Solved Geometry Right Triangle Test Review Find The Missing Chegg
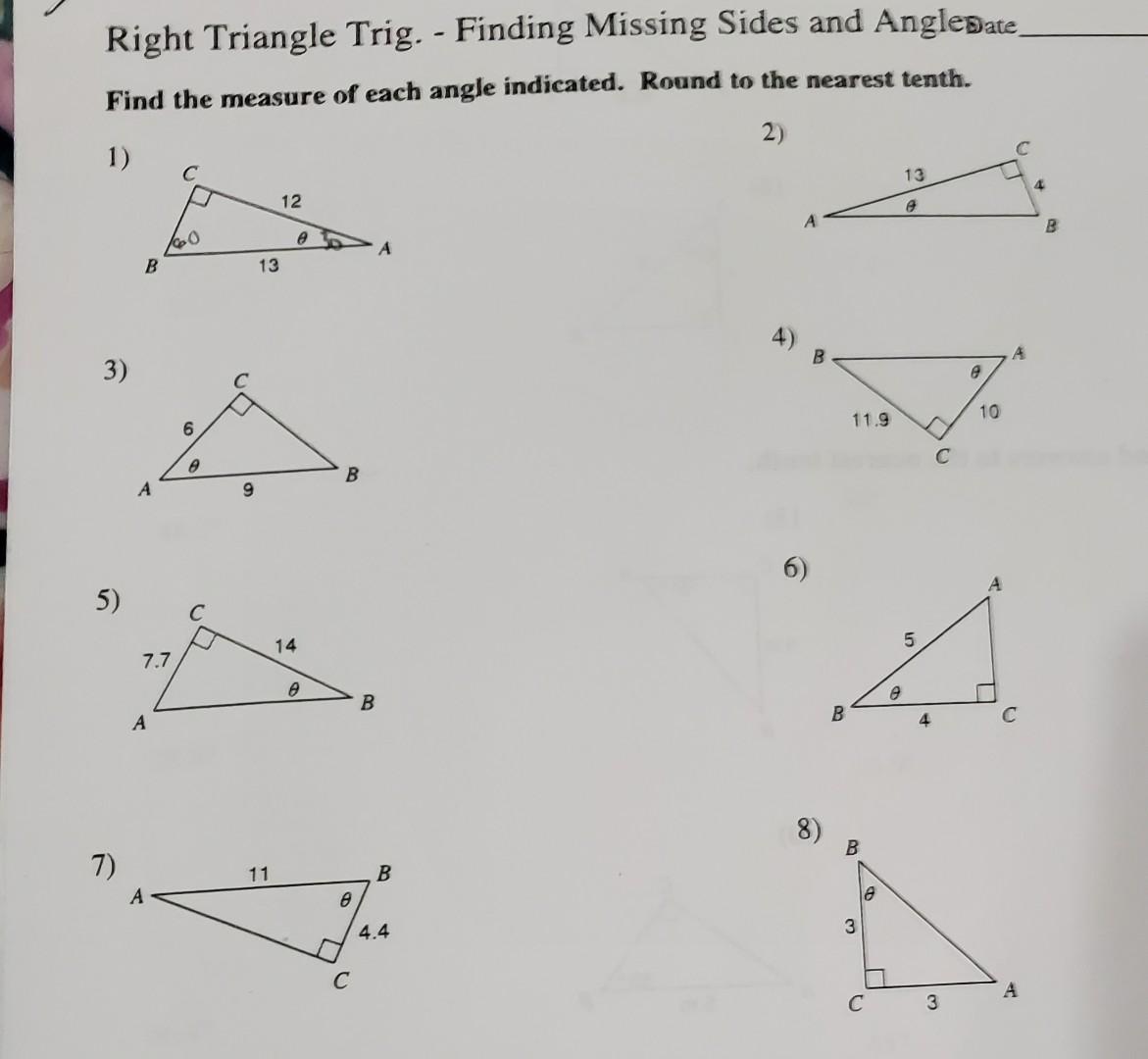
Solved Right Triangle Trig Finding Missing Sides And Chegg Your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: geometry right triangle test review find the missing length indicated. leave your answer in simplest radical form. 16 0 100. here’s the best way to solve it. Solution. solve each right triangle by finding the missing angles and sides. round side lengths to the nearest tenth and angles to the nearest whole number. 1891 f 2 m g <g = eg = ef=.

