Tertiary Consumers Definition
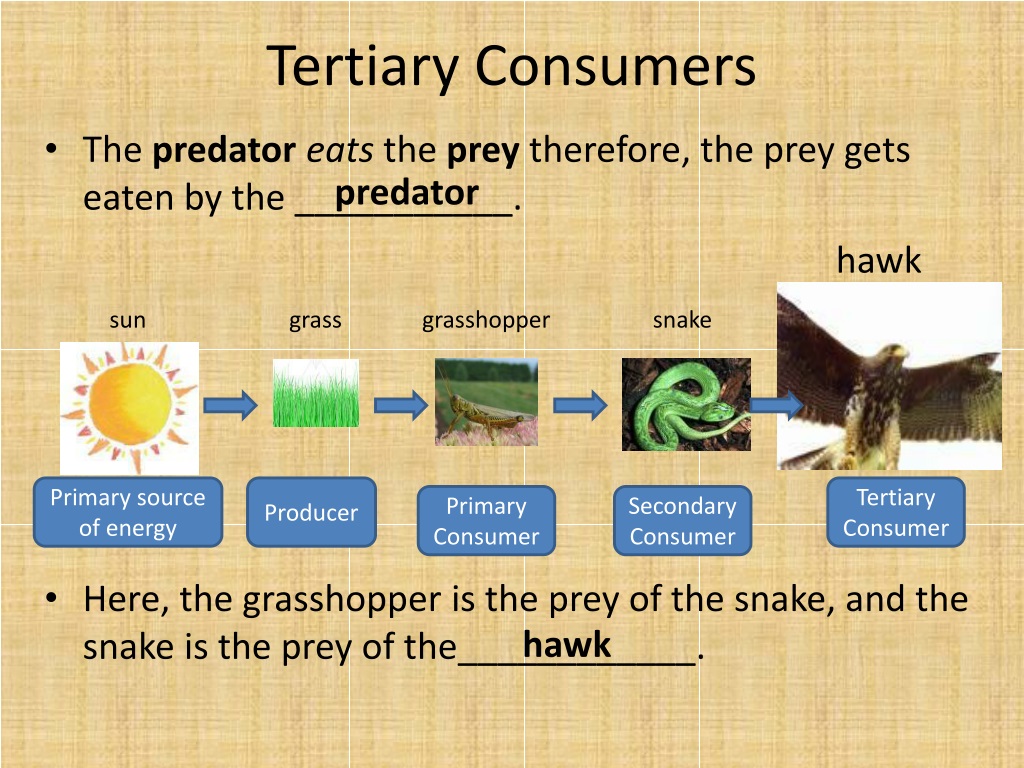
Ppt Food Chains Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 9522090 A tertiary consumer is an animal that eats primary and secondary consumers, usually a carnivore or an omnivore. learn how tertiary consumers fit into the food chain, their ecological role and some examples of tertiary consumers in different habitats. A tertiary consumer is a fourth trophic level after producers, primary consumers, and secondary consumers. it eats both primary and secondary consumers as its main source of food. learn about some examples of tertiary consumers in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems and their ecological roles.
