Solved Find The Principal Unit Normal Vector To The Curve At Chegg
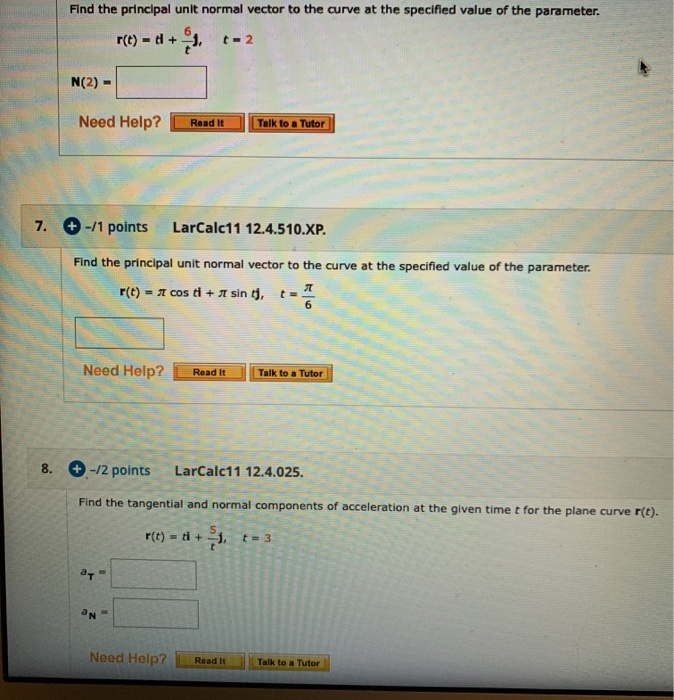
Solved Find The Principal Unit Normal Vector To The Curve At Chegg Find the principal unit normal vector to the curve at the specified value of the parameter. r(t) = π cos ti π sin tj, t = π 6 your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. In this video, we solve problem 12.4.016 from the larson and edwards calculus: early transcendental functions text, 7th edition. we're given a vector value f.
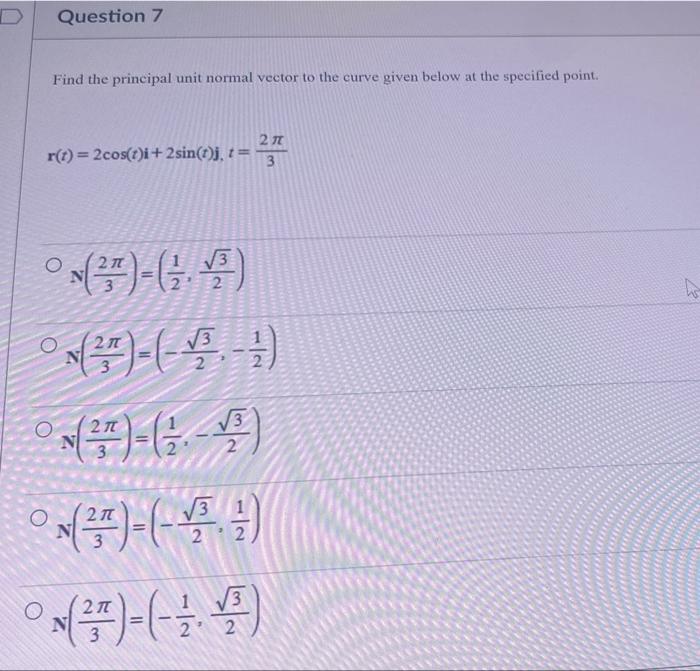
Solved Find The Principal Unit Normal Vector To The Curve The principal unit normal vector. a normal vector is a perpendicular vector. given a vector v in the space, there are infinitely many perpendicular vectors. our goal is to select a special vector that is normal to the unit tangent vector. geometrically, for a non straight curve, this vector is the unique vector that point into the curve. The curve lies in the plane z=1, so the principal unit normal vector \vec{n}(\pi) will lie in the same plane (and the same plane as \vec{t}(\pi)), it will be perpendicular to \vec{n}(\pi), and it will point directly toward the center of curvature, which in this case is the center (0,0,1) of the ellipse that the curve is tracing out in the plane. The unit normal vector and the binormal vector form a plane that is perpendicular to the curve at any point on the curve, called the normal plane. in addition, these three vectors form a frame of reference in three dimensional space called the frenet frame of reference (also called the tnb frame) (figure 7). Anyway, here is a general process to find the unit normal. first of all you should parametrize your curve by arclength, which is given by. s(t) = ∫t 0 ∥r′(x)∥dx = 5t. s (t) = ∫ 0 t ‖ r ′ (x) ‖ d x = 5 t. as a function of s s, r r can be rewritten as r(s) =(3 sin s 5, 3 cos s 5, 45s) r (s) = (3 sin s 5, 3 cos s 5, 4 5 s). the.

Comments are closed.