Solved For The Right Triangle Find The Missing Quantity Chegg A right triangle's hypotenuse. the hypotenuse is the largest side in a right triangle and is always opposite the right angle. (only right triangles have a hypotenuse). the other two sides of the triangle, ac and cb are referred to as the 'legs'. in the triangle above, the hypotenuse is the side ab which is opposite the right angle, ∠c ∠ c. Find the length of [latex]ap\text{.}[ latex] 75. find an exact value for the area of each triangle. 76. find an exact value for the perimeter of each parallelogram. 77. find the area of the outer square. find the dimensions and the area of the inner square. what is the ratio of the area of the outer square to the area of the inner square? 78. If we ignore the height of the person, we solve the following triangle: figure 1.4.10. given the angle of depression is 53 ∘, ∠a in the figure above is 37 ∘. we can use the tangent function to find the distance from the building to the park: tan37 ∘ = opposite adjacent = d 100 tan37 ∘ = d 100 d = 100tan37 ∘ ≈ 75.36 ft. For example, the area of a right triangle is equal to 28 in² and b = 9 in. our right triangle side and angle calculator displays missing sides and angles! now we know that: a = 6.222 in; c = 10.941 in; α = 34.66° β = 55.34° now, let's check how finding the angles of a right triangle works: refresh the calculator. pick the option you need.
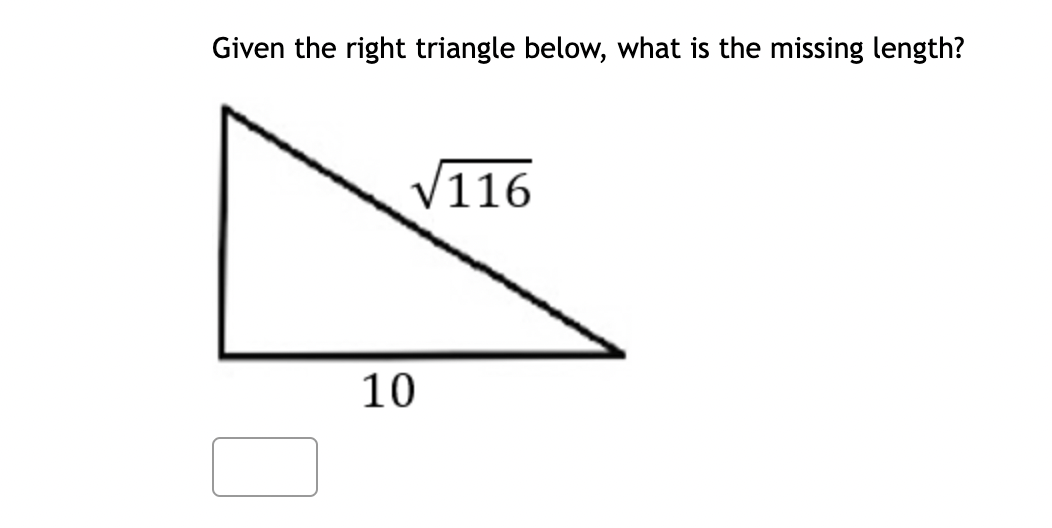
Solved Given The Right Triangle Below What Is The Missing Chegg If we ignore the height of the person, we solve the following triangle: figure 1.4.10. given the angle of depression is 53 ∘, ∠a in the figure above is 37 ∘. we can use the tangent function to find the distance from the building to the park: tan37 ∘ = opposite adjacent = d 100 tan37 ∘ = d 100 d = 100tan37 ∘ ≈ 75.36 ft. For example, the area of a right triangle is equal to 28 in² and b = 9 in. our right triangle side and angle calculator displays missing sides and angles! now we know that: a = 6.222 in; c = 10.941 in; α = 34.66° β = 55.34° now, let's check how finding the angles of a right triangle works: refresh the calculator. pick the option you need. Round off the calculated length to the nearest tenths. 10. solve for the measure of ∠ m by analyzing the triangle below. round off the angle measure to one decimal place only. 11. analyze the. Example 1: right triangle. problem: find the missing side length of a right triangle with one side measuring 3 cm and the hypotenuse measuring 5 cm. solution: use the pythagorean theorem: a^2 b^2 = c^2. plug in the known values: 3^2 b^2 = 5^2. simplify: 9 b^2 = 25. subtract 9 from both sides: b^2 = 16.
