Six Trigonometric Functions Graph Examples
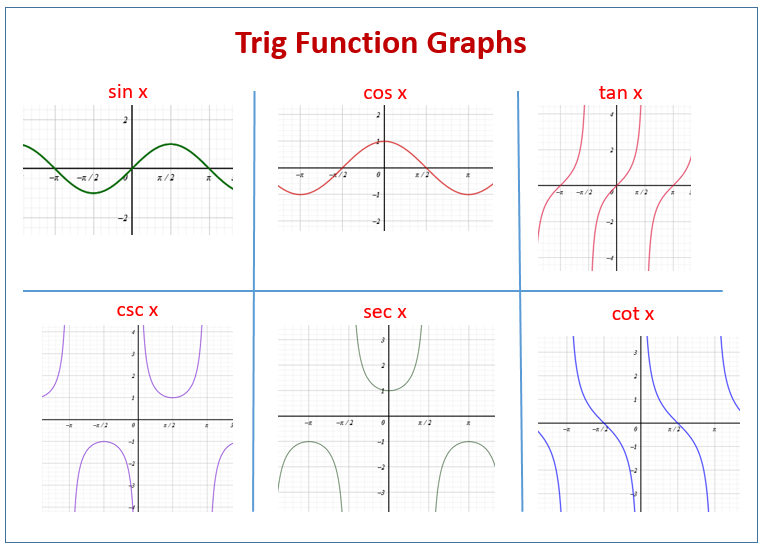
Six Trigonometric Functions Graph Examples Trigonometric functions are the basic six functions that have a domain input value as an angle of a right triangle, and a numeric answer as the range. the trigonometric function (also called the 'trig function') of f(x) = sinθ has a domain, which is the angle θ given in degrees or radians, and a range of [ 1, 1]. Definition: trigonometric functions. let p = (x, y) be a point on the unit circle centered at the origin o. let θ be an angle with an initial side along the positive x axis and a terminal side given by the line segment op. the trigonometric functions are then defined as. sinθ = y. cscθ = 1 y. cosθ = x. secθ = 1 x.
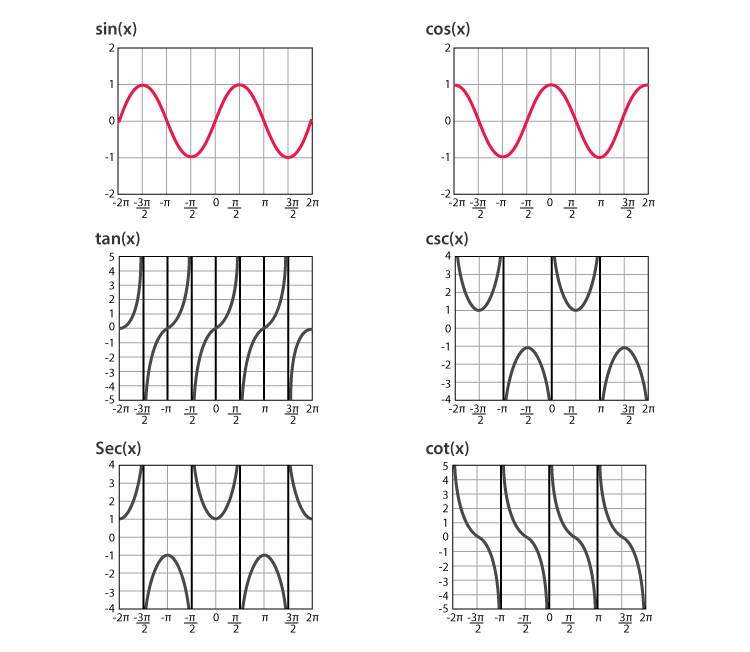
Six Trigonometric Functions Graph Examples Solved examples on trigonometric functions. example 1: find the values of sin 45°, cos 60° and tan 60°. solution: using the trigonometric table, we have. sin 45° = 1 √2. cos 60° = 1 2. tan 60° = √3. example 2: evaluate sin 105° degrees. solution: sin 105° can be written as sin (60° 45°) which is similar to sin (a b). Trigonometric functions are the functions given in the terms of six trigonometric ratios. there are six trigonometric functions. these are six trigonometric functions sin x, cos x, tan x, cosec x, sec x and cot x. learn more about trigonometric functions in detail in this article by geeksforgeeks. For example see the graph of the sin function, often called a sine wave, above. for more see graph of the sine function; graph of the cosine function; graph of the tangent function; pure audio tones and radio waves are sine waves in their respective medium. derivatives of the trig functions. each of the functions can be differentiated in calculus. Amplitude is a indication of how much energy a wave contains. 2. graphs of y = a sin bx and y = a cos bx introduces the period of a trigonometric graph. 3. graphs of y = a sin (bx c) and y = a cos (bx c) helps you to understand the displacement (or phase shift) of a trigonometric curve. 4 graphs of tan x, cot x, sec x and csc x are not as.
