Solved 1 Draw The Production Possibility Curve 2 At Point Chegg

Solved 1 Draw The Production Possibility Curve 2 At Point Chegg Economics questions and answers. 1. draw the production possibility curve 2. at point c what is the cost of 100,000 more pizzas? 3. at point c what is the cost of 1,000 more robots? 4. on the diagram above label the point of unattainable combinations g 5. on the same diagram label the point of underemployment h 6. See answer. question: 1. draw the production possibilities curve from the above information 2. from the curve what is the opportunity cost of moving from a. point 1 to point 2 b. point 2 to point 3 c. point 3 to point 4 d. point 4 to point 5 e. point 5 to point 6 f point 6 to point 7 3. explain the reason the increasing opportunity cost 4.
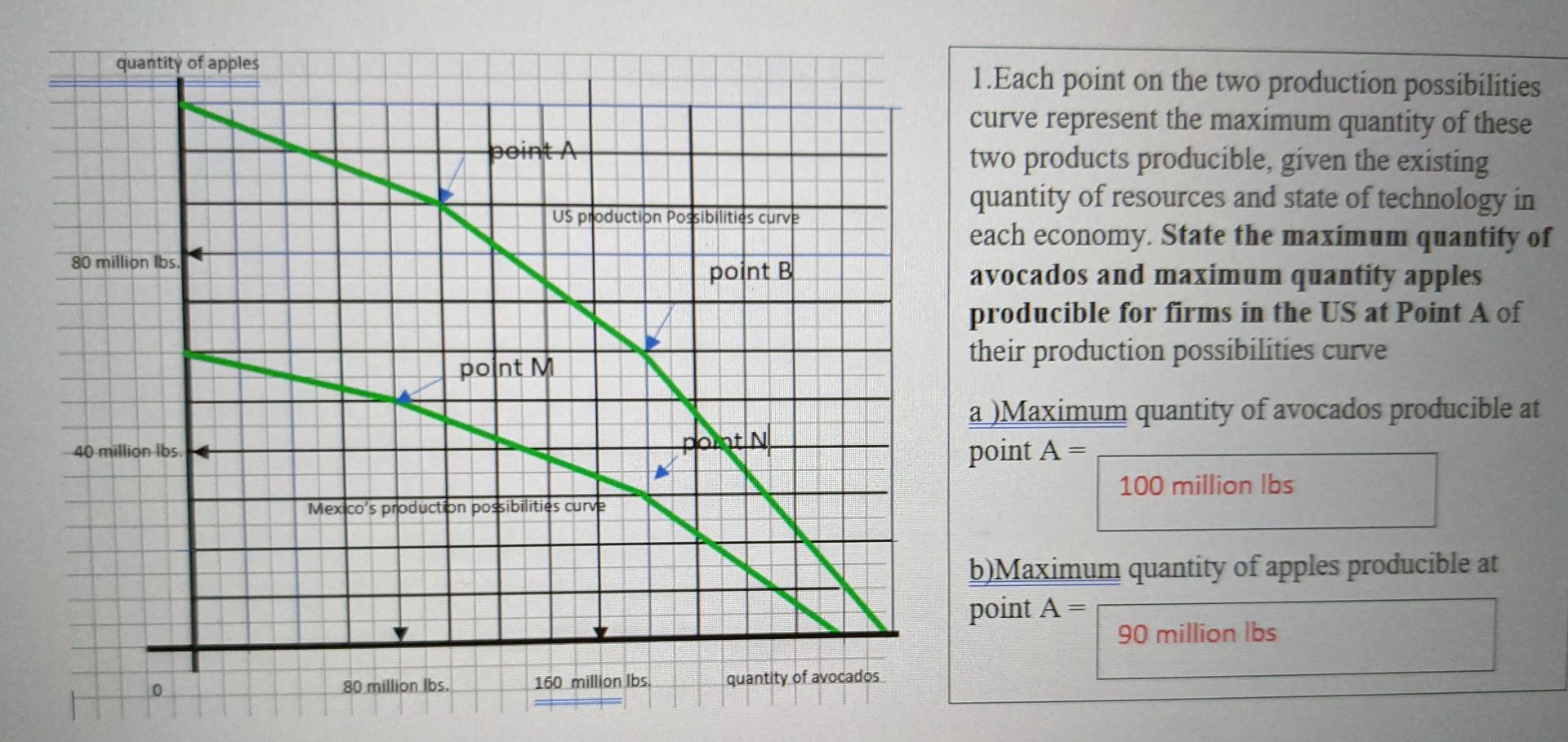
Solved 1 Each Point On The Two Production Possibilities Chegg For example, point r is productively inefficient because it is possible at choice c to have more of both goods: education on the horizontal axis is higher at point c than point r (e 2 is greater than e 1), and healthcare on the vertical axis is also higher at point c than point r (h 2 is great than h 1). Question: production possibility wor 1. draw the production possibility curve 2. at point c what is the cost of 100,000 more pizzas? 3. at point c what is the cost of 1,000 more robots? 4. can we produce 700,000 pizzas and 7600 robots? 5. label the following two points:a) underemployment of factors f b) unattainable combination of factors g 6. Economics questions and answers. 1). draw a production possibility curve based on the information. (2 pts) 2). if the economy is currently operating at point c, what is the opportunity cost of moving to point d and to point b? (2 pts) 3). what must happen if the economy wants to produce a combination of 17,000 laptops and 14,000 tons of wheat. The most important difference between the two graphs, though, is that a budget constraint is a straight line, while a production possibilities curve is typically bowed outwards, i.e. concave towards the origin. the reason for this difference is pretty simple: the slope of a budget line is defined as the ratio of the prices of the two goods or.

Comments are closed.