ∈ b and x 6∈a (by set. Show that for any sets a and b, a = ( a ∩ b ) ∪ ( a – b ) and a ∪ ( b – a ) = ( a ∪ b ) explanation: to prove: a = (a ∩ b) υ (a – b) let x ∈ a. case i. x ∈ a ∩ b. then, x ∈ (a ∩ b) ⊂ (a υ b) υ (a – b) case ii.
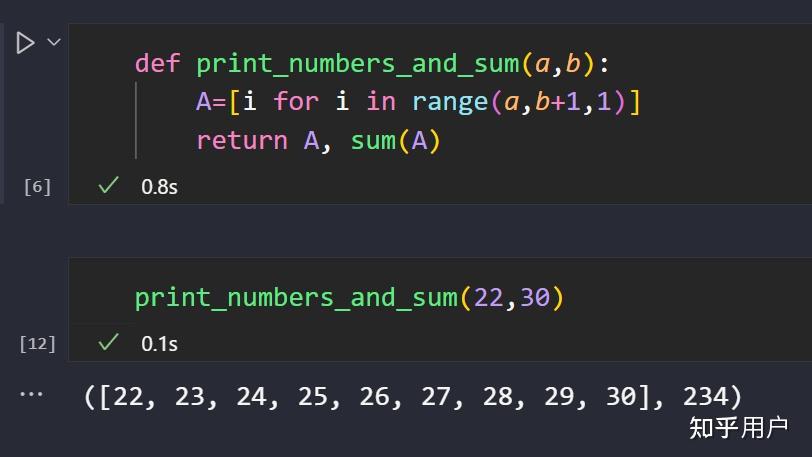
给定两个整数a和 B 输出从a到 B 的所有整数以及这些数的和 含a与 B 知乎 Identity 1. let a and b be sets. show that a∪(b −a) = a∪b proof. a∪(b −a) = a∪(b ∩ac) set difference = a∪(ac ∩b) commutative = (a∪ac)∩(a∪b) distributive = u ∩(a∪b) complement = a∪b identity proof. let x ∈ a ∪ (b − a). then x ∈ a or x ∈ (b − a) by definition of union. so x ∈ b and x 6∈a (by set. Show that for any sets a and b, a = ( a ∩ b ) ∪ ( a – b ) and a ∪ ( b – a ) = ( a ∪ b ) explanation: to prove: a = (a ∩ b) υ (a – b) let x ∈ a. case i. x ∈ a ∩ b. then, x ∈ (a ∩ b) ⊂ (a υ b) υ (a – b) case ii. ∈ (a ∪ b) c, and then you show that x ∈ ac ∩ bc. and for the second containment, you suppose x ∈ ac ∩ bc, and then you show that x ∈ (a ∪ b) c. to fill in the steps of these arguments, you use the procedural versions of the definitions of complement, union, and intersection, and at crucial points you use de morgan’s laws of. From (1) and (2) we infer that s = r or (a ∪ b)’ = a’ ∩ b’. thus, this theorem is proved. proof of (a ∩ b)’ = a’ ∪ b’: the second de morgan's theorem or law of intersection can be mathematically proved using the following steps: let g = (a ∩ b)' and h = a' u b'. we would now prove that g = h by proving g ⊂ h and h ⊂ g.

г гѓїрџ єв On Twitter гѓїгѓёгѓјгѓўгѓёгѓ гѓјг гѓ гѓѓгѓ рџџ рџ гѓ г љгѓњгѓёгѓ Https Mirrativ Page Link ∈ (a ∪ b) c, and then you show that x ∈ ac ∩ bc. and for the second containment, you suppose x ∈ ac ∩ bc, and then you show that x ∈ (a ∪ b) c. to fill in the steps of these arguments, you use the procedural versions of the definitions of complement, union, and intersection, and at crucial points you use de morgan’s laws of. From (1) and (2) we infer that s = r or (a ∪ b)’ = a’ ∩ b’. thus, this theorem is proved. proof of (a ∩ b)’ = a’ ∪ b’: the second de morgan's theorem or law of intersection can be mathematically proved using the following steps: let g = (a ∩ b)' and h = a' u b'. we would now prove that g = h by proving g ⊂ h and h ⊂ g.
