Solved In Figure 1 1 A Shift Of The Production Chegg

Solved In Figure 1 1 п їa Shift Of The Production Chegg In figure 1.1, a shift of the production possibilities curve from pp 1 to pp 2 could be caused by: select one: a. an increase in the quality of raw materials available b. a shift of factors of production from one industry to another. c. more labor. d. all of the above could cause the shift. Question: in figure 1.4, a shift of the production possibilities curve from pp1 to pp2 could be caused by. in figure 1. 4, a shift of the production possibilities curve from pp 1 to pp 2 could be caused by. here’s the best way to solve it.
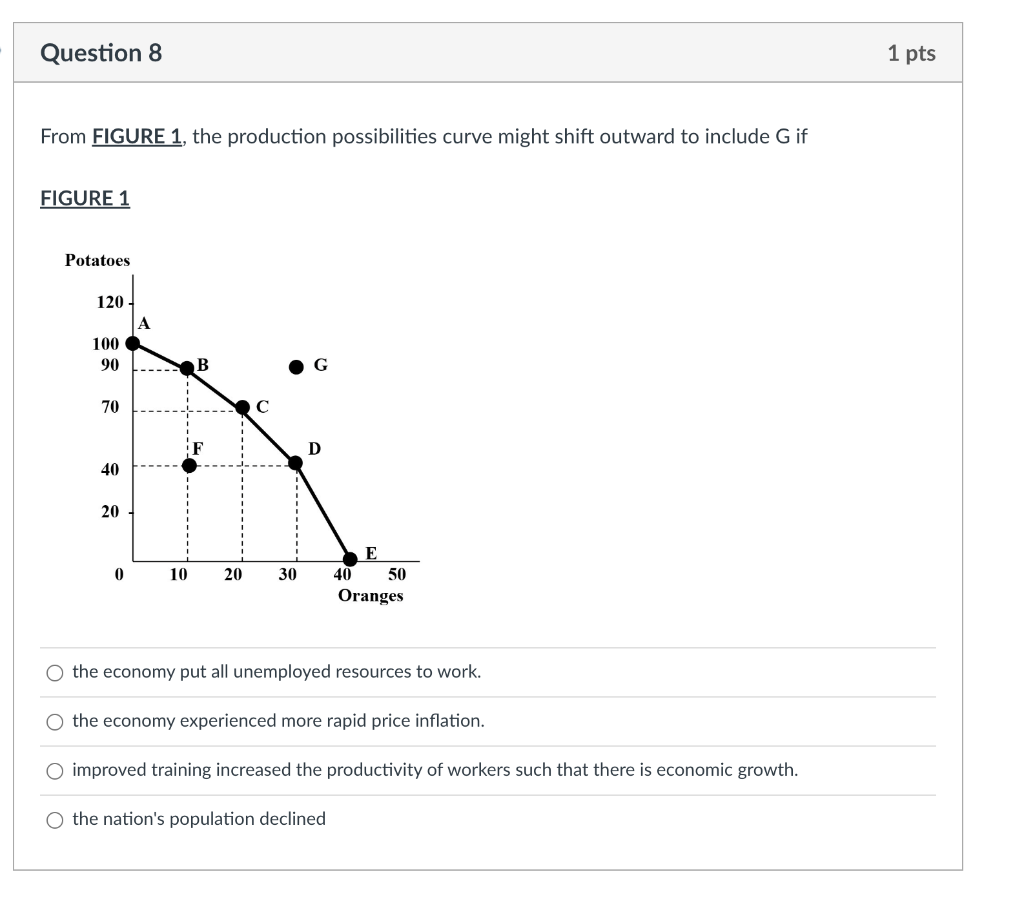
Solved From Figure 1 The Production Possibilities Curve Chegg A shift of factors of production from. in figure 1.1, a shift of the production possibilities curve from ppc1 to ppc2 could be caused by: [please note that ppc2 is the inner curve] a. an decrease in the quantity of raw materials available. b. a shift of factors of production from one industry to another. c. Keep in mind that some texts will call it the production possibilities curve (ppc) while this post calls it the production possibilities frontier. both names describe the same concept. in the real world there are several events that can occur that would cause the ppf to shift, or cause changes in its shape. Question: in figure 1.3, a shift of the production possibilities curve from pp1 to pp2 could be caused by 18) a) the use of improved production technology.b) a decrease in the quantity of raw materials available.c) a decline in the production skills of workers.d) all of the choices are correct.19) other things being equal, an increase in taxes will. 1.1 basic economic concepts: scarcity. 1.2 resource allocation and economic systems. 1.3 production possibilities curve (ppc) 1.4 comparative advantage and trade. 1.5 cost benefit analysis. 1.6 marginal analysis and consumer choice. unit 2 – supply and demand. unit 3 – production, cost, and the perfect competition model.

Comments are closed.