Tech Breakdown Types Of 3d Printing Fdm Vs Sla 3d Printing
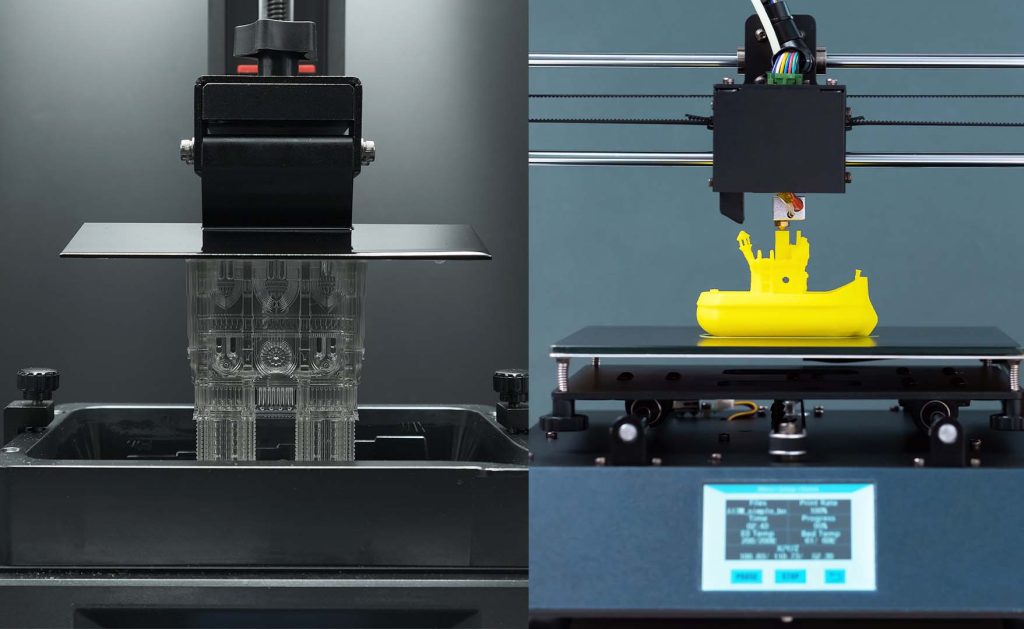
3d Printing Technology Comparison Fdm Vs Sla Fdm 3d printers are many people’s first introduction to 3d printing technology; they are the most common type of 3d printer in k 12 schools and even in many university makerspaces. in design, engineering, and manufacturing businesses, fdm printers are mostly relied upon for quick proof of concept models that can be agreed upon by design teams. Fdm 3d printers feature larger build volumes than sla printers, enabling them to perform certain short run additive manufacturing tasks in addition to prototyping full size, ready to use parts and models. traditional filaments continue to evolve with integrated features such as acid and chemical resistance, low friction, and high strength.

Fdm Vs Sla Vs Sls How To Choose The Right 3d Printing Technol Fdm produces parts by melting thermoplastic filament using an extrusion. but sls produced parts by sintering powdered filament using a high power laser. at the same time, sla produces parts through the uv curing process. the operation principles make the 3d printing technologies different from each other. When it comes to production quality and precision, sla 3d printing clearly beats fdm models, hands down. sla leverages its ultra fine resin curing mechanism to produce extremely high print resolution down to 25 50 microns axially. smooth curving geometries and miniature details can be replicated with ease. Fdm vs sla part comparison. fdm on the left, sla on the right. sla 3d printed parts on the other hand have far smoother surface finishes and are almost always more accurate in terms of both resolution and accuracy. stereolithography printer usually print with layer sizes of between 0.05mm and 0.01mm, noticeably better than most fdm 3d printers. Stereolithography (sla) is a 3d printing technology that builds parts by polymerizing a liquid photopolymer resin with a uv laser one layer at a time. fused deposition modeling (fdm) is a 3d printing technology that builds parts by extruding a melted plastic onto the build plate one layer at a time.

Fdm Vs Sla Choosing The Right 3d Printing Technology By Vexmatec Fdm vs sla part comparison. fdm on the left, sla on the right. sla 3d printed parts on the other hand have far smoother surface finishes and are almost always more accurate in terms of both resolution and accuracy. stereolithography printer usually print with layer sizes of between 0.05mm and 0.01mm, noticeably better than most fdm 3d printers. Stereolithography (sla) is a 3d printing technology that builds parts by polymerizing a liquid photopolymer resin with a uv laser one layer at a time. fused deposition modeling (fdm) is a 3d printing technology that builds parts by extruding a melted plastic onto the build plate one layer at a time. Each technology has their own set of strengths and weaknesses and will define the characteristics of the printed object. this week, we will be looking at three most used types of 3d printer technology: fused deposition modeling (fdm), stereolithography (sla), dls, and selective laser sintering (sls). The layer height options for sla start at 0.004 in. (0.102mm), which greatly reduces the appearance of layer lines compared to fdm whose builds typically start at layer heights of 0.008 in. 0.005 in. (0.2 0.12mm). when it comes to feature size, the precision of the uv laser is like drawing with a fine tipped artist’s pen.

Tech Breakdown Types Of 3d Printing Fdm Vs Sla 3d Printing Youtube Each technology has their own set of strengths and weaknesses and will define the characteristics of the printed object. this week, we will be looking at three most used types of 3d printer technology: fused deposition modeling (fdm), stereolithography (sla), dls, and selective laser sintering (sls). The layer height options for sla start at 0.004 in. (0.102mm), which greatly reduces the appearance of layer lines compared to fdm whose builds typically start at layer heights of 0.008 in. 0.005 in. (0.2 0.12mm). when it comes to feature size, the precision of the uv laser is like drawing with a fine tipped artist’s pen.

Comments are closed.