Tertiary Consumers Examples
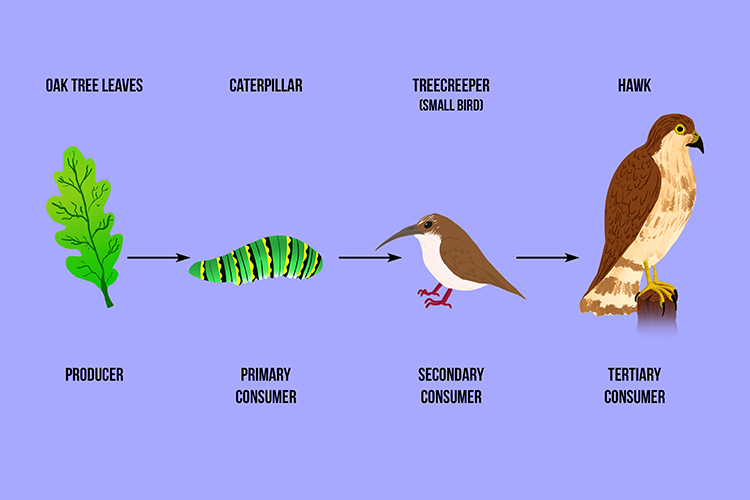
A Tertiary Consumer Eats Secondary Animals In The Food Chain Learn what a tertiary consumer is and how it fits into the food chain or web. find out examples of tertiary consumers in terrestrial, marine and freshwater ecosystems, and how they affect the balance of the ecosystem. Learn what a tertiary consumer is, who are some examples of tertiary consumers in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, and what functions they perform in food chains. a tertiary consumer is a fourth trophic level after producers, primary consumers, and secondary consumers, and can be a carnivore or an omnivore.

Food Chain And Food Webs Explained Tertiary consumers are apex predators that eat both secondary and primary consumers in the food chain. learn about their meaning, pronunciation, examples and role in ecosystem balance with a z animals. Consumers are organisms that consume (eat) other organisms to sustain themselves. organisms that are consumers include heterotrophs like some animals, fungi, and bacteria. a tertiary consumer is an organism that obtains the energy it needs from consuming other consumers at different levels, from eating primary consumers or secondary consumers. Learn what a tertiary consumer is, how it functions in an ecosystem, and see examples of tertiary consumers in different habitats. a tertiary consumer is an animal that eats other animals from lower trophic levels, such as big cats, humans, and sharks. Tertiary consumers are essential for controlling the populations of secondary consumers and preventing overpopulation of species in lower trophic levels. in aquatic biomes, examples of tertiary consumers include sharks, larger predatory fish like tuna, and marine mammals such as dolphins and whales.

Trophic Pyramid Definition Examples Britannica Learn what a tertiary consumer is, how it functions in an ecosystem, and see examples of tertiary consumers in different habitats. a tertiary consumer is an animal that eats other animals from lower trophic levels, such as big cats, humans, and sharks. Tertiary consumers are essential for controlling the populations of secondary consumers and preventing overpopulation of species in lower trophic levels. in aquatic biomes, examples of tertiary consumers include sharks, larger predatory fish like tuna, and marine mammals such as dolphins and whales. Tertiary consumers are animals that eat carnivores, the third level of consumers in a food chain. learn about some common tertiary consumers, such as sharks, big cats, crocodiles, pythons, and eagles, and how they differ from apex predators. Examples of tertiary consumers include large carnivores like lions, sharks, and eagles. they contribute to biodiversity by regulating the populations of other species within their ecosystems. the energy available to tertiary consumers is significantly lower than that available to primary producers due to energy loss at each trophic level.

Comments are closed.