Taoism Vs Buddhism Vs Confucianism
Taoism Vs Confucianism What Is The Difference Between Daoism And Confucianism, taoism, and buddhism constitute the essence of the traditional chinese culture. the relationship among the three has been marked by both contention and complementation in history, with confucianism playing a more dominant role. confucius (kongzi, 551 479 b.c.), the founder of confucianism, stresses "ren" (benevolence, love) and. Since the word dharma means doctrine, law, way, teaching, or discipline, other dharmas are rejected. taoism has many similarities with buddhism. taoists are neutral against other dharmic religions. goal of religion. to attain enlightenment and be released from the cycle of rebirth and death, thus attaining nirvana.

Confucianism Vs Buddhism Vs Taoism Realpolitik Of The Three Teachings The core philosophy of confucianism is that rules and rituals are needed to correct the degeneration of people. the core belief of taoism is that there is a natural harmony between heaven and earth, which can be discovered by anyone. vinegar tasters is a common subject in traditional chinese religious painting. Confucianism, taoism, and buddhism are considered the “three pillars” of ancient chinese society. as philosophies and religions, they not only influenced spirituality, but also government, science, the arts, and social structure. though their specific beliefs and teachings have occasionally been at odds with each other, there has been much. In chinese philosophy, the three teachings (chinese: 三 教; pinyin: sān jiào; vietnamese: tam giáo, chữ hán: 三教) are confucianism, taoism, and buddhism. the learning and the understanding of the three teachings are traditionally considered to be a harmonious aggregate within chinese culture. [1] literary references to the "three. Here are five key differences between them: 1. philosophical roots: confucianism, established by the philosopher confucius around the 5th century bce, focuses on social harmony and moral integrity. taoism, attributed to lao tzu and further developed by philosophers like zhuangzi, prioritizes living in harmony with the tao, or the fundamental.
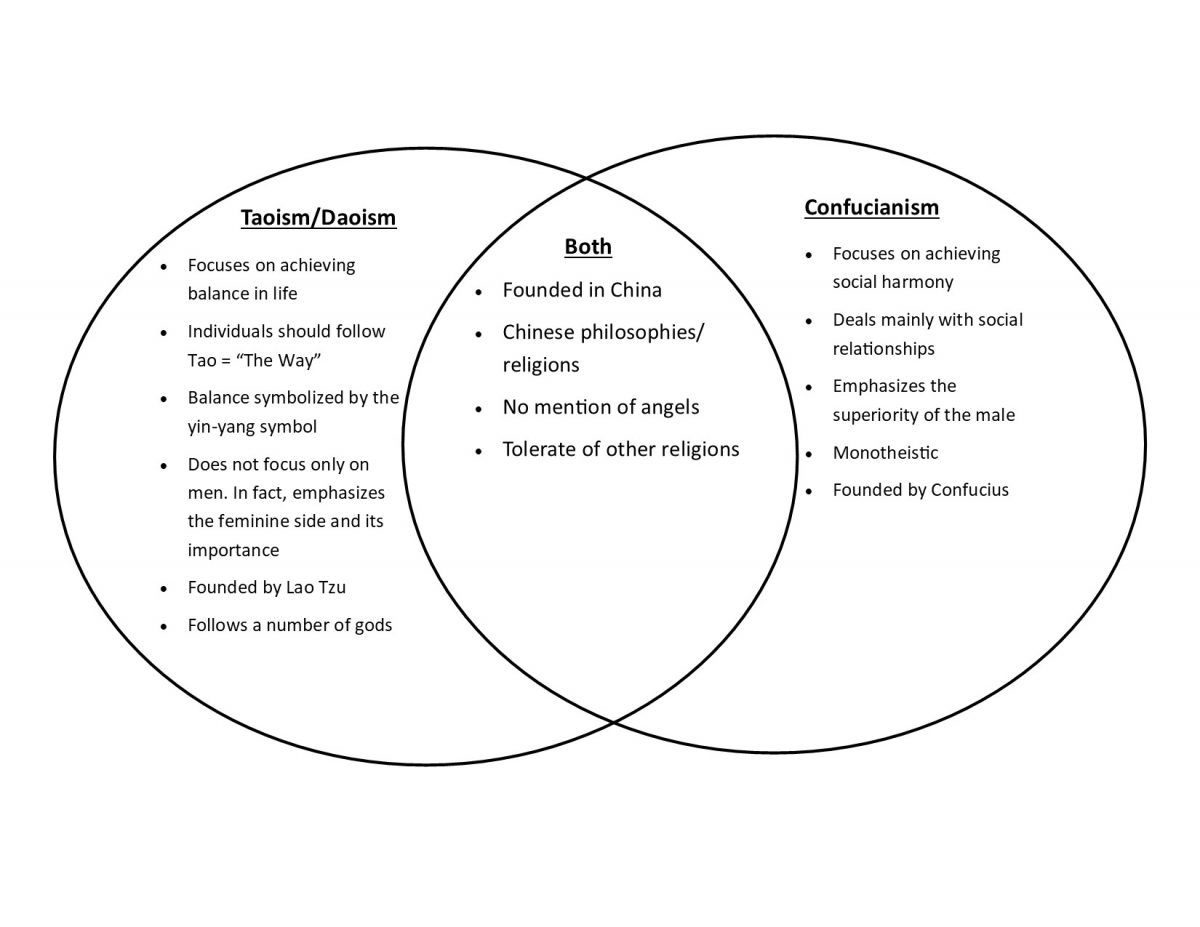
Confucianism And Taoism вђ Ghs208 01 Spring 2020 China And The Islamic In chinese philosophy, the three teachings (chinese: 三 教; pinyin: sān jiào; vietnamese: tam giáo, chữ hán: 三教) are confucianism, taoism, and buddhism. the learning and the understanding of the three teachings are traditionally considered to be a harmonious aggregate within chinese culture. [1] literary references to the "three. Here are five key differences between them: 1. philosophical roots: confucianism, established by the philosopher confucius around the 5th century bce, focuses on social harmony and moral integrity. taoism, attributed to lao tzu and further developed by philosophers like zhuangzi, prioritizes living in harmony with the tao, or the fundamental. The encounter between buddhism and chinese culture gave rise to a unique blend of ideas and practices, resulting in the development of chinese buddhism. this form of buddhism incorporated elements from taoism and confucianism, creating a rich tapestry of spiritual beliefs and practices. The four major religions of the far east are hinduism, buddhism, confucianism, and taoism. hinduism, a polytheistic religion and perhaps the oldest of the great world religions, dates back about 6,000 years. hinduism comprises so many different beliefs and rituals that some sociologists have suggested thinking of it as a grouping of.

Comments are closed.