Solution Anatomy And Physiology Of The Renal System High Yield Notes

Solution Anatomy And Physiology Of The Renal System High Yield Notes This osmosis high yield note provides an overview of anatomy and physiology of the renal system essentials. all osmosis notes are clearly laid out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently. find more information about anatomy and physiology of the renal system. A cuplike structure, collects the urine at the end of each papilla. the calices join together to form the renal pelvis. study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like these two parts together make up the renal system, the renal system is responsible for, urinary tract includes: and more.

Renal Osmosis Hy Pathology Notes Atf Atf 2 Renal System High Yieldо Summary. the renal system, also known as the urinary system, is made up of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. the kidneys, a pair of organs located in the back of the abdominal cavity, filter waste products from the blood in the form of urine. the urine passes down through the ureters, which are muscular tubes connecting the kidneys to. Anatomy lecture notes section 6: the renal (urinary) system the urinary system is also called the renal system, and, as seen below it consists of the following: the kidneys (2), both of which constantly filter, cleanse and regulate the blood and body fluids. each kidney has a ureter which is a tube that leaves the kidneys and carries the urine. Understanding kidney anatomy and physiology is important for nursing practice. it enables understanding of the aetiology and treatment of kidney function disorders. this is the first article in a series about this topic. anatomy of the kidney external anatomy an adult kidney typically measures 12cm long, 6cm wide and 3cm deep (mahadevan, 2019). Its net effect is to conserve and increase water levels in the plasma by reducing the excretion of sodium, and thus water, from the kidneys. in a negative feedback loop, increased osmolality of the ecf (which follows aldosterone stimulated sodium absorption) inhibits the release of the hormone (figure 26.3.1).
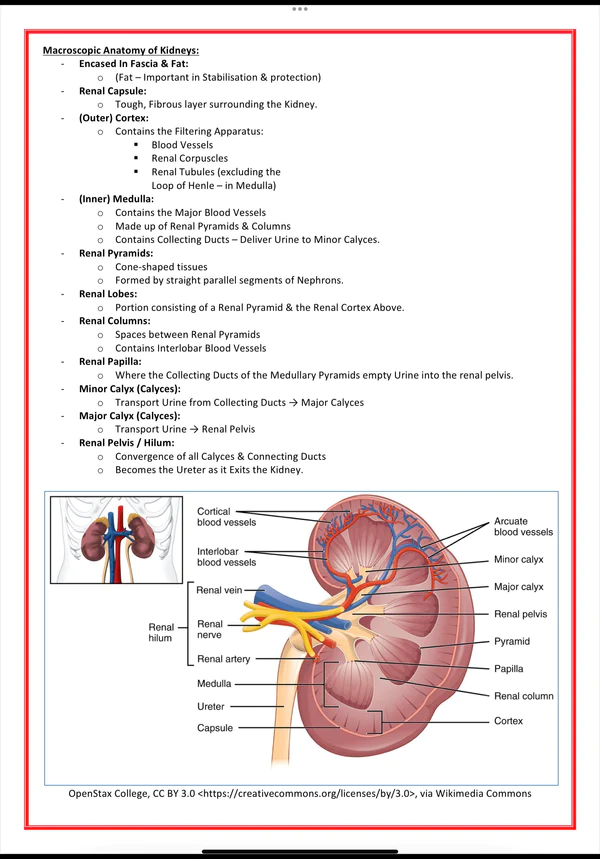
Urinary Renal System рџ є Discover High Yield Medical Study Notes Understanding kidney anatomy and physiology is important for nursing practice. it enables understanding of the aetiology and treatment of kidney function disorders. this is the first article in a series about this topic. anatomy of the kidney external anatomy an adult kidney typically measures 12cm long, 6cm wide and 3cm deep (mahadevan, 2019). Its net effect is to conserve and increase water levels in the plasma by reducing the excretion of sodium, and thus water, from the kidneys. in a negative feedback loop, increased osmolality of the ecf (which follows aldosterone stimulated sodium absorption) inhibits the release of the hormone (figure 26.3.1). Anatomy. the kidneys are retroperitoneal structures that filter blood and produce urine. excrete excess salts, fluid, and waste products (e.g., uric acid, urea, and creatine) from the body. resorb nutrients back into the blood. secrete erythropoietin and renin. hydroxylate 25 hydroxy vitamin d into 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin d. The renal system, which is also called the urinary system, is a group of organs in the body that filters out excess fluid and other substances from the bloodstream. the purpose of the renal system is to eliminate wastes from the body, regulate blood volume and pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulate blood ph.

Renal Physiology Notes Anatomy And Physiology Renal System Anatomy. the kidneys are retroperitoneal structures that filter blood and produce urine. excrete excess salts, fluid, and waste products (e.g., uric acid, urea, and creatine) from the body. resorb nutrients back into the blood. secrete erythropoietin and renin. hydroxylate 25 hydroxy vitamin d into 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin d. The renal system, which is also called the urinary system, is a group of organs in the body that filters out excess fluid and other substances from the bloodstream. the purpose of the renal system is to eliminate wastes from the body, regulate blood volume and pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulate blood ph.

Comments are closed.