Solved A Calculate The Unit Tangent Vector Principal Unit Chegg

Solved A Calculate The Unit Tangent Vector Principal Unit Chegg (a) calculate the unit tangent vector, principal unit normal vector, binormal vector and curvature of vector valued functions; r (t) = 2 cos 2 π t i 2 sin 2 π t j − 2 k (10marks) (b) given that the line integral equation of ∫ c x y d x (x y) d y where c is the curve, calculate; i) a straight line from the point (0, 0) to (1, 1) (3. (a) calculate the unit tangent vector, principal unit normal vector, binormal vector and curvature of vector valued functions; r(t)=2cos2πti 2sin2πtj−2k your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on.

Solved A Calculate The Unit Tangent Vector Principal Unit Chegg The principal unit normal vector. a normal vector is a perpendicular vector. given a vector v in the space, there are infinitely many perpendicular vectors. our goal is to select a special vector that is normal to the unit tangent vector. geometrically, for a non straight curve, this vector is the unique vector that point into the curve. The unit tangent vector t(t) of a vector function is the vector that’s 1 unit long and tangent to the vector function at the point t. remember that |r'(t)| is the magnitude of the derivative of the vector function at time t. the unit normal vector n(t) of the same vector function is the ve. To find the unit tangent vector for a vector function, we use the formula t (t)= (r' (t)) (||r' (t)||), where r' (t) is the derivative of the vector function and t is given. we’ll start by finding the derivative of the vector function, and then we’ll find the magnitude of the derivative. those two values will give us everything we need in. The tangent line at a point is calculated from the derivative of the vector valued function r(t) r (t). notice that the vector r′(π 6) r ′ (π 6) is tangent to the circle at the point corresponding to t = π 6 t = π 6. this is an example of a tangent vector to the plane curve defined by r(t) = costi sintj r (t) = cos t i sin t j.
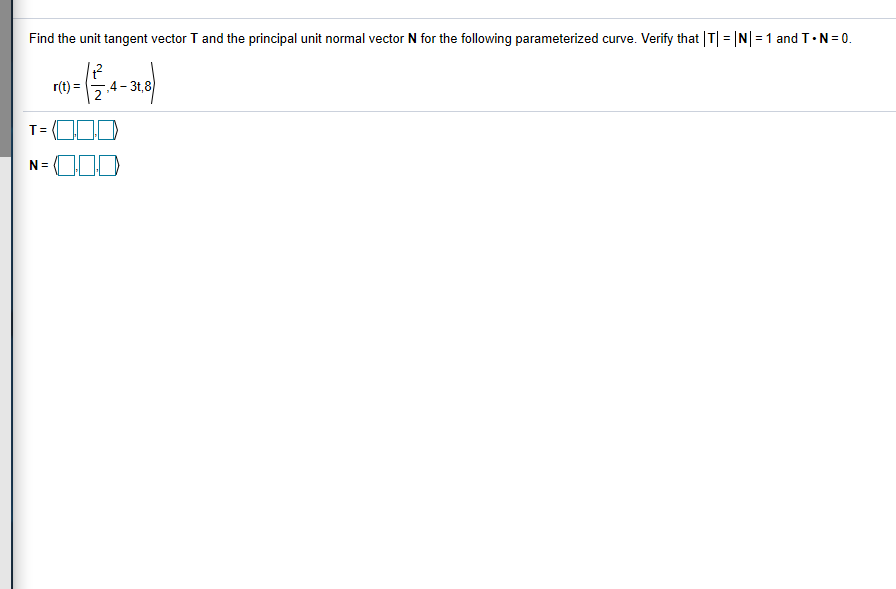
Solved Find The Unit Tangent Vector T And The Principal Unit To find the unit tangent vector for a vector function, we use the formula t (t)= (r' (t)) (||r' (t)||), where r' (t) is the derivative of the vector function and t is given. we’ll start by finding the derivative of the vector function, and then we’ll find the magnitude of the derivative. those two values will give us everything we need in. The tangent line at a point is calculated from the derivative of the vector valued function r(t) r (t). notice that the vector r′(π 6) r ′ (π 6) is tangent to the circle at the point corresponding to t = π 6 t = π 6. this is an example of a tangent vector to the plane curve defined by r(t) = costi sintj r (t) = cos t i sin t j. The unit tangent vector is exactly what it sounds like: a unit vector that is tangent to the curve. to calculate a unit tangent vector, first find the derivative r ′ (t). r ′ (t). second, calculate the magnitude of the derivative. the third step is to divide the derivative by its magnitude. The principal unit normal vector can be challenging to calculate because the unit tangent vector involves a quotient, and this quotient often has a square root in the denominator. in the three dimensional case, finding the cross product of the unit tangent vector and the unit normal vector can be even more cumbersome.

Solved A Calculate The Unit Tangent Vector Principal Unit Chegg The unit tangent vector is exactly what it sounds like: a unit vector that is tangent to the curve. to calculate a unit tangent vector, first find the derivative r ′ (t). r ′ (t). second, calculate the magnitude of the derivative. the third step is to divide the derivative by its magnitude. The principal unit normal vector can be challenging to calculate because the unit tangent vector involves a quotient, and this quotient often has a square root in the denominator. in the three dimensional case, finding the cross product of the unit tangent vector and the unit normal vector can be even more cumbersome.

Solved Find The Unit Tangent Vector T And The Principal Unit

Comments are closed.