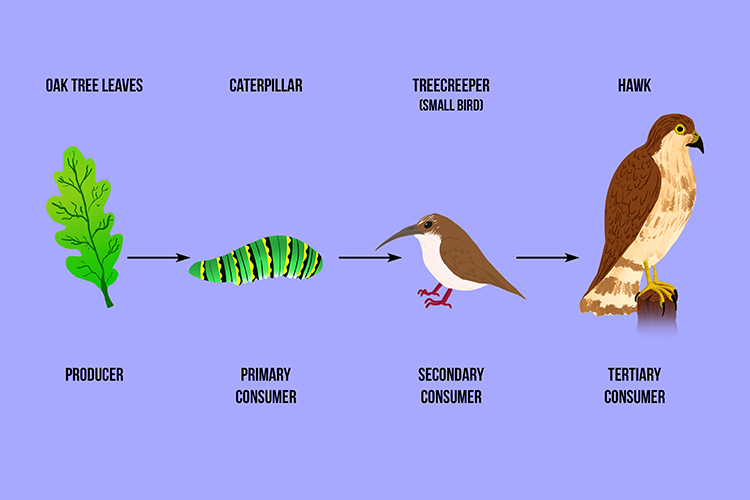
A Tertiary Consumer Eats Secondary Animals In The Food Chain Consumers are organisms that consume (eat) other organisms to sustain themselves. organisms that are consumers include heterotrophs like some animals, fungi, and bacteria. a tertiary consumer is an organism that obtains the energy it needs from consuming other consumers at different levels, from eating primary consumers or secondary consumers. Tertiary consumers are organisms that occupy the highest trophic level in a food chain and primarily feed on secondary consumers. they play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by regulating the populations of species below them in the food chain. in aquatic biomes, tertiary consumers can include large predatory fish, marine mammals, and seabirds, which rely on various lower. Learn what a tertiary consumer is, how it functions in an ecosystem, and what examples of tertiary consumers exist. a tertiary consumer is an animal that eats other animals, and is at the highest trophic level in a food chain. A tertiary consumer is an organism that occupies the third trophic level in a food chain, primarily feeding on secondary consumers. these consumers are typically carnivorous and play a crucial role in regulating populations of secondary consumers, thereby maintaining balance in ecosystems. tertiary consumers are often top predators, meaning they have few or no natural enemies, and their.
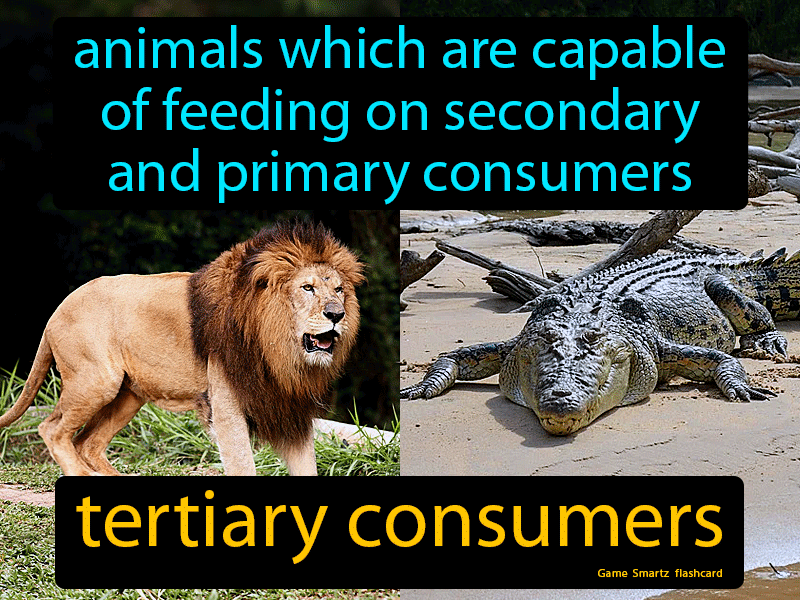
Tertiary Consumers Definition Image Gamesmartz Learn what a tertiary consumer is, how it functions in an ecosystem, and what examples of tertiary consumers exist. a tertiary consumer is an animal that eats other animals, and is at the highest trophic level in a food chain. A tertiary consumer is an organism that occupies the third trophic level in a food chain, primarily feeding on secondary consumers. these consumers are typically carnivorous and play a crucial role in regulating populations of secondary consumers, thereby maintaining balance in ecosystems. tertiary consumers are often top predators, meaning they have few or no natural enemies, and their. Tertiary consumers are organisms that occupy the highest trophic levels in food chains, primarily feeding on secondary consumers. they play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by controlling the populations of primary and secondary consumers. these consumers are typically carnivores and can be found at the top of food webs, influencing energy flow and nutrient cycling. Tertiary consumer examples. some examples of tertiary consumers include sharks, sea lions, eagles, hawks, lions, tigers, crocodiles, pythons, and polar bears. these animals rule their range, eating both secondary and primary consumers and easily defending their territories from other species. many tertiary consumers also don’t have to compete.

Comments are closed.