Signs Of Sepsis In Neonates

Signs Of Sepsis In Neonates Sepsis in newborns, or neonatal sepsis, is a serious medical condition that occurs when a baby younger than 28 days old has a life threatening response to an infection. bacterial infections are the most common cause of neonatal sepsis. if your newborn has sepsis, it’s a medical emergency. your baby needs urgent treatment with antibiotics. Neonates with clinical signs of sepsis should have a complete blood count (cbc), differential with smear, blood culture, urine culture (not necessary for evaluation of early onset sepsis), and lumbar puncture (lp), if clinically feasible, as soon as possible. neonates with respiratory symptoms require chest x ray.
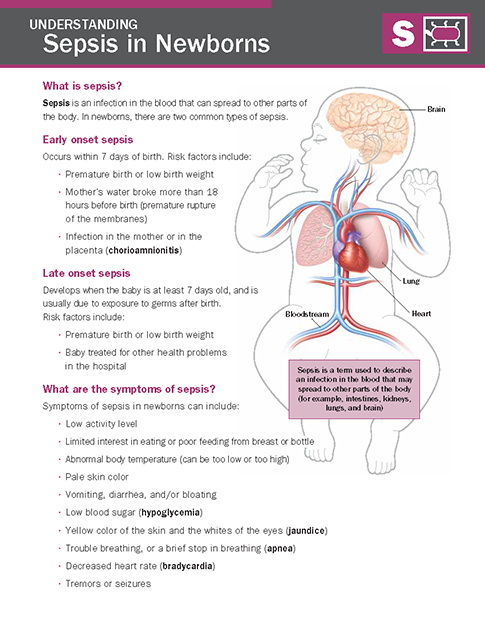
Sepsis In Newborns Nicu Parent Education Resources Neonatal sepsis is an infection involving the bloodstream in infants under 28 days old. it remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality among neonates, especially in middle and lower income countries [1]. neonatal sepsis is divided into 2 groups based on the time of presentation after birth: early onset sepsis (eos) and late onset sepsis (los). eos refers to sepsis in neonates at or. Introduction. sepsis is an important cause of morbidity and mortality among newborn infants. although the incidence of sepsis in term and late preterm neonates is low, the potential for serious adverse outcomes is of such great consequence that caregivers should have a low threshold for evaluation and treatment for possible sepsis in neonates. Following sepsis, some children may continue to experience physical and emotional symptoms. some possible long term effects of sepsis include: tiredness and weakness. insomnia. nightmares. changes. Sepsis is a serious bodywide reaction to infection spread through the blood. newborns with sepsis appear generally ill—they are listless, do not feed well, often have a gray color, and may have a fever or a low body temperature. the diagnosis is based on the symptoms and the presence of bacteria, a virus, or a fungus in the blood, urine, or.

Neonatal Sepsis Signs And Symptoms Following sepsis, some children may continue to experience physical and emotional symptoms. some possible long term effects of sepsis include: tiredness and weakness. insomnia. nightmares. changes. Sepsis is a serious bodywide reaction to infection spread through the blood. newborns with sepsis appear generally ill—they are listless, do not feed well, often have a gray color, and may have a fever or a low body temperature. the diagnosis is based on the symptoms and the presence of bacteria, a virus, or a fungus in the blood, urine, or. Key points about newborn sepsis. newborn sepsis is a severe infection in an infant younger than 28 days old. a newborn may become infected before, during, or after birth. newborn sepsis can be hard to diagnose. early diagnosis and treatment are the best ways to stop sepsis. antibiotic medicine is started as soon as possible. Neonatal sepsis is caused by bacterial, viral or fungal infection. it is classified as either early onset (<48 72 hours) or late onset (>48 72 hours) sepsis. the presentation can be non specific, so diagnosis requires a high index of suspicion. key investigations include a septic screen (blood, csf and urine cultures, fbc and crp) with further.
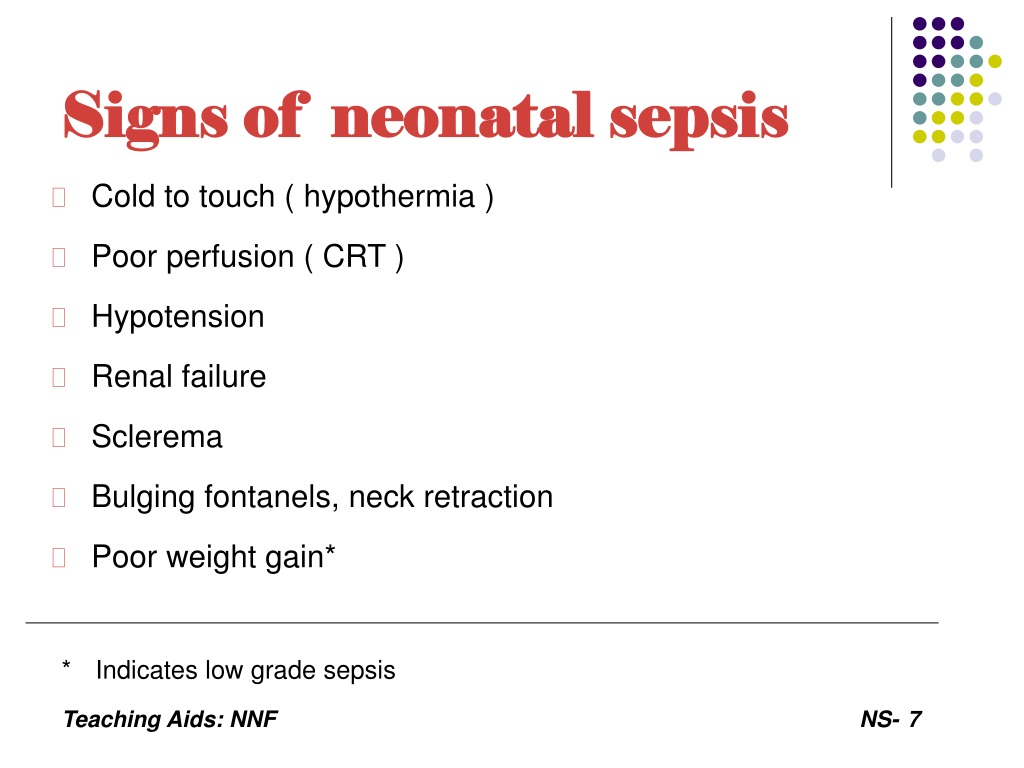
Ppt Neonatal Sepsis Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 9427803 Key points about newborn sepsis. newborn sepsis is a severe infection in an infant younger than 28 days old. a newborn may become infected before, during, or after birth. newborn sepsis can be hard to diagnose. early diagnosis and treatment are the best ways to stop sepsis. antibiotic medicine is started as soon as possible. Neonatal sepsis is caused by bacterial, viral or fungal infection. it is classified as either early onset (<48 72 hours) or late onset (>48 72 hours) sepsis. the presentation can be non specific, so diagnosis requires a high index of suspicion. key investigations include a septic screen (blood, csf and urine cultures, fbc and crp) with further.

Comments are closed.