Simple Random Sampling Definition Steps Examples
Simple Random Sampling Applications Advantages And Disadvantages Step 3: randomly select your sample. this can be done in one of two ways: the lottery or random number method. in the lottery method, you choose the sample at random by “drawing from a hat” or by using a computer program that will simulate the same action. in the random number method, you assign every individual a number. Other techniques. simple random sampling is a technique in which each member of a population has an equal chance of being chosen through an unbiased selection method. each subject in the sample is given a number, and then the sample is chosen randomly. this method is considered “simple” because it’s straightforward and implements a random.
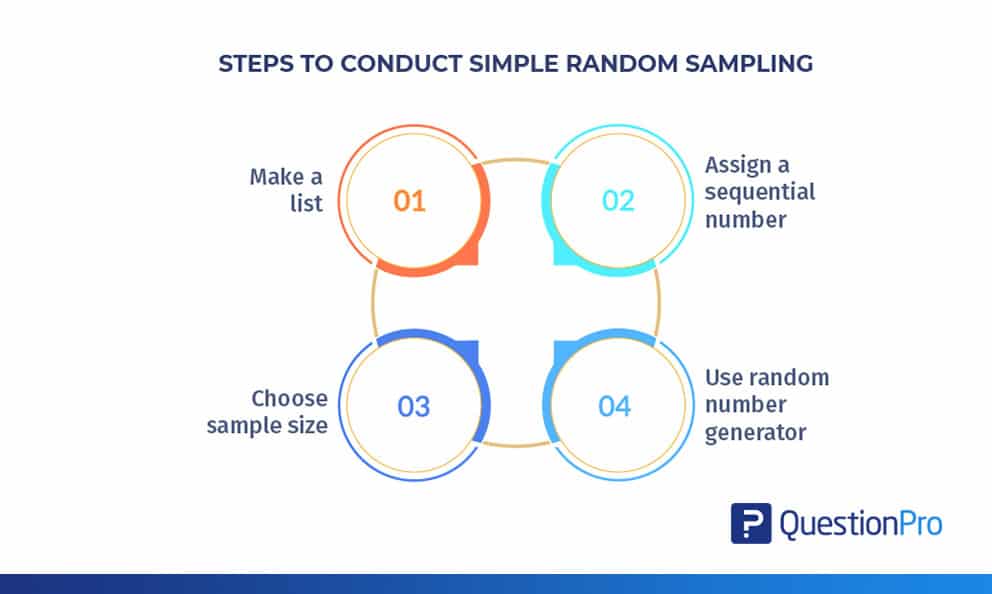
Simple Random Sampling Definition And Examples Questionpro Simple random sampling (srs) is a probability sampling method where researchers randomly choose participants from a population. all population members have an equal probability of being selected. this method tends to produce representative, unbiased samples. for example, if you randomly select 1000 people from a town with a population of. Step 2: choose the sample size. before picking the units within a population, we need to determine how many to select. this sample size may be constrained by the amount of time, capital rationing. N: the population size. in this case, n = 50 and n = 500. so, the formula for calculating the probability of selecting a simple random sample of 50 employees from a population of 500 is: 50 500 * (500 50) (500 1) = 0.1 * 0.902 = 0.0902, or 9.02%. therefore, the probability of selecting a sample of 50 employees using simple random sampling is 9. Simple random sampling: definition and examples. simple random sampling is a statistical method in which everyone in a population has an equal chance of being selected into a sample. the sample represents a smaller and more manageable portion of the people that can be studied and analyzed. it’s a fundamental technique to gather data and make.

Comments are closed.