Stratified Blocked Randomization

Patient Block Stratified Randomization Procedure Download Scientific Graphic breakdown of stratified random sampling. in statistics, stratified randomization is a method of sampling which first stratifies the whole study population into subgroups with same attributes or characteristics, known as strata, then followed by simple random sampling from the stratified groups, where each element within the same subgroup are selected unbiasedly during any stage of the. Block randomization. if we consider only the balance in number of subjects in a study involving two treatment groups a and b, then a and b can be repeatedly allocated in a randomized block design with predefined block size. here, a selection bias is inevitable because a researcher or subject can easily predict the allocation of the group.
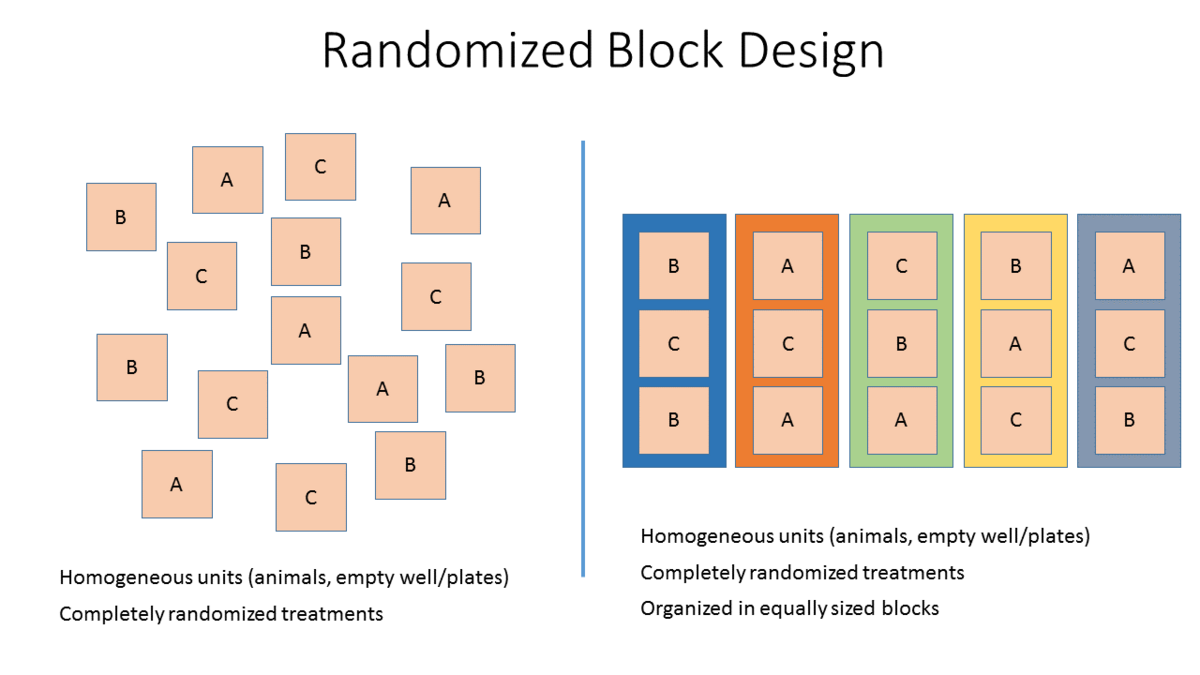
Randomisation And Blinding Premier Implementation of randomization in clinical trials is due to a. bradford hill who designed the first randomized clinical trial evaluating the use of streptomycin in treating tuberculosis in 1946 [9, 12, 13]. reference [14] provides a good summary of the rationale and justification for the use of randomization in clinical trials. Specifically, randomization was stratified by study center and number of active joints (≤ 2 vs. > 2, referred to as “few” or “many” in what follows), with blocked randomization within each stratum using a block size of two. Stratified randomization is achieved by generating a separate block for each combination of covariates, and subjects are assigned to the appropriate block of covariates. after all subjects have been identified and assigned into blocks, simple randomization is performed within each block to assign subjects to one of the groups. Two articles published in jama used restrictions on the randomization procedure: bilecen et al 5 used permuted block randomization, a restricted randomization method used to help ensure the balance of the number of patients assigned to each treatment group. 3 kim et al 6 used a stratified randomization scheme together with permuted block.

Block Randomization Youtube Stratified randomization is achieved by generating a separate block for each combination of covariates, and subjects are assigned to the appropriate block of covariates. after all subjects have been identified and assigned into blocks, simple randomization is performed within each block to assign subjects to one of the groups. Two articles published in jama used restrictions on the randomization procedure: bilecen et al 5 used permuted block randomization, a restricted randomization method used to help ensure the balance of the number of patients assigned to each treatment group. 3 kim et al 6 used a stratified randomization scheme together with permuted block. Stratified randomization is used to obviate the unintentional impact that population characteristics or other independent variables, or “covariates,” may have on the trial result. 3, 7, 19 for stratified randomization, a subject is first placed in a specific stratum based on his her baseline characteristics, then randomization is applied to that stratum to determine their treatment group. Randomization helps to ensure that a certain proportion of patients receive each treatment and that the treatment groups being compared are similar in both measured and unmeasured patient characteristics. 1,2 simple or unrestricted, equal randomization of patients between 2 treatment groups is equivalent to tossing a fair coin for each patient.

Stratified Block Randomization Profile Download Scientific Diagram Stratified randomization is used to obviate the unintentional impact that population characteristics or other independent variables, or “covariates,” may have on the trial result. 3, 7, 19 for stratified randomization, a subject is first placed in a specific stratum based on his her baseline characteristics, then randomization is applied to that stratum to determine their treatment group. Randomization helps to ensure that a certain proportion of patients receive each treatment and that the treatment groups being compared are similar in both measured and unmeasured patient characteristics. 1,2 simple or unrestricted, equal randomization of patients between 2 treatment groups is equivalent to tossing a fair coin for each patient.

Comments are closed.