Similarities And Differences Between Virtue Theory Utilitarianism And
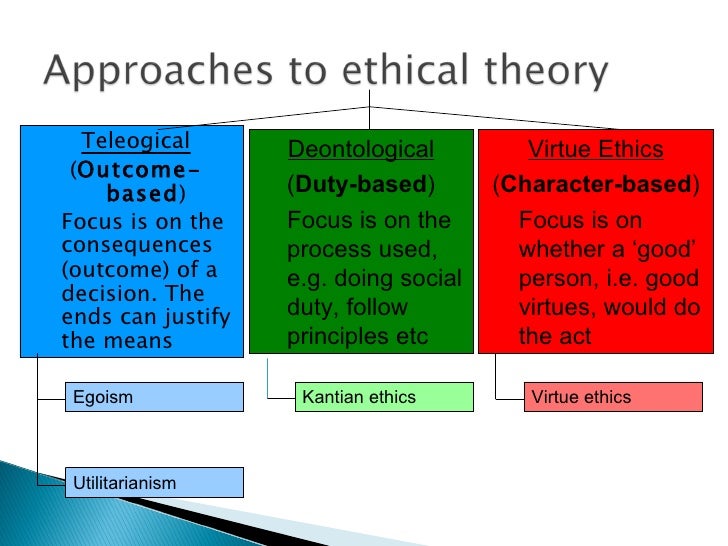
Similarities And Differences Between Virtue Theory Utilitarianism And In this article, we will explore the three main ethical theories – virtue ethics, utilitarianism, and deontology – in more detail. we will look at their similarities and differences, how they are applied in practice, and how they can help us make more informed ethical decisions. the first theory is virtue ethics. this theory focuses on the. Conclusion. virtue ethics is a moral theory that is concerned with the moral character or goodness of the individual carrying out an act while utilitarianism is the moral theory that states an action is right if it is useful or is beneficial for a majority. the main difference between virtue ethics utilitarianism is that virtue ethics focuses.

Similarities And Differences Between Virtue Theory Utilitarianism And Virtue ethics is based on the development of good character traits, utilitarianism focuses on achieving the greatest good for the greatest number of people, and deontology emphasizes following moral rules regardless of the outcome. each approach has its own implications and limitations, but by understanding them all, individuals can make more. Virtue ethics or virtue theory was originally proposed by aristotle (384 322 bce) to deal with the question of how humans can find and maintain happiness. aristotle was ultimately interested in. Virtue ethics for ethical decision making. virtue ethics is a compelling ethical theory that emphasizes the development of virtuous character traits, such as honesty, courage, compassion, and fairness. it provides a framework for ethical decision making that prioritizes human flourishing and well being. One of the main differences lies in their focus. deontology emphasizes the inherent nature of an action, while utilitarianism focuses on the consequences it produces. another difference is the role of moral rules and duties. deontology places a strong emphasis on following moral rules and fulfilling duties, regardless of the consequences.

15 Virtue Ethics Examples 2024 Virtue ethics for ethical decision making. virtue ethics is a compelling ethical theory that emphasizes the development of virtuous character traits, such as honesty, courage, compassion, and fairness. it provides a framework for ethical decision making that prioritizes human flourishing and well being. One of the main differences lies in their focus. deontology emphasizes the inherent nature of an action, while utilitarianism focuses on the consequences it produces. another difference is the role of moral rules and duties. deontology places a strong emphasis on following moral rules and fulfilling duties, regardless of the consequences. Virtue theory, utilitarianism, and deontological theory have both similarities and differences. the foundation of utilitarianism theory is in the principle of utility. this principle emphasizes the need to rely on reason and not metaphysics. furthermore, the law of greatest happiness is the main ideology behind this theory. 2. utilitarian ethics. the action is good if the consequences are good. utilitarian ethics (aka consequentialism) is outcome focused; it holds that actions are moral if they maximize the greatest.

ёяшн юааsimilaritiesюаб юааbetweenюаб юааvirtueюаб юааtheoryюаб юааutilitarianismюаб And Deontologic Virtue theory, utilitarianism, and deontological theory have both similarities and differences. the foundation of utilitarianism theory is in the principle of utility. this principle emphasizes the need to rely on reason and not metaphysics. furthermore, the law of greatest happiness is the main ideology behind this theory. 2. utilitarian ethics. the action is good if the consequences are good. utilitarian ethics (aka consequentialism) is outcome focused; it holds that actions are moral if they maximize the greatest.

Comments are closed.