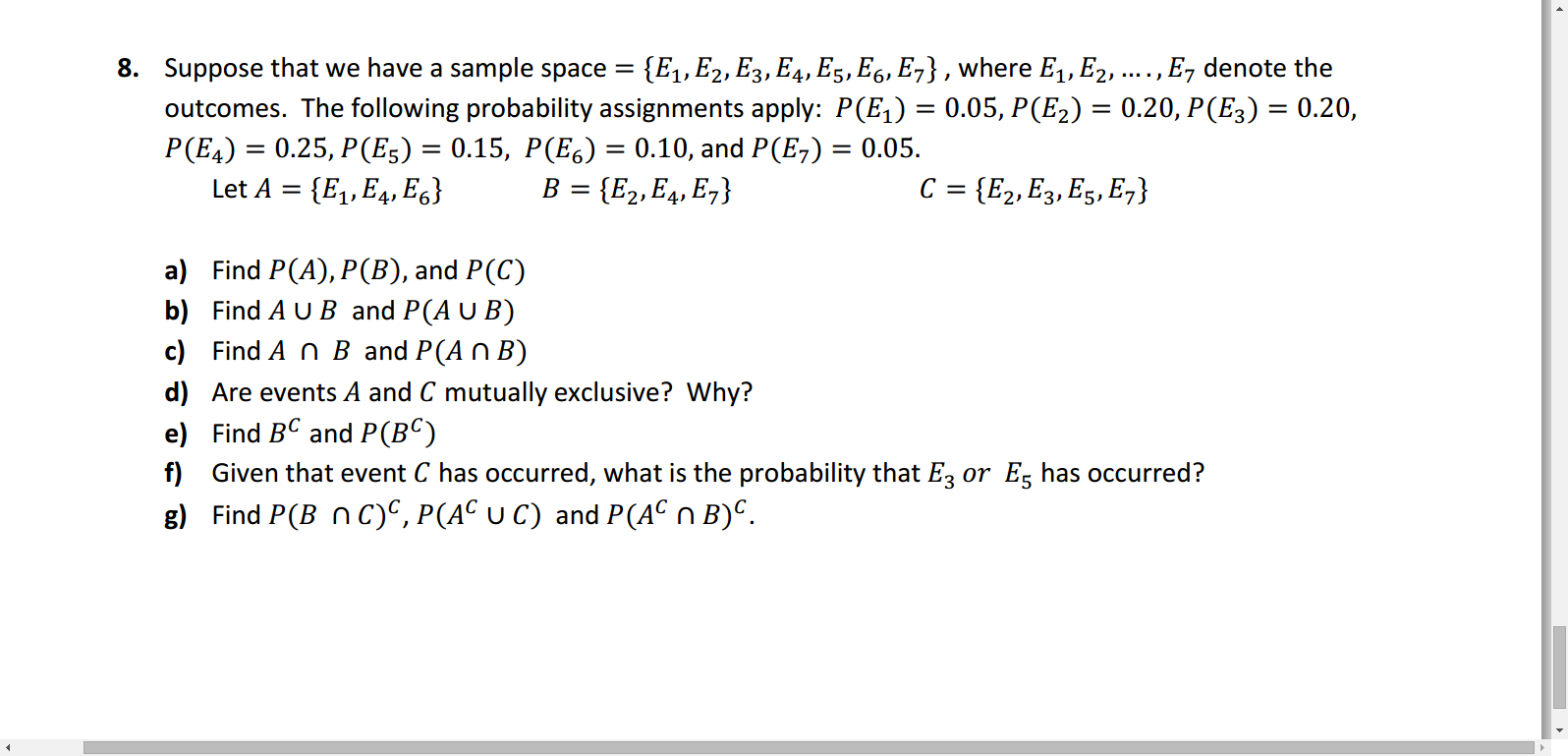
Solved Suppose That We Have A Sample Space E1 E2 E3 E4 Chegg

Comments are closed.