Systolic And Diastolic Blood Pressure Ratio Diagram
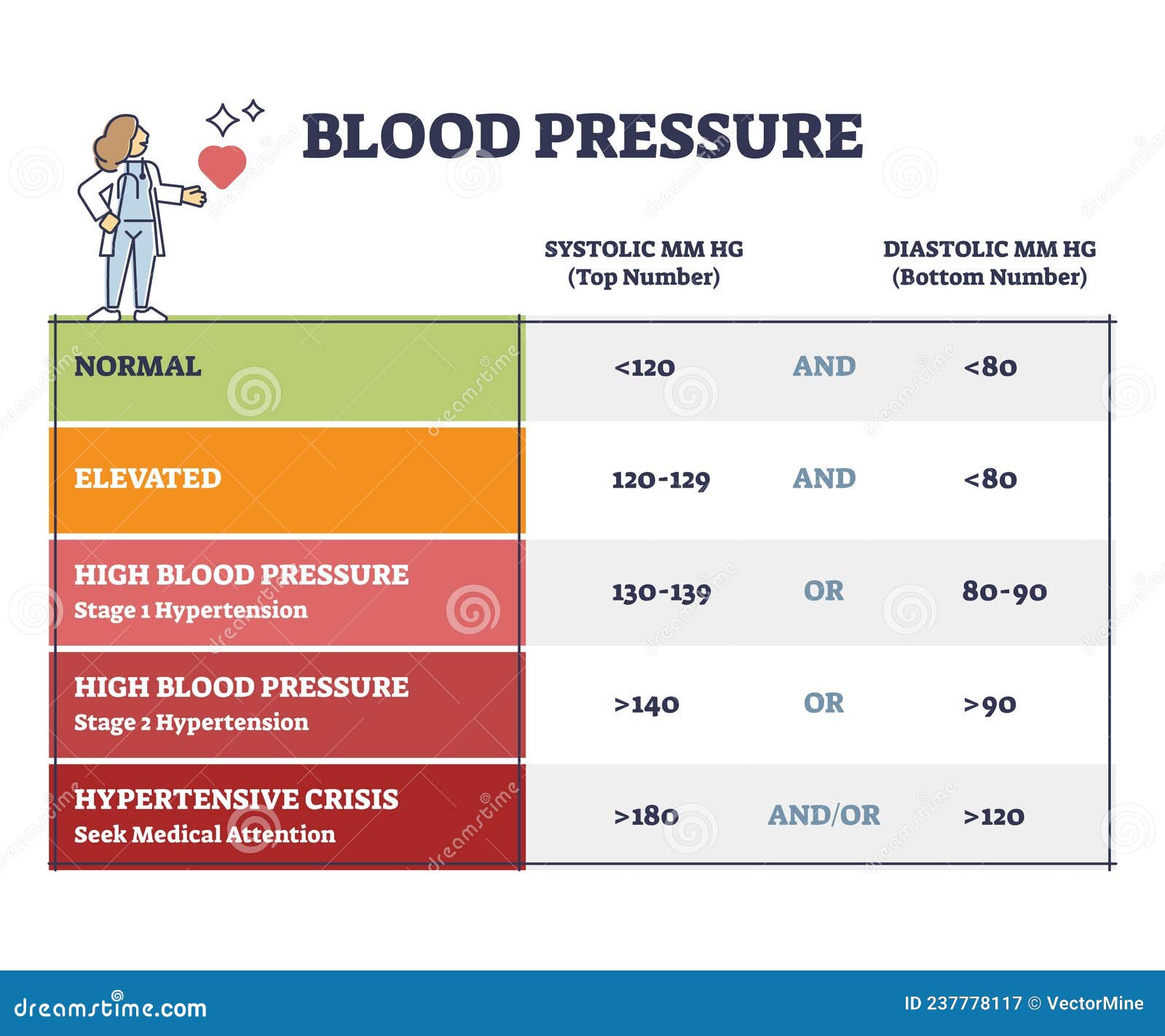
Blood Pressure With Systolic And Diastolic Number Chart Outline Diagramођ A higher systolic or diastolic reading may be used to diagnose high blood pressure. but the systolic blood pressure tells more about risk factors for heart disease for people over 50. as people get older, their systolic blood pressure usually goes up because: large arteries become stiffer. there is more plaque buildup over time. This blood pressure chart can help you figure out if your blood pressure is at a healthy level. it also can help you understand if you need to take some steps to improve your numbers. blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm hg). a blood pressure reading has two numbers. top number, called systolic pressure.

Systolic And Diastolic Blood Pressure Ratio Diagram As the ventricular pressure exceeds the pressure in the outflow tract, the semilunar valves open, allowing blood to leave the ventricle. this is the ejection phase of the cardiac cycle. the amount of blood left in the ventricle at the end of systole is known as the end systolic volume (afterload, between 40 – 50 ml of. Systolic and diastolic blood pressures. arterial blood pressure in the larger vessels varies between systolic and diastolic pressures. when systemic arterial blood pressure is measured, it is recorded as a ratio of two numbers (e.g., 120 80 is a normal adult blood pressure), expressed as systolic pressure over diastolic pressure. Wigger’s diagram. wigger’s diagram is used to demonstrate the varying pressures in the atrium, ventricle, and artery during one cardiac cycle (figure 2). intracardiac pressures are different within the right and left sides of the heart. the left side has higher pressure, as it has to pump blood through the whole body, compared to the right. In general, an individual’s “blood pressure,” or systemic arterial pressure, refers to the pressure measured within large arteries in the systemic circulation. this number splits into systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. blood pressure is traditionally measured using auscultation with a mercury tube sphygmomanometer. it is measured in millimeters of mercury and expressed.

Comments are closed.