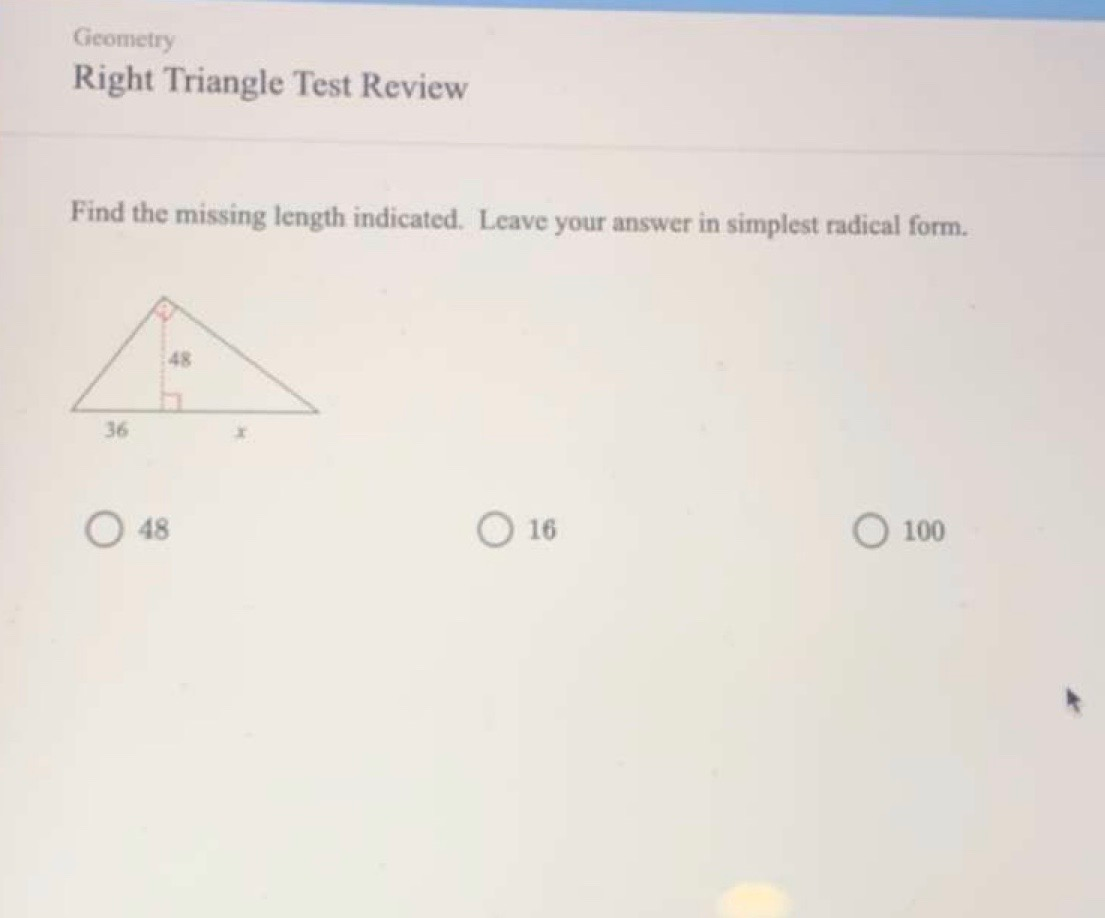
Solved Geometry Right Triangle Test Review Find The Missing Chegg Round off the calculated length to the nearest tenths. 10. solve for the measure of ∠ m by analyzing the triangle below. round off the angle measure to one decimal place only. 11. analyze the. Example 1: right triangle. problem: find the missing side length of a right triangle with one side measuring 3 cm and the hypotenuse measuring 5 cm. solution: use the pythagorean theorem: a^2 b^2 = c^2. plug in the known values: 3^2 b^2 = 5^2. simplify: 9 b^2 = 25. subtract 9 from both sides: b^2 = 16.

Comments are closed.