Surgical Anatomy Exam Of The Wrist Hand Fingers

Surgical Anatomy Exam Of The Wrist Hand Fingers Youtube Midcarpal instability. examiner stabilizes distal radius and ulna with non dominant hand and moves patients wrist from radial deviation to ulnar deviation, whilst applying an axial load. a positive test occurs when a clunk is felt when the wrist is ulnarly deviated. ulnar carpal abutement. tests for tfcc tear or ulnar carpal impingement. The physical examination of the hand and wrist can be very rewarding because the majority of the anatomy is readily available to the examiner’s fingertips. one may palpate, stretch, or stress most of the underlying structures. therefore, armed with a broad knowledge of the anatomy of the distal upper extremity, one may develop a quick.
Wrist Hand Examination Easy Tutorial Orthofixar 2024 Hold the wrist passively in extension and ask the patient to extend their fingers (ed) flex the fingers to 90 o at the mcp joints and ask the patient to extend their fingers again (lumbricals) ask the patient to supinate the hands: check the flexors of the hand, asking the patient to. flex the wrist against resistance. The hand and the wrist are complex. they have a higher concentration of joints than any other part of the body. 1 the accompanying video and this print supplement describe the anatomy of the hand. Tunnels: the wrist has 6 dorsal and 2 volar (or palmar) compartments (or tunnels) that transport tendons to the hand. the 1st (most radial) tunnel transports the abductor pollicis longus and the extensor pollicis brevis tendons. these tendons represent the radial border of the “anatomic snuffbox.”. Physical examination of the wrist requires knowledge of wrist anatomy and pathology to make a diagnosis or narrow the differential diagnosis. symptoms are provoked by palpation and signs are produced by manipulation. negative findings elsewhere in the wrist are important. final diagnosis may require diagnostic imaging. by having all three methods of assessment agree one is assured of correct.
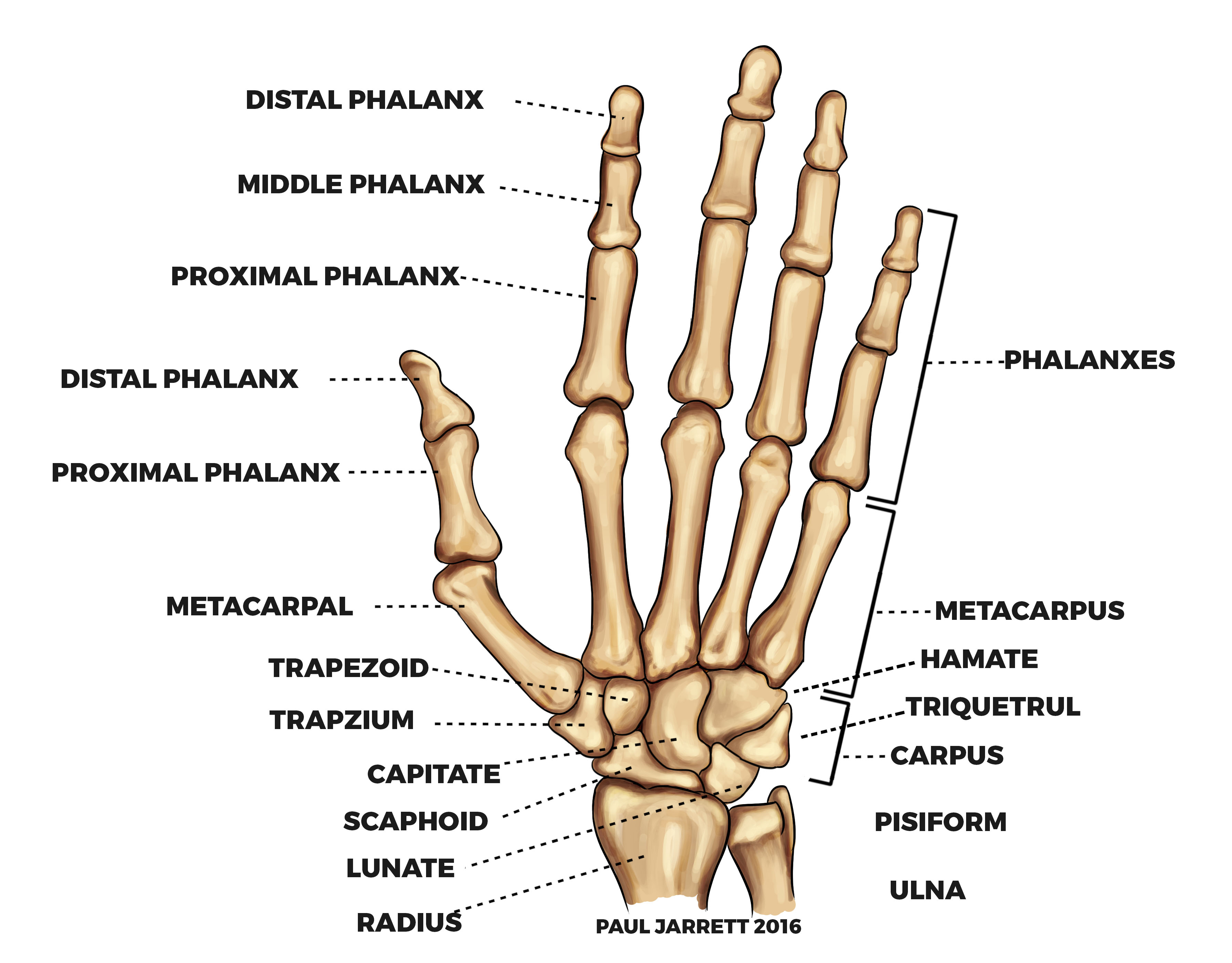
Mr Paul Jarrett Hand And Wrist Anatomy Murdoch Orthopaedic Clinic Tunnels: the wrist has 6 dorsal and 2 volar (or palmar) compartments (or tunnels) that transport tendons to the hand. the 1st (most radial) tunnel transports the abductor pollicis longus and the extensor pollicis brevis tendons. these tendons represent the radial border of the “anatomic snuffbox.”. Physical examination of the wrist requires knowledge of wrist anatomy and pathology to make a diagnosis or narrow the differential diagnosis. symptoms are provoked by palpation and signs are produced by manipulation. negative findings elsewhere in the wrist are important. final diagnosis may require diagnostic imaging. by having all three methods of assessment agree one is assured of correct. A complete examination of the wrist requires both an accurate history and a thorough understanding of carpal anatomy, biomechanics, and pathology. a thorough examination may necessitate evaluation of the radial and ulnar aspects of the carpus as well as potential extra articular causes of wrist pain. a carefully obtained history is essential to focus the examination. our standard approach to. This hand and wrist examination osce guide provides a clear step by step approach to examining the hand and wrist, with an included video demonstration. the hand and wrist examination can be broken down into five key components: look, feel, move, function and special tests. this can be helpful as an aide memoire if you begin to feel like you.

Comments are closed.