Structural Cracking In Reinforced Concrete

Why Does Concrete Crack How To Prevent Repair It Types of cracking. cracks in concrete can be classified into different types. main types are discussed briefly in this article. flexural cracks: these cracks may occur in reinforced concrete elements after the hardening state. flexural cracks are vertical cracks that develop at the tension zone of the member up to their neutral axis. When the tensile strength of the material is exceeded, concrete will crack. cracks may propagate at much lower stresses than are required to cause crack initiation (aci 446.1r). in massive concrete elements, tensile stresses are caused by differential shrinkage between the surface and the interior concrete.
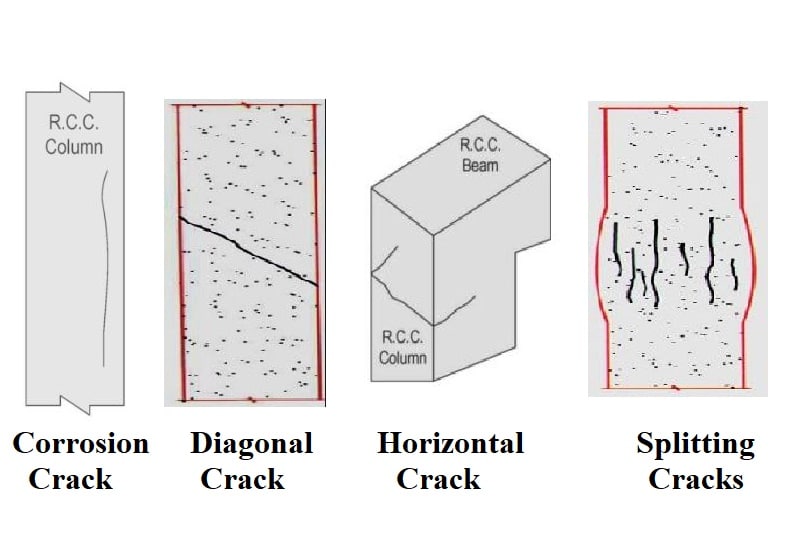
4 Types Of Cracks In Concrete Columns And Their Causes Video Included Abstract. cracks and cavities belong to two basic forms of damage to the concrete structure, which may reduce the load bearing capacity and tightness of the structure and lead to failures and catastrophes in construction structures. one of the most prevalent faults in concrete constructions is cracking, which, if left unchecked, can greatly. Cracks and cavities belong to two basic forms of damage to the concrete structure, which may reduce the load bearing capacity and tightness of the structure and lead to failures and catastrophes in construction structures. excessive and uncontrolled cracking of the structural element may cause both corrosion and weakening of the adhesion of the reinforcement present in it. moreover, cracking. Cracking can occur in both hardened and fresh, or plastic, concrete as a result of volume changes and repeated loading. this involves tensile stresses being loaded onto the concrete, the cracks occurring when the force exceeds its maximum tensile strength. it is important to understand the reasons why cracking occurs, the type of crack formed. Is directed primarily to the general reader in need of working information on the structural behavior and the cracking of reinforced concrete. the reader, however, is assumed to be familiar with the basic concepts of mechanics of materials. 1.2 scope chapter 2 presents the principles of reinforced concrete design and describes the behavior of a.

Store By Chalmers Studentkгґr Restraint Cracking Of Reinforced Cracking can occur in both hardened and fresh, or plastic, concrete as a result of volume changes and repeated loading. this involves tensile stresses being loaded onto the concrete, the cracks occurring when the force exceeds its maximum tensile strength. it is important to understand the reasons why cracking occurs, the type of crack formed. Is directed primarily to the general reader in need of working information on the structural behavior and the cracking of reinforced concrete. the reader, however, is assumed to be familiar with the basic concepts of mechanics of materials. 1.2 scope chapter 2 presents the principles of reinforced concrete design and describes the behavior of a. A solution on the safe side is obtained when the maximum possible concrete strain between two cracks is considered equal to the cracking strain of the concrete (ε cr = f ctm e c) and the maximum concrete force in this stage is considered with regard to the so called effective area a c,eff. under these assumptions, the maximum transfer length. However, severe damage, such as cracking and spalling, has been reported in reinforced concrete (rc) structures following large scale earthquakes, as shown in fig. 1. fig. 1 (a) and (b) show the cracked non structural wall and the damaged beam of the railway bridge, respectively.
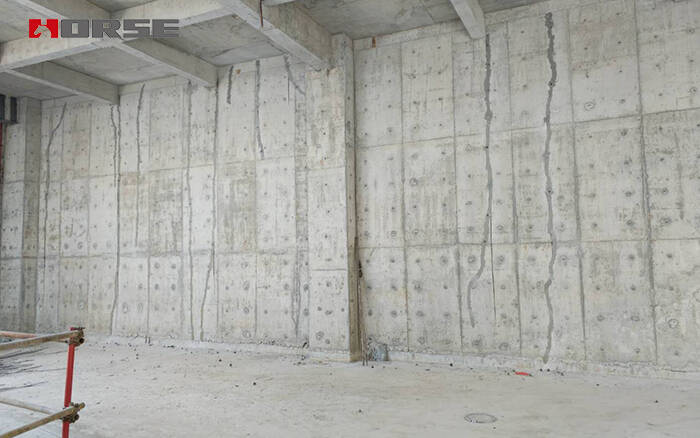

Cracks In Reinforced Concrete Rc Structural Members A solution on the safe side is obtained when the maximum possible concrete strain between two cracks is considered equal to the cracking strain of the concrete (ε cr = f ctm e c) and the maximum concrete force in this stage is considered with regard to the so called effective area a c,eff. under these assumptions, the maximum transfer length. However, severe damage, such as cracking and spalling, has been reported in reinforced concrete (rc) structures following large scale earthquakes, as shown in fig. 1. fig. 1 (a) and (b) show the cracked non structural wall and the damaged beam of the railway bridge, respectively.

Comments are closed.