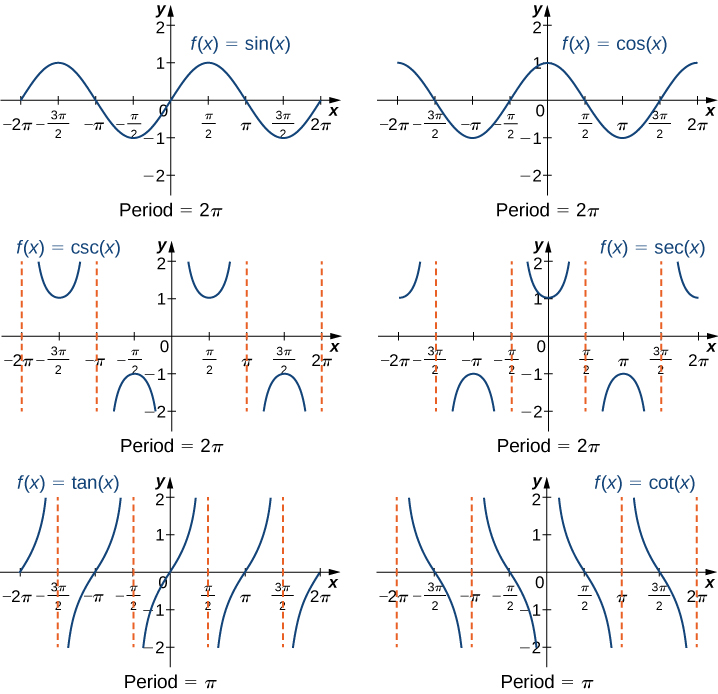
Six Trigonometric Functions Graph Examples For example see the graph of the sin function, often called a sine wave, above. for more see graph of the sine function; graph of the cosine function; graph of the tangent function; pure audio tones and radio waves are sine waves in their respective medium. derivatives of the trig functions. each of the functions can be differentiated in calculus. Amplitude is a indication of how much energy a wave contains. 2. graphs of y = a sin bx and y = a cos bx introduces the period of a trigonometric graph. 3. graphs of y = a sin (bx c) and y = a cos (bx c) helps you to understand the displacement (or phase shift) of a trigonometric curve. 4 graphs of tan x, cot x, sec x and csc x are not as. Trigonometric functions are functions related to an angle. there are six trigonometric functions: sine, cosine, tangent and their reciprocals cosecant, secant, and cotangent, respectively. sine, cosine, and tangent are the most widely used trigonometric functions. their reciprocals, though used, are less common in modern mathematics. Example 1. graph one full period of the function y = −2 sin 3x y = − 2 sin 3 x. the amplitude in this case is 2, 2, but since the coefficient is negative, this sine graph will begin by first going to the minimum value. the period of the graph will be 2π b, 2 π b, or in this case 2π 3 2 π 3 instead of 2π. 2 π.

6 Trigonometric Functions Graphs Math Is Fun Trigonometric functions are functions related to an angle. there are six trigonometric functions: sine, cosine, tangent and their reciprocals cosecant, secant, and cotangent, respectively. sine, cosine, and tangent are the most widely used trigonometric functions. their reciprocals, though used, are less common in modern mathematics. Example 1. graph one full period of the function y = −2 sin 3x y = − 2 sin 3 x. the amplitude in this case is 2, 2, but since the coefficient is negative, this sine graph will begin by first going to the minimum value. the period of the graph will be 2π b, 2 π b, or in this case 2π 3 2 π 3 instead of 2π. 2 π.

Comments are closed.