Small Cells Challenges

Self Optimization Technologies For Small Cells Challenges And Small cell networks have the same challenges to match the performance of integrated base stations with a disaggregated, virtualized and potentially multivendor platform. but it is somewhat easier to address them in a small cell environment, partly because the workloads are lighter than in an urban macrocell, but also because the small cell industry was built on an open ecosystem to start with. The small cell shift. originally developed to support the transition from 3g to 4g in densely populated areas, small cell deployments will play a critical role in bolstering 5g’s reach and availability. the challenge, though, is that the radios needed to facilitate “true” 5g—with high bandwidth, millimeter wave (mmwave) frequencies.

How To Overcome The Challenges Of Deploying Small Cells Youtube Small cell technology is instrumental in realizing the full potential of 5g networks by addressing coverage, capacity, and latency challenges in diverse environments. deploying small cells is a critical strategy for building robust and efficient 5g networks to meet the growing demands of the modern, connected world. Dense deployment of small cells over traditional macrocells is considered as a key enabling technique for the emerging 5g cellular networks. however, a fundamental challenge is to provide an economical and ubiquitous backhaul connectivity to these small cells. there is a wide range of backhaul solutions that together can address the backhaul challenges of 5g networks. in this context, this. One difference is how small cells and femtocells connect back to the network. a small cell connects on a dedicated link. a femtocell connects back on the internet. another difference is a femtocell is private, while a small cell is a public network. femtocells are also smaller than small cells around the size of a paperback book or smaller. 5g small cell networks. there are different types of 5g small cells; femtocells, picocells, and microcells, all providing different coverage limits. broadly speaking, femtocells reach 10 meters, picocells 200 meters, and microcells around two kilometers. and the term small cell is a catch all that describes all the above mobile base stations.
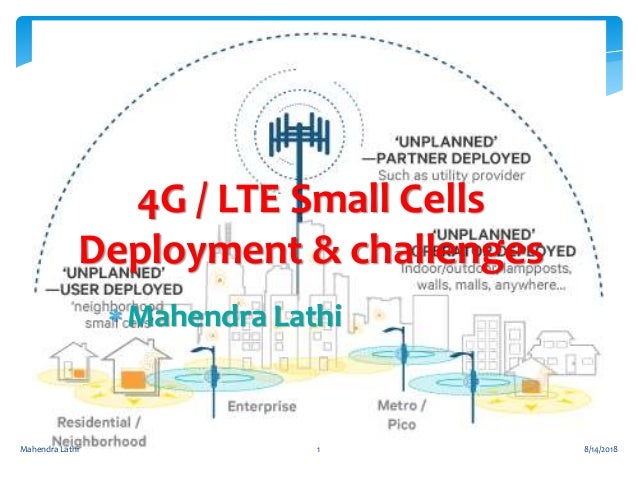
4g Lte Small Cells Deployment Challenges One difference is how small cells and femtocells connect back to the network. a small cell connects on a dedicated link. a femtocell connects back on the internet. another difference is a femtocell is private, while a small cell is a public network. femtocells are also smaller than small cells around the size of a paperback book or smaller. 5g small cell networks. there are different types of 5g small cells; femtocells, picocells, and microcells, all providing different coverage limits. broadly speaking, femtocells reach 10 meters, picocells 200 meters, and microcells around two kilometers. and the term small cell is a catch all that describes all the above mobile base stations. According to a fortune business insights report, global investment in 5g small cell technology is set to increase from $175 million recorded in 2019, to $15.9 billion by 2026; a cagr of 81.9%. small cells will be an important part of 5g roll out, especially in urban areas and in indoor settings, as millimetre wave (mmwave) experiences a high. These megabit or gigabit speed gadgets can be installed on the ceilings and walls of homes and offices to boost the radio frequency (rf) signal strength of cellular networks. 5g networks are becoming increasingly dependent on indoor small cells. this trend is likely to continue as more 5g small cells are deployed in offices, homes and apartments.

Telecoms Infrastructure Blog Small Cell Installation Challenges According to a fortune business insights report, global investment in 5g small cell technology is set to increase from $175 million recorded in 2019, to $15.9 billion by 2026; a cagr of 81.9%. small cells will be an important part of 5g roll out, especially in urban areas and in indoor settings, as millimetre wave (mmwave) experiences a high. These megabit or gigabit speed gadgets can be installed on the ceilings and walls of homes and offices to boost the radio frequency (rf) signal strength of cellular networks. 5g networks are becoming increasingly dependent on indoor small cells. this trend is likely to continue as more 5g small cells are deployed in offices, homes and apartments.

Comments are closed.