Structural Analysis Of Trusses вђ Method Of Joints
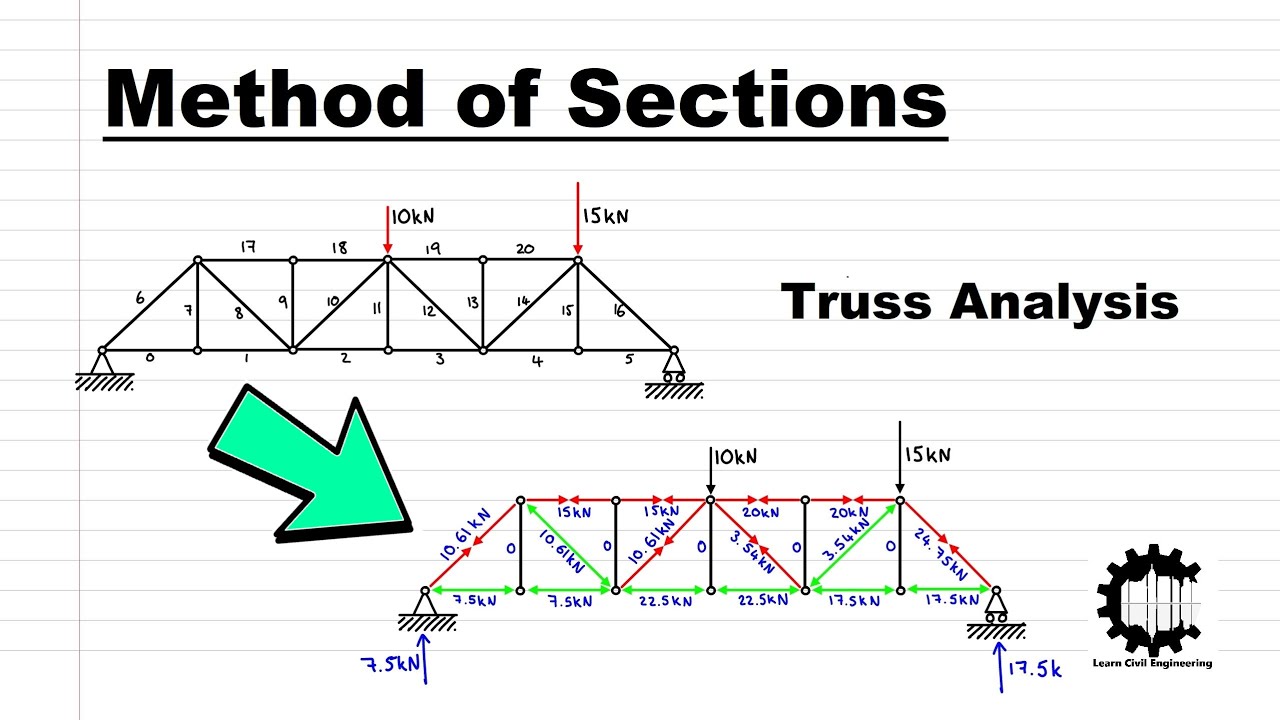
Method Of Sections Truss Analysis Example Structural Analysis Youtube Using the method of sections and method of joints to work out the internal forces in statically determinate trusses. by dr seán carroll. in this tutorial we’re going to focus on trusses, also known as pin jointed structures. we’ll discuss their strengths and the common methods of manual truss analysis. we’re going to start at the very. Analysis of truss structure method of joints method of sections zero force members summary. summary. method of joints vs method of sections use method of joints when you need to know element forces throughout the structure. two equations of equilibrium per joint. method of sections provides a short cut for solution of forces in a few specified.
