Solved 1 Prove That For Any Sets A B And C Within A Che
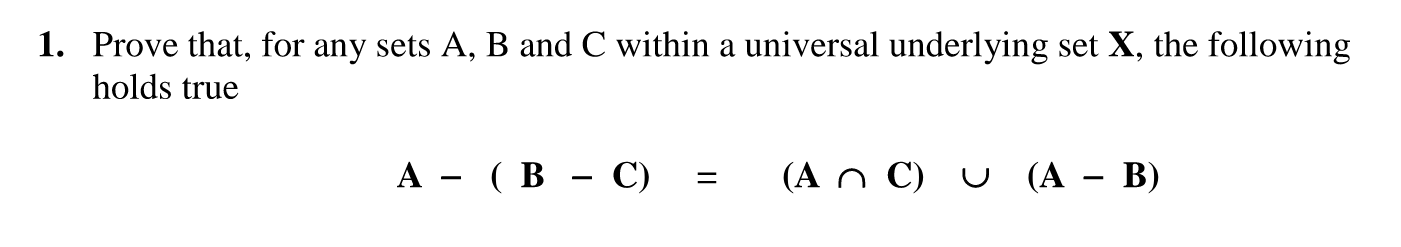
Solved 1 Prove That For Any Sets A B And C Within A Prove that for any sets a, b, c within a universe u, you may use set identities in the proof. your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. Cs103handout 07 summer 2019guide to proofs on setsjune 28, 2019richard feynman, one of the greatest physicists of the twentieth century, gave a. famous series of lectures on physics while a professor at caltech. those lectures have been recorded for posterity and are.
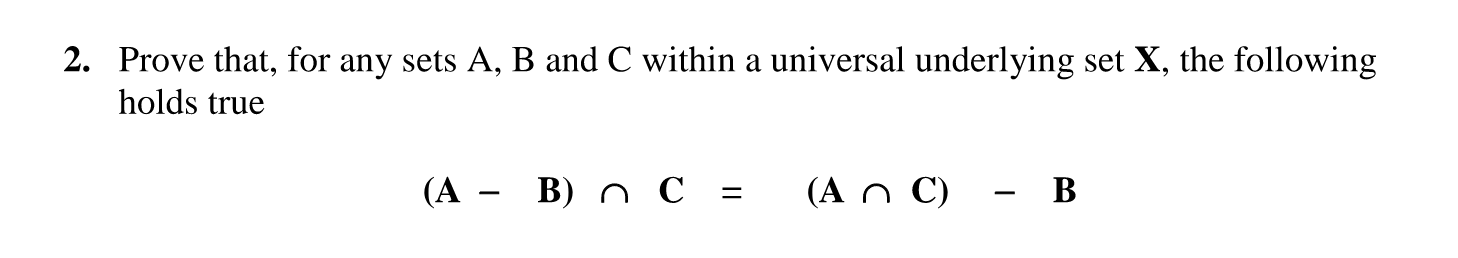
Solved Prove That For Any Sets A B And C Within A Universa Proof technique 1. state or restate the theorem so you understand what is given (the hypothesis) and what you are trying to prove (the conclusion). theorem 4.1.1: the distributive law of intersection over union. if a, b, and c are sets, then a ∩ (b ∪ c) = (a ∩ b) ∪ (a ∩ c). proof. proof technique 2. Let's prove the first. the second is similarly proven and is an exercise for you. we have each of the following statements implying the next. x ∈ a ∩ (b ∪ c) x ∈ a ∩ (b ∪ c) x ∈ a x ∈ a and x ∈ b ∪ c x ∈ b ∪ c. x ∈ a x ∈ a and x ∈ b x ∈ b or x ∈ c x ∈ c. x ∈ a x ∈ a or x ∈ b x ∈ b and x ∈ a x ∈ a. Construct an algebraic proof that for all sets a, b, and c, (a ∪ b) − c = (a − c) ∪ (b − c). cite a property from theorem 6.2.2 for every step of the proof. solution: let a, b, and c be any sets. then (a ∪ b) − c = (a ∪ b) ∩ cc by the set difference law = c c ∩ (a ∪ b) by the commutative law for ∩. Now let b = \ {a, b, c\}. notice that b = a \cup \ {c\}. we can determine the subsets of b by starting with the subsets of a in (5.1.10). we can form the other subsets of b by taking the union of each set in (5.1.10) with the set \ {c\}.
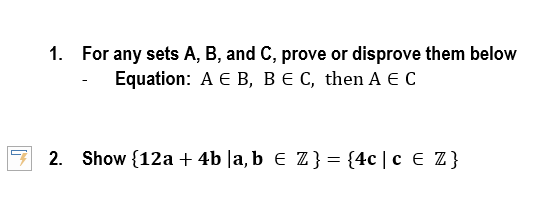
Solved 1 For Any Sets A B And C Prove Or Disprove Them Che Construct an algebraic proof that for all sets a, b, and c, (a ∪ b) − c = (a − c) ∪ (b − c). cite a property from theorem 6.2.2 for every step of the proof. solution: let a, b, and c be any sets. then (a ∪ b) − c = (a ∪ b) ∩ cc by the set difference law = c c ∩ (a ∪ b) by the commutative law for ∩. Now let b = \ {a, b, c\}. notice that b = a \cup \ {c\}. we can determine the subsets of b by starting with the subsets of a in (5.1.10). we can form the other subsets of b by taking the union of each set in (5.1.10) with the set \ {c\}. Edit2: the distributive property of the logical connectives ∧, ∨ ∧, ∨ may be verified by corresponding truth tables. it is important to note, that ∩, ∪ ∩, ∪ are defined operations in the theory of sets while the underlying logic (where you proceed with your reasoning with ∧, ∨ ∧, ∨) is the first order logic (of set theory). I'm studying for an exam and they were suggested as good study material but i don't understand how either would be solved. suppose a ⊆ b. prove that for every set c, c \ b ⊆ c \ a. prove that if a ⊆ b and a ⊆ c then a ⊆ b ∩ c. i believe you can solve both by contradiction but i get lost after a few steps.

Solved 01 A Prove That For Any Sets A B And C B A Chegg Edit2: the distributive property of the logical connectives ∧, ∨ ∧, ∨ may be verified by corresponding truth tables. it is important to note, that ∩, ∪ ∩, ∪ are defined operations in the theory of sets while the underlying logic (where you proceed with your reasoning with ∧, ∨ ∧, ∨) is the first order logic (of set theory). I'm studying for an exam and they were suggested as good study material but i don't understand how either would be solved. suppose a ⊆ b. prove that for every set c, c \ b ⊆ c \ a. prove that if a ⊆ b and a ⊆ c then a ⊆ b ∩ c. i believe you can solve both by contradiction but i get lost after a few steps.

Solved C Prove That For Any Sets A B And C Chegg

Comments are closed.