Skin Knowledge Knowledge About The Skin

Skin General Knowledge Simply Knowledge Welcome to the american academy of dermatology’s youth education program, good skin knowledge. the goal is to teach young people the facts about common skin, hair, and nail conditions. misunderstanding can lead to teasing and bullying, which is associated with anxiety and depression. these fun, easy to use lesson plans teach children. Good skin knowledge lesson plan library. module 1: intro to the skin. lesson focuses on skin essentials, function, and care. module 2: daily skin care. lesson focuses on hand, skin and face washing, showering, shaving, and sunscreen essentials. module 3: the truth about the skin. lesson focuses on preventing the spread of germs, warts, fungi.

Structure And Function Of Skin Skin Layer And Diagram The skin is the body’s largest organ, made of water, protein, fats and minerals. your skin protects your body from germs and regulates body temperature. nerves in the skin help you feel sensations like hot and cold. your skin, along with your hair, nails, oil glands and sweat glands, is part of the integumentary (in teg you me i nt a ree) system. Anything that interferes with skin function or causes changes in appearance (see effects of aging on the skin) can have major consequences for physical and mental health. many problems that appear on the skin are limited to the skin. sometimes, however, the skin provides clues to a disorder that affects the entire body. Temperature regulation: skin perspires to cool the body and contracts the vascular system in the dermis to conserve heat. control of sensation: nerve endings in skin make it sensitive to pressure, vibration, touch, pain and temperature. regeneration: skin is able to repair wounds. It is a fleshy surface with hair, nerves, glands and nails. it consists of hair follicles which anchor hair strands into the skin. it acts as a barrier between outside and inside environment. the skin has different thicknesses and textures. e.g. the skin under the eyes is as thin as paper but is thick at the soles of the feet and palm.
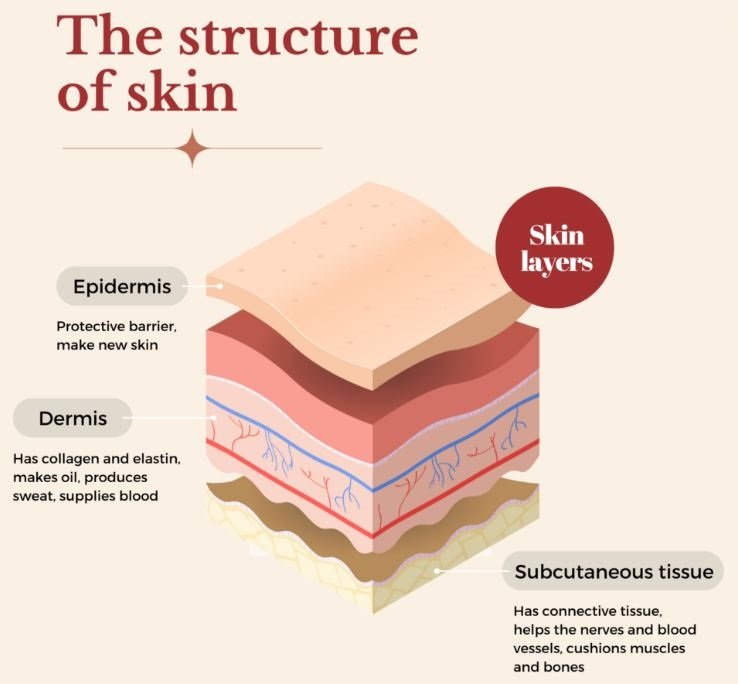
Basic Knowledge Of Skin The Nature Atelier Temperature regulation: skin perspires to cool the body and contracts the vascular system in the dermis to conserve heat. control of sensation: nerve endings in skin make it sensitive to pressure, vibration, touch, pain and temperature. regeneration: skin is able to repair wounds. It is a fleshy surface with hair, nerves, glands and nails. it consists of hair follicles which anchor hair strands into the skin. it acts as a barrier between outside and inside environment. the skin has different thicknesses and textures. e.g. the skin under the eyes is as thin as paper but is thick at the soles of the feet and palm. Temperature. extreme temperatures, and the speed of change between them, impact on skin. in cold conditions skin reacts by narrowing the blood vessels to protect the body from losing too much heat. sustained cold temperatures reduce sebaceous gland secretion and cause skin to dry out. read more in dry skin. A skin appendage that grows from follicles in the dermis. contains medulla, cortex, and cuticle. functions include conservation of body heat, sensation, and protection of the skin. most prominent on the scalp, pubis, axilla, extremities, and face. see also “ phases of hair growth ”. hair shaft.

Comments are closed.