Superior Mesenteric Artery Wikidoc
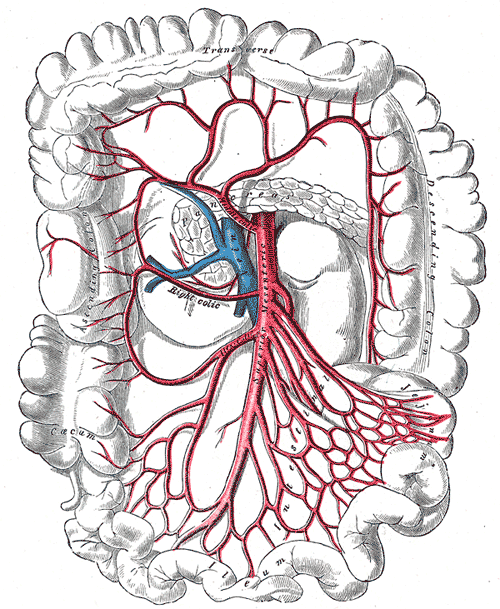
Superior Mesenteric Artery Wikidoc Template:infobox artery. editor in chief: c. michael gibson, m.s., m.d. in human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (sma) arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies the intestine from the lower part of the duodenum to the left colic flexure and the pancreas. Superior mesenteric artery (sma) syndrome is a rare, life threatening gastrointestinal disorder characterized by a compression of the third portion of the duodenum by the abdominal aorta and the overlying superior mesenteric artery. the syndrome is typically caused by a decreased angle of 6°–25° between the aorta and the sma (compared to a.
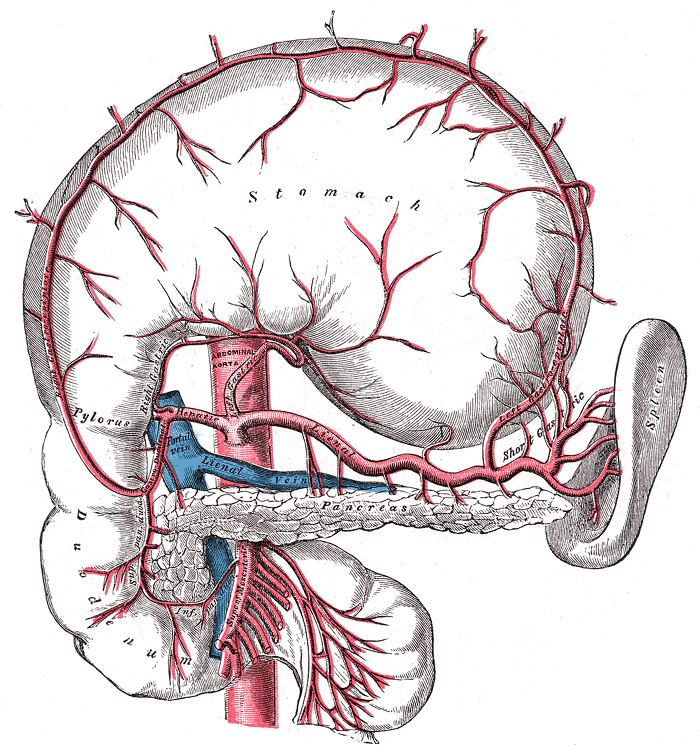
Superior Mesenteric Artery Wikidoc 14749. anatomical terminology. [edit on wikidata] in human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (sma) is an artery which arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies blood to the intestine from the lower part of the duodenum through two thirds of the transverse colon. Superior mesenteric artery syndrome is a rare cause of proximal small bowel obstruction and is linked to notable morbidity and mortality when the diagnosis is delayed. while superior mesenteric artery syndrome is rare, the morbidity and mortality associated with its complications make it a crucial differential to consider when concerned for bowel obstruction, especially in the setting of. The blood supply to the rectum arises from the superior, middle and inferior rectal arteries. the superior mesenteric artery arises from the abdominal aorta at the level of the first lumbar vertebral body l1, approximately a centimeter below the coeliac trunk. it arises above the renal arteries (that arise at vertebral level l1 l2). Superior mesenteric artery (sma) syndrome is a gastro vascular disorder in which the third and final portion of the duodenum is compressed between the abdominal aorta (aa) and the overlying superior mesenteric artery. this rare, potentially life threatening syndrome is typically caused by an angle of 6–25° between the aa and the sma, in.

Comments are closed.