Solved 1 A Using The Method Of Successive Approximations Chegg
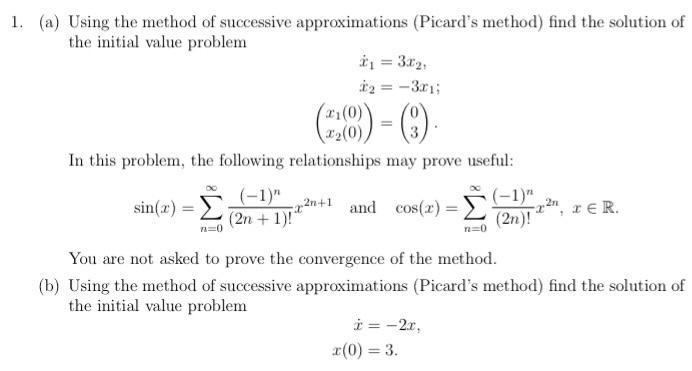
Solved 1 A Using The Method Of Successive Approximations Chegg (a) using the method of successive approximations (picard's method) find the solution of the initial value problem ity = 5.2, 12 = 5.2017 : (0) 32(0) (68) = 0) in this problem, the following relationships may prove useful: ( 1)" sin() ( 1)" (2 1)! and cos(x) er you are not asked to prove the convergence of the method. Math. advanced math. advanced math questions and answers. 1. (a) using the method of successive approximations (picard's method) find the solution of the initial value problem y = 5.2, 22 = 521; 0) ) (738) = (5) in this problem, the following relationships may prove useful: ( 1)" sin () ( 1)" (2n 1)! and cos (r) ter (2)! you are not asked to.

Solved 1 A Using The Method Of Successive Approximations Chegg Then the followings are equivalent: (1) is a solution of the ivp, (2) is a solution of the integral equation. (proof: in class) note. from this equivalence relation, we can show the solution existence and uniqueness for one of the two (i.e., ivp or ie) whichever is easier to prove. it is indeed true that the existence and uniquenss for ie is. 2.8: approximating solution using method of successive approximation (also called picard’s iteration method). ivp: y′ = f (t;y), y(t0) = y0. note: can always translate ivp to move initial value to the origin and translate back after solving: hence for simplicity in section 2.8, we will assume initial value is at the origin: y′ = f (t;y. When are the successive approximations using picard's method for solving an ode, are the terms of the taylor expansion of the solution of the ode 0 solve $\frac{dy}{dx} = x^2y x$ using method of successive approximations where $\phi(0) =0$. Newton’s method. newton’s method (also known as the newton raphson method) is a successive approximation method for finding the roots of a function. recall that the roots of a function f(x) are the values of x such that f(x) = 0. you can read more about newton’s method here. here is how newton’s method works: we guess some x0.

Solved 1 A Using The Method Of Successive Approximations Chegg When are the successive approximations using picard's method for solving an ode, are the terms of the taylor expansion of the solution of the ode 0 solve $\frac{dy}{dx} = x^2y x$ using method of successive approximations where $\phi(0) =0$. Newton’s method. newton’s method (also known as the newton raphson method) is a successive approximation method for finding the roots of a function. recall that the roots of a function f(x) are the values of x such that f(x) = 0. you can read more about newton’s method here. here is how newton’s method works: we guess some x0. Question: 1. (a) using the method of successive approximations (picard's method) find the solution of the initial value problem 1 = 3.2 12 = 3313 (18) in this problem, the following relationships may prove useful: ( 1)" sin(x) = 5 220 1 and cos(x) = ( 1)" 22, xer (2n 1)! (2n)! ), no n=0 you are not asked to prove the convergence of the method. Example 1. solve the initial value problem with the initial condition using the method of successive approximations. let . clearly is continuous on all of and also is continuous on all of and so a unique solution exists. we can express our first order differential equation as . define .

Comments are closed.