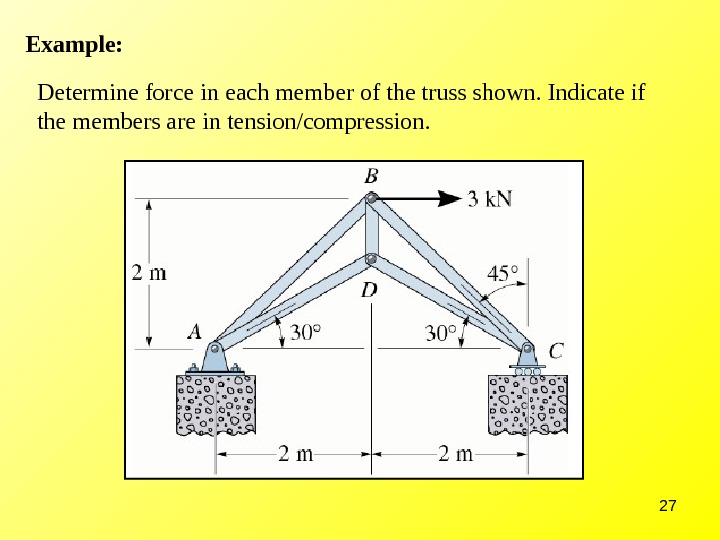
Structural Analysis Of Trusses вђ Method Of Joints Step 2: consider one of the supports: now that we have the reaction forces we can start the analysis of the rest of this truss structure. firstly, we look to one of our known forces – in this case, we will consider the left support reaction of 2.5 kn. since we know this force occurs at this point, we will consider just this point in isolation. 5.6.2 analysis of trusses by method of joint. this method is based on the principle that if a structural system constitutes a body in equilibrium, then any joint in that system is also in equilibrium and, thus, can be isolated from the entire system and analyzed using the conditions of equilibrium. the method of joint involves successively. Figure 5.4.1: the first step in the method of joints is to label each joint and each member. treating the entire truss structure as a rigid body, draw a free body diagram, write out the equilibrium equations, and solve for the external reacting forces acting on the truss structure. this analysis should not differ from the analysis of a single. 5.2 method of joints. the method of joints is a form of particle analysis. after solving for the reaction forces, you solve for the unknown forces at each joint until you have found the value of each member. you start with your model: convert the constraints into reaction forces with the appropriate labels: now solve for the reaction forces (r.
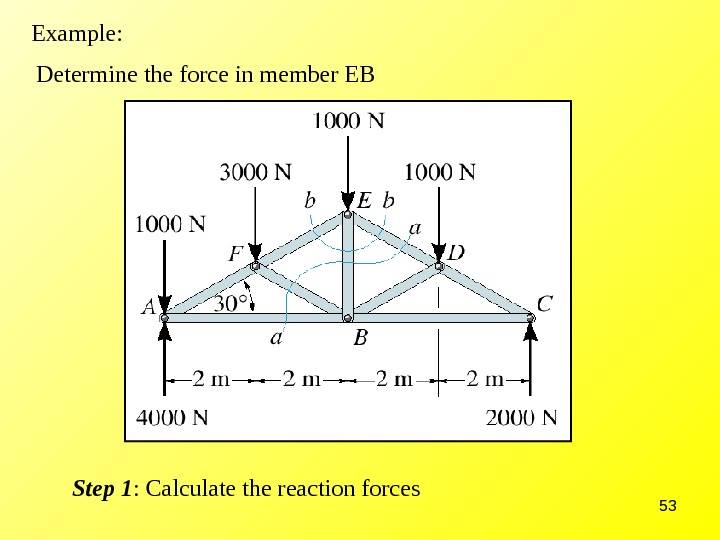
Structural Analysis Of Trusses вђ Method Of Joints Figure 5.4.1: the first step in the method of joints is to label each joint and each member. treating the entire truss structure as a rigid body, draw a free body diagram, write out the equilibrium equations, and solve for the external reacting forces acting on the truss structure. this analysis should not differ from the analysis of a single. 5.2 method of joints. the method of joints is a form of particle analysis. after solving for the reaction forces, you solve for the unknown forces at each joint until you have found the value of each member. you start with your model: convert the constraints into reaction forces with the appropriate labels: now solve for the reaction forces (r. For truss analysis, the point of concurrency (of the members’ axes) in a physical joint is considered as the location of the joint in the truss diagram. figure 6.6 shows examples of joints and their truss diagrams. fig. 6.6 physical trusses and their diagrams at joints. the above assumptions result in a truss member acting as a two force member. Method of joints entire truss is in equilibrium if and only if all individual pieces (truss members and connecting pins) are in equilibrium. truss members are two force members: equilibrium satisfied by equal, opposite, collinear forces. tension: member has forces elongating. compression: member has forces shortening.

Structural Analysis Of Trusses Trusses вђ Method Of Joints Pdf D For truss analysis, the point of concurrency (of the members’ axes) in a physical joint is considered as the location of the joint in the truss diagram. figure 6.6 shows examples of joints and their truss diagrams. fig. 6.6 physical trusses and their diagrams at joints. the above assumptions result in a truss member acting as a two force member. Method of joints entire truss is in equilibrium if and only if all individual pieces (truss members and connecting pins) are in equilibrium. truss members are two force members: equilibrium satisfied by equal, opposite, collinear forces. tension: member has forces elongating. compression: member has forces shortening.

Comments are closed.