Standard Potential Pveducation

Standard Potential Pveducation Electrochemical potential; nernst equation; basic battery operation; ideal battery capacity; 10.3 battery non equilibrium; 10.4. battery characteristics; battery efficiency; battery capacity; battery charging and discharging parameters; battery lifetime and maintenance; battery voltage; other electrical battery parameters; summary and. The data below tabulates standard electrode potentials (e °), in volts relative to the standard hydrogen electrode (she), at: absolute partial pressure 101.325 kpa (1.00000 atm; 1.01325 bar) for each gaseous reagent — the convention in most literature data but not the current standard state (100 kpa). variations from these ideal conditions.

Standard Potential For all half reactions, changing the direction of the reaction changes the sign of the standard potential, such that the reduction reaction of lithium above has a standard potential of e0 = 3.04 v. similarly, an element with 7 electrons in its outer shell (say cl), will have a higher electrochemical potential than cl which has gained an. Solar cell efficiency records. standard solar spectra. periodic table. units and conversions. physical constants. equations for photovoltaics. equations in tex. graphs with sliders. korean version pdf. Standard potential. batteries are transforming our renewable energy economy. lithium ion has scaled production, but remains constrained by capital intensity, long duration performance, mineral supply, and safety. new battery technologies that avoid these issues and that can be deployed quickly and efficiently are necessary. standard potential. This implies that the potential difference between the co and cu electrodes is 1.10 v − 0.51 v = 0.59 v. in fact, that is exactly the potential measured under standard conditions if a cell is constructed with the following cell diagram: co (s) ∣ co2 (aq, 1m) ∥ cu2 (aq, 1m) ∣ cu(s) e° = 0.59 v.

Standard Potentials Video Tutorials Practice Problems Channels Standard potential. batteries are transforming our renewable energy economy. lithium ion has scaled production, but remains constrained by capital intensity, long duration performance, mineral supply, and safety. new battery technologies that avoid these issues and that can be deployed quickly and efficiently are necessary. standard potential. This implies that the potential difference between the co and cu electrodes is 1.10 v − 0.51 v = 0.59 v. in fact, that is exactly the potential measured under standard conditions if a cell is constructed with the following cell diagram: co (s) ∣ co2 (aq, 1m) ∥ cu2 (aq, 1m) ∣ cu(s) e° = 0.59 v. The positive value for the standard cell potential indicates the process is spontaneous under standard state conditions. check your learning use the data in table 17.1 to predict the spontaneity of the oxidation of bromide ion by molecular iodine under standard state conditions, supporting the prediction by calculating the standard cell. Glossary standard cell potential \( (e^\circ \ce{cell})\) the cell potential when all reactants and products are in their standard states (1 bar or 1 atm or gases; 1 m for solutes), usually at 298.15 k; can be calculated by subtracting the standard reduction potential for the half reaction at the anode from the standard reduction potential for the half reaction occurring at the cathode.

4 Standard Potentials Youtube The positive value for the standard cell potential indicates the process is spontaneous under standard state conditions. check your learning use the data in table 17.1 to predict the spontaneity of the oxidation of bromide ion by molecular iodine under standard state conditions, supporting the prediction by calculating the standard cell. Glossary standard cell potential \( (e^\circ \ce{cell})\) the cell potential when all reactants and products are in their standard states (1 bar or 1 atm or gases; 1 m for solutes), usually at 298.15 k; can be calculated by subtracting the standard reduction potential for the half reaction at the anode from the standard reduction potential for the half reaction occurring at the cathode.
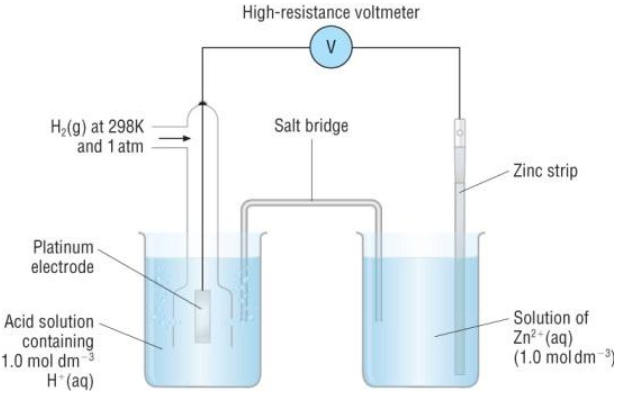
Standard Electrode Potential W3schools

Comments are closed.