Showing The Multiplier Effect On A Graph
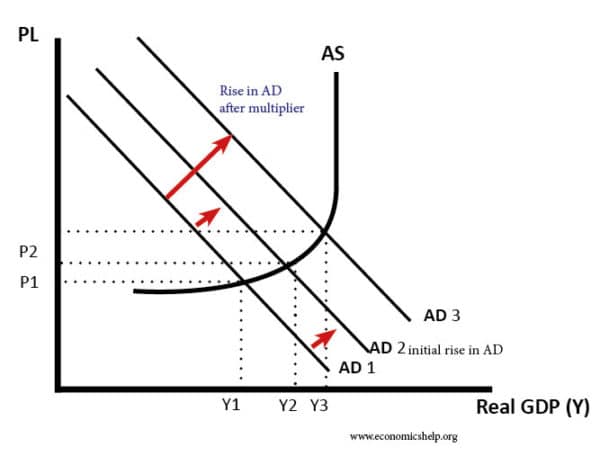
The Multiplier Effect Economics Help The last video of the aggregate expenditure lesson explores the multiplier effect on the ae graph. as one can see, an increase in autonomous spending (holdin. The multiplier effect. 2 november 2019 by tejvan pettinger. the fiscal multiplier effect occurs when an initial injection into the economy causes a bigger final increase in national income. for example, if the government increased spending by £1 billion but this caused real gdp to increase by a total of £1.7 billion, then the multiplier would.

Explaining The Multiplier Effect Tutor2u Economics The multiplier effect. the multiplier effect is defined as the change in income to the permanent change in the flow of expenditure that caused it. in other words, the multiplier effect refers to the increase in final income arising from any new injections. injections are additions to the economy through government spending, money from exports. The multiplier effect is also visible on the keynesian cross diagram. figure b.11 shows the example we have been discussing: a recessionary gap with an equilibrium of $700, potential gdp of $800, the slope of the aggregate expenditure function (ae 0) determined by the assumptions that taxes are 30% of income, savings are 0.1 of after tax income, and imports are 0.1 of before tax income. This video talks about the multiplier effect. we also look at a numerical example and see how we can visualize the effect of multiplier on a graph.#multiplie. The power of the multiplier effect is that an increase in expenditure has a larger increase on the equilibrium output. the increase in expenditure is the vertical increase from ae0 to ae1. however, the increase in equilibrium output, shown on the horizontal axis, is clearly larger. thus, the spending multiplier, Δy Δae, is greater than one.

Reading The Multiplier Effect Macroeconomics This video talks about the multiplier effect. we also look at a numerical example and see how we can visualize the effect of multiplier on a graph.#multiplie. The power of the multiplier effect is that an increase in expenditure has a larger increase on the equilibrium output. the increase in expenditure is the vertical increase from ae0 to ae1. however, the increase in equilibrium output, shown on the horizontal axis, is clearly larger. thus, the spending multiplier, Δy Δae, is greater than one. The multiplier effect refers to the proportional amount of increase, or decrease, in final income that results from an injection, or withdrawal, of capital. the multiplier effect measures the. Multiplier effect. how to draw the multiplier effect on a diagramtwitter: twitter econplusdalfacebook: facebook econplusdal 16519.
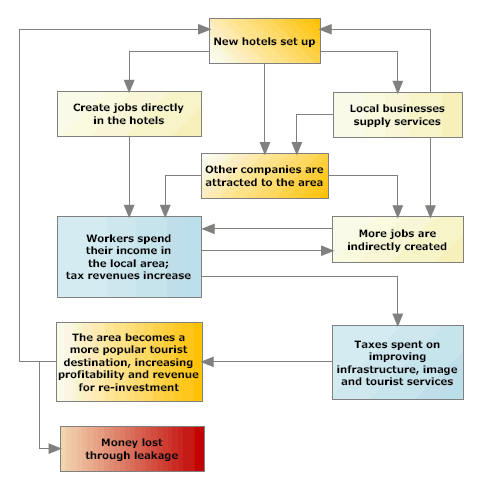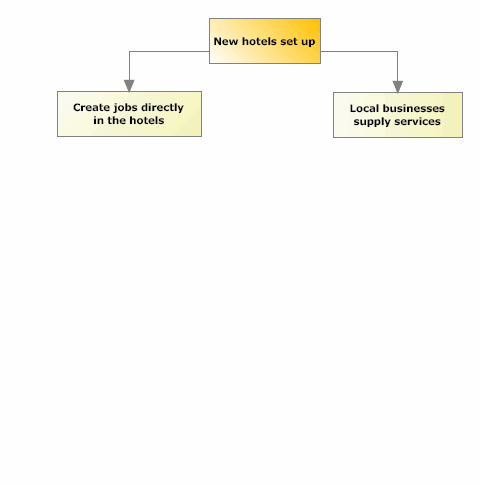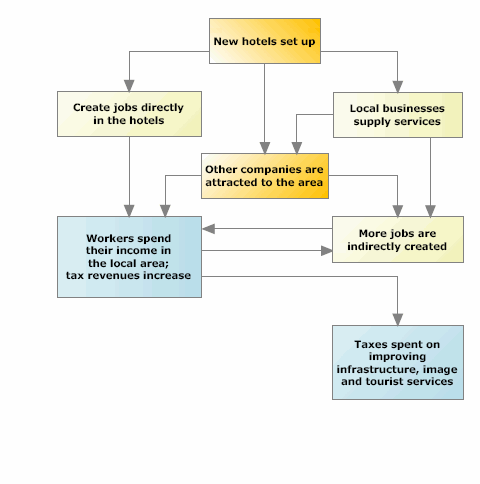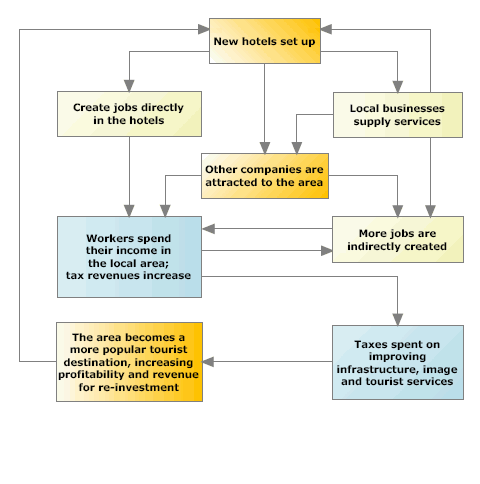
Tourism Multiplier Effect The multiplier effect refers to the proportional amount of increase, or decrease, in final income that results from an injection, or withdrawal, of capital. the multiplier effect measures the. Multiplier effect. how to draw the multiplier effect on a diagramtwitter: twitter econplusdalfacebook: facebook econplusdal 16519.

Showing The Multiplier Effect On A Graph Youtube

Comments are closed.